The (Eukaryotic) Cell - Introduction
-
Upload
kathy-frondorf -
Category
Education
-
view
207 -
download
5
description
Transcript of The (Eukaryotic) Cell - Introduction

The Cell
• Cell Overview
• The Plasma Membrane
• Key Organelles

Numbers, Variety, Sizes• 50 – 106 Trillion cells in the body
• ~200 different kinds of cells in bodynerve, blood, muscle, liver, kidney
• Length: 2 microns over 1 meterPlatelets = 2 micronsnerve cells = over 3 feet long

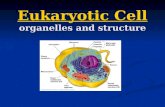
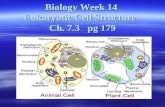
Generalized Cell

Cellular Components
• Plasma Membrane
• Nucleus
• Organelles
• Cytosol: water, ions, nutrients, waste products
• Granules: glycogen, melanin

The Plasma Membrane

The Fluid Mosaic Model
Phospholipid bilayer structural support
Cholesterol fluidity, flexibility
Proteins (many kinds) receptors enzymes transporters ion channels specialized connections

Crossing The Plasma Membrane
Mechanisms:• Passive
NO ATP required
• Active
ATP Required
• Simple Diffusion (High -> Low concentration)
• Osmosis (water mvt)
• Facilitated Transport (transporter protein)
• Active Transport(Low -> High concentration)• Sodium/Potassium pump(Mvt of Larger molecules)• Endocytosis• Exocytosis

Key Organelles
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Golgi
Endoplasmicreticulum

NucleusDouble plasma membrane with large pores
Nucleolus for ribosome synthesis
Chromatin(DNA-protein)Extended—barely visibleCondensed--visible

Ribosomes
Protein synthesis (translation of mRNA)
free or associated with endoplasmic reticulum
2 subunits made in nucleolus from nucleic acids and proteins

Endoplasmic ReticulumA continuous membrane system:
Nuclear Membrane-Rough ER-Smooth ER
Rough ER (Ribosomes, newly synthesized proteins)
Smooth ER (Lipid synthesis, transport)

MitochondriaPowerhouse of the Cell
Site of Aerobic respiration:O2 used in oxidation of glucose, fats to produce ATP
Vary in # and size within cells
Double membrane

Golgi Apparatus
Packaging & Transport