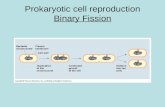
Prokaryotic cell reproduction Binary Fission. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. Essential Questions What are the functions of the major cell structures?
-
Upload
shanon-chase -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
3
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cell Structure. Essential Questions What are the functions of the major cell structures?

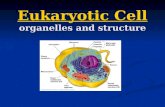
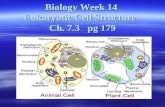
Eukaryotic Cell Structure

Essential Questions
What are the functions of the major cell structures?

Organelles
“Little organs” Specialized structures of the cell Each organelle has unique functions These organelles allow the cell to
function properly

Organelle Groups
Cell biologists divide organelles into three groups based on their location Nucleus: nucleolus, chromatin, nuclear
envelope Cytoplasm: mitochondria, vacuole,
Golgi apparatus, centrioles, lysosomes, ribosomes, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum
Surface: cell membrane, cell wall

Nucleus
1. Nucleus Control center of the
cell Contains nearly all
cell DNA 2. Nuclear Envelope
Surrounds the nucleus
Contains nuclear pores
Allows material to move into and out of the nucleus

Nucleus cont…
3. Chromatin Consists of DNA
bound to a protein Condenses to form
chromosomes 4. Nucleolus
Small, dense region Assembly of
ribosomes begin here

5. Cytoplasm
The portion of the cell outside the nucleus
Contains many organelles Gel-like substance that protects the
organelles Allows movement

Cytoplasmic Organelles
6. Ribosome Small particles of
RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm
Responsible for the assembly of proteins
Follows coded instructions from the nucleus
Numerous in cells active in protein synthesis

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Site where lipid
components, proteins and other materials are exported from the cell
7. Rough ER Involved in the
synthesis of proteins Ribosomes are found
on its surface 8. Smooth ER
Contains collections of enzymes
Synthesis of membrane lipids
Detoxification of drugs

9. Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Bodies) Proteins in the rough
ER move next into the Golgi Apparatus
It modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for storage or secretion
Ships proteins to their final destination

10. Lysosomes Small organelles filled
with enzymes “clean up crew” Digestion, or
breakdown, of lipids, carbohydrates, and proteins so the rest of the cell can use them
Removes dead organelles

11. Vacuoles Saclike structures that
stores materials Plant cells: the
vacuoles is a single, large central organelle filled with liquid
Allows for support of leaves and flowers
Help maintain homeostasis
Also found in some animal cells

12. Mitochondria Power house of the
cell Responsible for
providing the cell with energy
Converts stored energy in food into compounds that the cells can use
Contains its own DNA Some scientists
believe that mitochondria, at one point, may have been a prokaryotic cell

13. Chloroplasts Only found in plant
cells Capture energy form
sunlight and convert it into chemical energy
This process is called photosynthesis
Contains chlorophyll Gives plants its
color

14. Centrioles Come from structures
called microtubules Located near the
nucleus Help to organize cell
division Only in Animal Cells

15. Cytoskeleton
A network of protein filaments that help the cell maintain its shape
Also aids in movement Flagellum Cilia

16. Cell membrane Cell membrane
regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Provides protection and support
17. Cell wall Main function is to
provide support and protection
Only in plant cells

TIME FOR A MINI QUIZ!!
Take out a piece of paper. Fold it in half length-wise (hot dog) Head one side “Animal Cell” and number
it 1-19 Label the other side “Plant Cell” and
number it 1-10 Label the organelles to their
corresponding numbers as you see them on each slide.
You may use your notes but NOT your books!

Nucleus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Rough ER
Smooth ER
Mitochondria
Golgi Body
Vacuole
Lysosome

Nucleus
Cell Membrane
Cytoplasm
Rough ER
Chloroplasts
Ribosome
Mitochondria
Golgi Body
Vacuole
Cell Wall