Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
-
Upload
david-henderson -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
1/29
CHAPTER 4
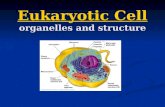
EUKARYOTIC CELL
STRUCTURE & FUNCTION
External Structures
Internal Structures
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
2/29
Overview of Eukaryotic CellStructure
Eukaryote: Protozoa, Algae, Fungi larger than prokaryotic cell
more complex than prokaryotic cell
contains membrane-bound organellesthat perform specific functions
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
3/29
Protozoa, Algae, Fungi
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
4/29
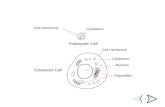
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
5/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
6/29
1. Cilia motility
5-20 m long
shorter and more numerous
than flagella
beat with two phases
2. Flagella
motility
100-200 m long
longer than cilia
eukaryotic flagellum moveslike a whip
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
7/29Ciliated protozoa Oxytrichasp.
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
8/29
Structure of Flagella and Cilia membrane-bound cylinders ~2m in diameter
9 pairs of microtubule doublets circle around 2 central tubules
9 + 2 arrangement called axoneme
basal body
at base of flagellum or cilium directs synthesis of flagella and cilia
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
9/29
3. Pellicle a thin layer supporting plasma membrane in various protozoa
not as strong or rigid as cell wall
provides characteristic shape to cell
Epidinium caudatum Pellicle of a mushroom
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
10/29
4. Cell Wall
rigid covering outside plasma membrane
variable compositions in eukaryotes
Algae - ?
Diatoms - ? Fungi - ?
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
11/29
Cellulose cell wall of algae Volvoxsp.
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
12/29
Silica shell of diatoms
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
13/29
Chitin & cellulose of fungi
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
14/29
5. Plasma Membrane almost as similar as prokaryotes
Fluid-mosaic structure
greater variety oflipids, includephosphoglycerides, sphingolipids andcholesterol
contains sterols that adds rigidity toplasma membrane
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
15/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
16/29
(1) is standard lipid bilayer(2) is a lipid raft.
Plasma Membrane
eucaryotic membranes contain
microdomains called lipid rafts
enriched for certain lipids and proteins
participate in a variety of cell processessuch as cell movement and transduction
http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/c6/Lipid_raft_organisation_scheme.svg -
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
17/29
Eukaryotic Cell InternalStructures
Nucleus
EndoplasmicReticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Ribosome
Lysosome Peroxisome
Vacuoles
Cytoplasmicmatrix
Cytoskeleton
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
18/29
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
19/29
Nucleus
largest organelle ineucaryotic cell
contains geneticmaterial
enclosed by nuclear
envelope contains chromatin
and nucleolus
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
20/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
21/29
Nucleus
Chromatin
dense fibrous materialwithin nucleus
contains genetic DNA
condenses to formchromosomes during cell
division mitosis/meiosis (refer
Prescotts Microbiology
pg. 92-94)
Nuclear envelope
double membrane (inner
& outer) structure that
surrounds nucleus
has nuclear pores
pores allow materials
to be transported intoor out of nucleus
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
22/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
23/29
Nucleus
Nucleolus
1 nucleolus per nucleus
not membrane-enclosed
important in ribosome synthesis
directs synthesis and processing of rRNA directs assembly of rRNA and ribosomal
proteins to form ribosomes
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
24/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
25/29
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
consists of networkof membranous
tubules andflattened sacs calledcisternae
internalcompartment of ER= cisternal space
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
26/29
Two types of ER:
rough ER
ribosomes attached, rough texture
smooth ER
lack of ribosomes, smooth texture
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Functions of ER: major site of cell membrane synthesis
transports proteins, lipids, and other materials to
Golgi apparatus
synthesis of lysosomes
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
27/29
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
28/29
Golgi Apparatus
membranous organellemade of cisternae stacked
on each other dictyosomes
stacks of cisternae
involves in modification,packaging, and secretionof materials throughsecretory vesicles
-
7/29/2019 Chap4.1 Eukaryotic Cell
29/29
cis face (associated with ER)
trans face
cis face differs from trans face in thickness,enzyme content and vesicle formation
movement ofmaterial