Cells Introduction Cell Theory, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic.
-
Upload
johnathon-godbolt -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
2
Transcript of Cells Introduction Cell Theory, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic.

Cells IntroductionCell Theory, Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic

Journal Entry (Name the organelle that best fits the
description.) 0 1. Cell Control Center that
contains DNA.
0 2. Allows materials to flow in and out of cell.
0 3. Supports and Protects the cell.
0 4. Makes usable energy for the cell.
0 5. stores food, water, and waste.
0 6. captures sunlight, to produce food.
0 7. Makes proteins.
0 8. clear jelly inside a cell.
0 9. makes ribosomes.
0 10. network of rods that maintains the cells shape

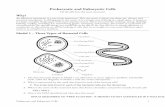
Prokaryotic Cell LabelingUnderneath the diagram. Explain the difference between
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. Why would a prokaryotic cell need something like a
capsule?

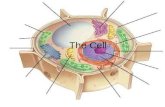
The Cell
Click icon to add picture
Cell Theory and Scientist

Scientist
0 1665: Robert Hooke0 Discovered and name cells
0 Leewenhoek: Discovered single cells through pond water. (single-lens microscope)
0 1830s: M. Schleiden0 All Plants-made of cells
0 T. Schwann0 All animals-made of cells
0 R. Virchow0 Known for the Cell Theory

Cell Theory
0 Definition: The Cell Theory is one of the basic principles of biology. Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to german scientists Theodor Schwann, Matthias Schleiden, and Rudolph Virchow.
0 The Cell Theory states:
0 •All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular.
0 •The cell is the basic unit of life.0 Cells, Tissue, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism
0 •Cells arise from pre-existing cells.

0http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4GUYdaM3QIY&feature=related
0http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vEmsaXA-go0&feature=fvwrel
0http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zafJKbMPA8&feature=related
0http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfzVWG2DnQ4&feature=related

New Ideas
0 •Energy flow occurs within cells.
0 •Heredity information (DNA) is passed on from cell to cell.
0 •All cells have the same basic chemical composition.

Draw a Venn Diagram on the next page.
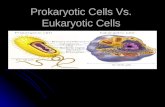
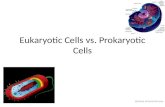
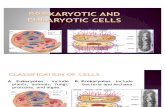
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic

Two Types of Cells
0All living organisms can be sorted into one of two groups depending on the fundamental structure of their cells.
0These two groups are the prokaryotes and the eukaryotes.
0Prokaryotes are organisms made up of cells that lack a cell nucleus or any membrane-encased organelles.
0Eukaryotes are organisms made up of cells that possess a membrane-bound nucleus (that holds genetic material) as well as membrane-bound organelles.

Anatomy of a Prokaryotic Cell
0 A typical prokaryotic cell might contain the following parts:
0 •cell wall0 •plasma membrane0 •cytoplasm0 •flagella and pili0 •nucleoid0 •plasmid0 Ribosomes

Anatomy of a Eukaryotic CellA typical eukaryotic cell might contain the
following parts:
0 •plasma membrane0 •nucleolus0 •nucleus0 •chromosomes0 •rhibosome0 •vesicle
0 •endoplasmic reticulum0 •Golgi apparatus0 •cytoskeleton0 •cytoplasm0 •lysosome0 •centrioles0 •mitochondria


The different cells
0http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gfzVWG2DnQ4&feature=related

All Cells HAVE!
01. DNA: the genetic material
02. PLASMA MEMBRANE: A phospholipid bilayer with proteins that separates the cell from the surrounding environment.
03. CYTOPLASM: The rest of the material of the cell.
04. RIBOSOMES: the organelles on which protein synthesis takes place.


Cell process – Synthesis of new molecules
0Synthesis means “making”0What organelles are involved in making new
molecules?0 Nucleus (contains instructions to make proteins)0 Ribosomes (make proteins)0 Rough endoplasmic reticulum (synthesizes proteins)0 Smooth endoplasmis reticulum (synthesizes lipids)0 Golgi body (modifies molecules)

Cell Processes -- Homeostasis
0Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment.
0Think of the organelles – which work together to perform homeostasis?0 Cell membrane (lets out waste, transports in nutrients)0 Cell wall (keeps cell shape)0 Lysosome (digests waste)0 Nucleus, ER, ribosomes, Golgi body (create new
molecules needed to maintain homeostasis)

Tour of the Cell
01. You will be watching Paul Andersons Pod Cast on the cell.
0This will review cell types, functions, and the major organelles.
0This will take about 15 Minutes.
0Homework: Cell Coloring Packet..Eukaryotic (animal and Plant), and Prokaryotic,