Cell theory/prokaryotic and eukaryotic
description
Transcript of Cell theory/prokaryotic and eukaryotic

INTRODUCTION TO CELLSp. 67 in INB

CELL THEORY
Cells are the foundation of all life and arise from other cells.
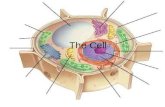
Inside all cells are active structures called organelles.
The activities that occur inside cells are called cellular processes.

LIST THREE SIMILARITIES AND THREE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND
EUKARYOTIC CELLS

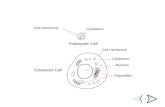
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
Both have…DNAa plasma membranecytoplasmribosomes
Both may have…cell wallsFlagella/cilia

CREATE A T-CHART – DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROKARYOTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS.
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells

PR
OK
AR
YO
TIC
CELLS
Click icon to add picture
Small and simple

EU
KA
RYO
TIC
CELLS
Larger and more complex

PR
OK
AR
YO
TIC
CELLS
Have no true nucleus

EU
KA
RYO
TIC
CELLS
Have a true nucleus

PR
OK
AR
YO
TIC
CELLSHave only a single “naked”
strand of circular DNA

EU
KA
RYO
TIC
CELLS
Have many strands of DNA enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus

PR
OK
AR
YO
TIC
CELLS
Are found in bacteria
Rod (oval) -shaped
Spiral-shaped
Round-shaped

EU
KA
RYO
TIC
CELLS
Are found in animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Plant cells
Animal cells
Protist cell

TICKET OUT THE DOOR
What is wrong with this statement?
Prokaryotic cells arise from air and water. They are
more complex versions of eukaryotic cells since
they have a nucleus with circular DNA and include
all bacteria and fungi.