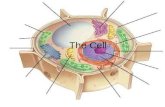
Eukaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell organelles and structure Eukaryotic Cell.
-
Upload
carol-hortense-poole -
Category
Documents
-
view
268 -
download
12
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell organelles and structure Eukaryotic Cell.

Eukaryotic Cellorganelles and structureorganelles and structure

Definition:Definition:
A cell containing a nucleus, in which A cell containing a nucleus, in which the genes or DNA is housedthe genes or DNA is housed

Eukaryotic Cell Ch. 8Eukaryotic Cell Ch. 8
BoundariesBoundaries Cell FunctionCell Function Assembly, Assembly,
Transport, Transport, and Storageand Storage
Energy Energy TransformersTransformers
Support and Support and LocomotionLocomotion

BoundariesBoundaries
Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Cell WallCell Wall
Click image to enlarge

Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane
Controls passage Controls passage of ions, nutrients, of ions, nutrients, wastewaste
Maintains Maintains chemical balance chemical balance in cell: in cell: homeostasishomeostasis
Free passageFree passage Use of proteins Use of proteins
require energyrequire energy

Cell WallCell Wall Additional boundary found Additional boundary found
outside the plasma membraneoutside the plasma membrane Inflexible structure found in Inflexible structure found in
plants, fungi, some protists, plants, fungi, some protists, and almost all bacteriaand almost all bacteria
NOT found in animal cellsNOT found in animal cells Plants-cellulose provides fiber Plants-cellulose provides fiber
in dietin diet Fungi-chitin(NFungi-chitin(N22-containing -containing
polysaccharide)polysaccharide) Also contain pectin-used in jello Also contain pectin-used in jello
and pie fillingand pie filling

Organelles that control cell Organelles that control cell functionfunction
What is a nucleus?What is a nucleus? Has a double-membraned nuclear Has a double-membraned nuclear
envelope, two bi-layers forms four envelope, two bi-layers forms four layers totallayers total
Contains Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, Contains Deoxyribonucleic acid, DNA, stored in long coils called stored in long coils called chromatinchromatin ChromatinChromatin changes into noticeable coils changes into noticeable coils
called chromosomes when a cell is ready to called chromosomes when a cell is ready to reproducereproduce
NucleolusNucleolus-site of ribosome synthesis-site of ribosome synthesis

Organelles that control cell Organelles that control cell functionfunction
What is a What is a ribosome?ribosome? Location in cell Location in cell
where enzymes and where enzymes and other proteins are other proteins are assembled assembled according to the according to the directions of DNAdirections of DNA
Considered Considered organelles, but not organelles, but not bound by a bound by a membranemembrane

Assembly, Transport, and Assembly, Transport, and StorageStorage
How does the cell assemble, How does the cell assemble, transport, and store materials?transport, and store materials?
Many of the organelles in the cell Many of the organelles in the cell area are involved in the synthesis of area are involved in the synthesis of proteins or the storage of materialsproteins or the storage of materials
Much of this assembly or storage Much of this assembly or storage takes place in the fluid inside the takes place in the fluid inside the cell, known as the cell, known as the cytoplasmcytoplasm

What is the cytoplasm?What is the cytoplasm? Location ?Location ?
Found outside the Found outside the nucleus surrounding all nucleus surrounding all of the organellesof the organelles
Consistency slightly Consistency slightly thicker than thicker than toothpastetoothpaste
About ½ the volume of About ½ the volume of the cellthe cell
Many important Many important chemical reactions chemical reactions happen herehappen here

Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum
What?What? Folded system of Folded system of
membranes that membranes that occupy a large portion occupy a large portion of the cytoplasmof the cytoplasm
Interconnected Interconnected compartments-large compartments-large surface area can be surface area can be packed into a small packed into a small area by folding the area by folding the surfacessurfaces

Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum
ER contains the ER contains the enzymes for almost enzymes for almost all of the cell’s all of the cell’s lipid synthesislipid synthesis
Rough ER-coated Rough ER-coated with ribosomeswith ribosomes
Smooth ER-lacking Smooth ER-lacking ribosomesribosomes
Cellular delivery Cellular delivery systemsystem

Golgi ApparatusGolgi Apparatus What is the Golgi Apparatus?What is the Golgi Apparatus? Series of closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs that Series of closely stacked, flattened membrane sacs that
receive newly synthesized proteins and lipids from the ER, receive newly synthesized proteins and lipids from the ER, and distributes them to the plasma membraneand distributes them to the plasma membrane
Modifies proteins and repackages them into Modifies proteins and repackages them into vesiclesvesicles

What is a vesicle?What is a vesicle?
Small membrane-bound packages Small membrane-bound packages that transport the newly made that transport the newly made proteins from the ER to the Golgi proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus, after pinching off of the apparatus, after pinching off of the ERER
These new packages can These new packages can incorporated into cell structure, incorporated into cell structure, expelled, or stored for later useexpelled, or stored for later use

What is a vacuole?What is a vacuole? Fluid-filled space in the cell surrounded by a Fluid-filled space in the cell surrounded by a
membrane that stores materials temporarilymembrane that stores materials temporarily Can store food, enzymes, and many other Can store food, enzymes, and many other
materials needed by the cell, including waste materials needed by the cell, including waste productsproducts
Can be a specialized water vacuole, ie. plantsCan be a specialized water vacuole, ie. plants

Recycling in the cellRecycling in the cell
LysosomeLysosome Digestive enzymesDigestive enzymes
Responsible for the disassembly of Responsible for the disassembly of things in the cellthings in the cell
Ex. Food, waste, bacteria, virusesEx. Food, waste, bacteria, viruses Membrane surrounding lysosome Membrane surrounding lysosome
prevents it from digesting the entire prevents it from digesting the entire cell’s protienscell’s protiens
Sometimes will fuse with a Sometimes will fuse with a vacuole to digest its contents, or vacuole to digest its contents, or the cell will tell a the cell will tell a lysosome to self- to self-destruct in order to destroy itselfdestruct in order to destroy itself
Ex. Tadpole tailEx. Tadpole tail

Energy TransformersEnergy Transformers
Cell requires energy to work and liveCell requires energy to work and live ChloroplastsChloroplasts
Found in plant and protist cells Found in plant and protist cells Disk-shaped organellesDisk-shaped organelles
MitochondriaMitochondria Found in all animal cellsFound in all animal cells Rod-shaped organellesRod-shaped organelles

What is a chloroplast?What is a chloroplast? Transform light energy into usable chemical energy that Transform light energy into usable chemical energy that
can be stored as food molecules(ie: starches and sugars)can be stored as food molecules(ie: starches and sugars) Energy from the sun is trapped inside stacks of inner Energy from the sun is trapped inside stacks of inner
membranes called membranes called grana, grana, and are surrounded by fluid and are surrounded by fluid called called stromastroma
Belongs to a group of Belongs to a group of storage organelles called storage organelles called plastidsplastids
PlastidsPlastidsStore starches and lipids, Store starches and lipids, and contain pigmentsand contain pigments
Named according to their Named according to their colorcolor
Chlorophyll=greenChlorophyll=green

What are mitochondria?What are mitochondria? Organelles in which food molecules are broken Organelles in which food molecules are broken
down to release energydown to release energy NOT found in prokaryotes-Why?NOT found in prokaryotes-Why? Energy is changed Energy is changed from chemical(food) from chemical(food) into usable Adenosine into usable Adenosine Triphosphate (Triphosphate (ATPATP) for ) for the cellthe cell
Outer and Inner Outer and Inner membrane are the sites membrane are the sites of electron transport of electron transport which generates ATPwhich generates ATP
Increased surface Increased surface area provided by folds area provided by folds called called cristaecristae

SupportSupport How does the cell support itself?How does the cell support itself?
In the last 20 years, we found out that the cell doesn’t just float In the last 20 years, we found out that the cell doesn’t just float aroundaround
CytoskeletonCytoskeleton Composed of tiny rods and filaments that form a frameworkComposed of tiny rods and filaments that form a framework Dynamic, constantly changing structure that provides support for the organelles Dynamic, constantly changing structure that provides support for the organelles
and maintaining cell shapeand maintaining cell shape Microtubules-Microtubules-thin, hollow cylinder made of proteinthin, hollow cylinder made of protein Microfilaments-Microfilaments-thin, solid protein fibersthin, solid protein fibers

LocomotionLocomotion How does the cell move?How does the cell move?
Special adapted structures for Special adapted structures for movementmovement
Can be distinguished by their Can be distinguished by their structures and the nature of structures and the nature of their actiontheir action
Major means of locomotion in Major means of locomotion in single-celled organismssingle-celled organisms
Cilia-very numerous, Cilia-very numerous, coordinated movementcoordinated movement
beating or wave-like, very beating or wave-like, very small and hair-like appearance small and hair-like appearance
Ex: Ex: ParameciumParamecium Flagella-longer projections that Flagella-longer projections that
move in a whip-like motionmove in a whip-like motion Usually only one or two per Usually only one or two per
cellcell Ex: sperm cellsEx: sperm cells

Any questions?Any questions?
““Oh yeah, it’s all coming together Oh yeah, it’s all coming together now!”-Krunknow!”-Krunk
Krunk’s New Groove Krunk’s New Groove
Click image to hear

Cell MembranesCell Membranes
Key ConceptsKey Concepts What are the main functions of the cell What are the main functions of the cell
membrane and the cell wall?membrane and the cell wall? What happens during diffusion?What happens during diffusion? What is osmosis?What is osmosis?

VocabularyVocabulary Cell Cell
membranemembrane Cell wallCell wall Lipid Lipid
bilayer bilayer ConcentratiConcentrati
onon DiffusionDiffusion EquilibriumEquilibrium OsmosisOsmosis IsotonicIsotonic
HypertonicHypertonic HypotonicHypotonic Facilitated Facilitated
diffusiondiffusion Active Active
transporttransport EndocytosiEndocytosi
ss PhagocytosPhagocytos
isis PinocytosisPinocytosis exocytosisexocytosis

Cell membraneCell membrane
Lipid Lipid bilayerbilayer

Cell Membrane Cell Membrane informationinformation
Flexible membrane contains proteinsFlexible membrane contains proteins Carbohydrates are attached to these Carbohydrates are attached to these
proteinsproteins Called a ‘mosaic’ because it consists of Called a ‘mosaic’ because it consists of
so many different molecules : fluid so many different molecules : fluid mosaic modelmosaic model
Functions:Functions: Protein = channels and pumps to move Protein = channels and pumps to move
materials acrossmaterials across Carbohydrates = chemical identification Carbohydrates = chemical identification
cards, cellular identification of each othercards, cellular identification of each other

Cell WallsCell Walls
Present in plants, algae, fungi, and Present in plants, algae, fungi, and many prokaryotes…many prokaryotes…
Location: Outside the cell membraneLocation: Outside the cell membrane Function: provide support and Function: provide support and
protection for the cellprotection for the cell Permeability: water, oxygen, carbon Permeability: water, oxygen, carbon
dioxide can all pass through the cell dioxide can all pass through the cell wallwall

Cell Wall CompositionCell Wall Composition Made of fibers of carbohydrates and Made of fibers of carbohydrates and
proteinsproteins Produced in the cell, then sent to the Produced in the cell, then sent to the
outside for assembly into the walloutside for assembly into the wall Plant cell walls: mostly Plant cell walls: mostly
cellulose(tough carb fiber)cellulose(tough carb fiber) Cellulose Cellulose is the is the main main “stuff” of “stuff” of wood and wood and paper!paper!

Diffusion Through Cell Diffusion Through Cell BoundariesBoundaries
Cells need liquid environments to Cells need liquid environments to survive!survive!
Measuring ConcentrationMeasuring Concentration Concentration = mass(amount of Concentration = mass(amount of
solutes) / solution(water)solutes) / solution(water) Example: 12 grams in 3 liter water Example: 12 grams in 3 liter water
= ???= ??? 4 g/L4 g/L

Diffusion Diffusion
Definition: the movement of particles from Definition: the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentrationof lower concentration
When the concentration of solute(particles) When the concentration of solute(particles) is the same throughout the system, the is the same throughout the system, the system has reached system has reached equilibriumequilibrium
This occurs with some particles and the This occurs with some particles and the cell membranecell membrane
Depends on random particle movement, Depends on random particle movement, therefore NO energy is required!therefore NO energy is required!Diffusion Video

OsmosisOsmosis
Definition: the diffusion of water through Definition: the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membranea selectively permeable membrane
How Osmosis WorksHow Osmosis Works IsotonicIsotonic HypertonicHypertonic HypotonicHypotonic
Passage of water from an area of high to Passage of water from an area of high to low concentration.low concentration.
Movie

IsotonicIsotonic
Concentration Concentration of solute and of solute and solution are solution are the same the same inside and inside and outside the outside the moleculemolecule

HypertonicHypertonic
Solute Solute concentration is concentration is greater outside greater outside than inside, than inside, therefore water therefore water flows out to flows out to equalize.equalize.

HypotonicHypotonic
Solute concentration Solute concentration is greater inside the is greater inside the cell than outside, cell than outside, the result is water the result is water moves into the cell.moves into the cell.
See Examples of Osmosis

Osmotic PressureOsmotic Pressure
Organisms must balance the intake and loss Organisms must balance the intake and loss of water in order to survive…of water in order to survive…
Because a typical cell contains salts, proteins, Because a typical cell contains salts, proteins, sugars, etc.---it will almost always be sugars, etc.---it will almost always be hypertonic, meaning water will rush in.hypertonic, meaning water will rush in. Needs to pump water out!Needs to pump water out! Fortunately, most cells in larger organisms are not Fortunately, most cells in larger organisms are not
surrounded by pure water, but isotonic substances surrounded by pure water, but isotonic substances like bloodlike blood
Plant cells are exposed to water, however their cell Plant cells are exposed to water, however their cell walls keep them from expanding too far and walls keep them from expanding too far and burstingbursting

Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion(Passive Transport)(Passive Transport)
Some molecules, like glucose, pass Some molecules, like glucose, pass through the cell membrane: they are through the cell membrane: they are large and charged, so they shouldn’t!large and charged, so they shouldn’t! How does this occur?How does this occur?
facilitated diffusion: the use of a protein channel to facilitated diffusion: the use of a protein channel to move a molecule across the cell membrane(NO move a molecule across the cell membrane(NO ENERGY)ENERGY)
Must be a higher to lower concentration Must be a higher to lower concentration movement…movement…
Specific protein channels are able to let specific Specific protein channels are able to let specific molecules pass through the membrane quicklymolecules pass through the membrane quickly
Movie

Facilitated Facilitated (Passive)Diffusion(Passive)Diffusion
Changes in the protein channel facilitate diffusion!

Active TransportActive Transport
What is active transport?What is active transport? Sometimes cells must move materials Sometimes cells must move materials
against the concentration gradient “uphill”against the concentration gradient “uphill” Smaller molecules = active transport Smaller molecules = active transport
using transport proteins sometimes using transport proteins sometimes referred to as a “pump”referred to as a “pump”
Ex: sodium, potassium, calcium ionsEx: sodium, potassium, calcium ions Larger molecules = active transport Larger molecules = active transport
using using endocytosisendocytosis and and exocytosis,exocytosis, which which change the shape of the cell membranechange the shape of the cell membrane

Active Transport: Active Transport: Molecular(small)Molecular(small)

Active Transport: Active Transport: Endocytosis(large)Endocytosis(large)
Phagocytosis- “cell-eating”-large Phagocytosis- “cell-eating”-large molecules, pieces of food, or entire molecules, pieces of food, or entire cells are taken into the cell by cells are taken into the cell by infoldings or pockets in the cell infoldings or pockets in the cell membranemembrane

Active Transport: Active Transport: Endocytosis(large)Endocytosis(large)
Pinocytosis: the formation of a Pinocytosis: the formation of a pocket around a liquid that is taken pocket around a liquid that is taken in and then stored in the cell as a in and then stored in the cell as a vacuolevacuole

Active Transport: Active Transport: Exocytosis(large)Exocytosis(large)
The membrane and an interior The membrane and an interior vacuole fuse to expel contents out of vacuole fuse to expel contents out of the cellthe cell Ex: removal of waterEx: removal of water

Section AssessmentSection Assessment
Describe the functions of the cell Describe the functions of the cell membrane.membrane.
What happens during diffusion? What happens during diffusion? Describe how water moves during osmosis.Describe how water moves during osmosis. What is the basic structure of a cell What is the basic structure of a cell
membrane?membrane? What is the difference between What is the difference between
phagocytosis and pinocyctosis?phagocytosis and pinocyctosis? What is the main way active transport What is the main way active transport
differs from diffusion?differs from diffusion?

7-4 The Diversity of 7-4 The Diversity of Cellular LifeCellular Life
Unicellular OrganismsUnicellular Organisms Multicellular OrganismsMulticellular Organisms
Specialized animal cellsSpecialized animal cells Specialized plant cellsSpecialized plant cells
Levels of OrganizationLevels of Organization TissuesTissues OrgansOrgans Organ SystemsOrgan Systems

UUnniicceelllluullaarr
OOrrggaanniissmmss
Recall that cells are the basic unit of Recall that cells are the basic unit of all living organismsall living organisms
Sometimes, a single cell is an Sometimes, a single cell is an organismorganism
These unicellular organisms: grow, These unicellular organisms: grow, develop, transform energy, and develop, transform energy, and reproducereproduce
Majority of life on Earth is unicellular!Majority of life on Earth is unicellular!

Unicellular LifeUnicellular Life EuglenaEuglena ParameciiParamecii
umum AmoebaAmoeba VolvoxVolvox Volvox 2Volvox 2 BioremediBioremedi
ationation

Multicellular OrganismsMulticellular Organisms
Organism made up of many cellsOrganism made up of many cells All multicellular organism depend on All multicellular organism depend on
communication and cooperation communication and cooperation among specialized cellsamong specialized cells

SSppeecciiaalliizzeedd aanniimmaall cceellllss



SSppeecciiaalliizzeedd
ppllaanntt cceellllss

LLeevveellss ooff
OOrrggaanniizzaattiioonn
Tissues(histology)Tissues(histology) Group of similar cells that perform a Group of similar cells that perform a
particular functionparticular function OrgansOrgans
Groups of tissues that work togetherGroups of tissues that work together Ex: each muscle, heartEx: each muscle, heart
Organ SystemsOrgan Systems A group of organs that work together to A group of organs that work together to
perform a specific functionperform a specific function RespiratoryRespiratory CirculatoryCirculatory