Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic T-Chart vs Eukaryotic...“EUKARYOTIC CELLS” ! !! !! !! !!!! Capsule...
2
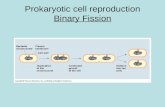
Directions; Create a T-chart on “Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells”. *Remember some characteristics may represent both types of cells. Place the characteristics “both” cells have in common directly on the line that separates the two columns. Most are unicellular Are 10 times larger Has Ribosomes Nucleoid Region containing DNA Most are multi-cellular Has a cell membrane Has Membrane-bound Organelles Bacteria Has DNA Has a nucleus Animal cells and fungal cells Cytoplasm and organelles “PROKARYOTIC CELLS” No membrane-bound Organelles No nucleus “EUKARYOTIC CELLS”
Transcript of Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic T-Chart vs Eukaryotic...“EUKARYOTIC CELLS” ! !! !! !! !!!! Capsule...

Directions; Create a T-chart on “Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells”. *Remember some characteristics may represent both types of cells. Place the characteristics “both” cells have in common directly on the line that separates the two columns.
Most are unicellular
Are 10 times larger
Has Ribosomes
Nucleoid Region containing
DNA
Most are multi-cellular
Has a cell membrane
Has Membrane-bound Organelles
Bacteria
Has DNA
Has a nucleus
Animal cells and fungal cells
Cytoplasm and organelles
“PROKARYOTIC CELLS”
No membrane-bound Organelles
No nucleus
“EUKARYOTIC CELLS”