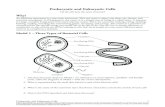
The Eukaryotic Cell The Basic Unit of Life. Why a Eukaryotic Cell? Eu= trueEu= true Eukaryotic...
-
Upload
kory-bryant -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of The Eukaryotic Cell The Basic Unit of Life. Why a Eukaryotic Cell? Eu= trueEu= true Eukaryotic...

TheEukaryotic Cell
The Basic Unit of Life

Why a Why a EukaryoticEukaryotic Cell? Cell?
• Eu= trueEu= true• Eukaryotic CellEukaryotic Cell
• Has membrane bound-organellesHas membrane bound-organelles• One of these organelles is a true nucleusOne of these organelles is a true nucleus
• Organisms with Eukaryotic CellsOrganisms with Eukaryotic Cells• Kingdom ProtistaKingdom Protista• Kingdom FungiKingdom Fungi• Kingdom PlantaeKingdom Plantae• Kingdom AnimaliaKingdom Animalia

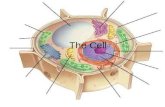
Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Found in:Found in:
• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal CellsFunctions:Functions:
• Boundary between the cell and the environmentBoundary between the cell and the environment• ““Gatekeeper” of the cellGatekeeper” of the cell
• Maintains different conditions inside and outside of Maintains different conditions inside and outside of the cellthe cell
• Allows materials to enter and exitAllows materials to enter and exit
• Gives the cell its shape and flexibilityGives the cell its shape and flexibility

Hydrophilic Head
Hydrophobic Tail
Protein

Cell WallCell Wall
Found in:Found in:• Plant cellsPlant cells• Also found in fungi cells, and bacterial cells but is Also found in fungi cells, and bacterial cells but is
composed of a different substancescomposed of a different substancesFunction:Function:• Protects and supports the cellProtects and supports the cellStructure:Structure:• Inflexible outer boundary surrounding the plasma Inflexible outer boundary surrounding the plasma
membranemembrane• In plants it is made of a polysaccharide; celluloseIn plants it is made of a polysaccharide; cellulose


NucleusNucleus
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Control center of the cellControl center of the cell• Contains genetic material called chromatinContains genetic material called chromatin
• Chromatin= DNA + protein mixtureChromatin= DNA + protein mixture
Structure:Structure:• Surrounded by a nuclear envelope/membraneSurrounded by a nuclear envelope/membrane


NucleolusNucleolus
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Manufactures ribosomesManufactures ribosomes
Structure:Structure:• Spherical structure inside the nucleusSpherical structure inside the nucleus

CytoplasmCytoplasm
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Site of many chemical reactionsSite of many chemical reactions
Structure:Structure:• ““Fluid” inside the plasma membraneFluid” inside the plasma membrane

Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic ReticulumFound in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal CellsFunction:Function:• ““Subway” system of the cellSubway” system of the cell• Move materials through the cellMove materials through the cellStructure:Structure:• Extensive system of internal membranesExtensive system of internal membranes• Rough” - contain ribosomes and manufactures Rough” - contain ribosomes and manufactures
proteinsproteins• ““Smooth” - Lipid synthesis and transportSmooth” - Lipid synthesis and transport


RibosomesRibosomes
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Site where enzymes and proteins are assembledSite where enzymes and proteins are assembled
Structure:Structure:• Found on the “Rough ER” and also free in the Found on the “Rough ER” and also free in the
cytoplasmcytoplasm

Golgi ApparatusGolgi Apparatus
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal CellsFunction:Function:• Receives proteins from the ER (packaged in Receives proteins from the ER (packaged in
vesicles) then packages, processes and vesicles) then packages, processes and distributes them to the rest of the celldistributes them to the rest of the cell
Structure:Structure:• Series of stacked, flattened membrane sacsSeries of stacked, flattened membrane sacs


VacuoleVacuole
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells• Often very large in plant cellsOften very large in plant cells
Function:Function:• Temporary storage for water, food, enzymes, Temporary storage for water, food, enzymes,
waste, and other materialswaste, and other materials
Structure:Structure:• Hollow, membrane-bound storage centerHollow, membrane-bound storage center


LysosomesLysosomes
Found in:Found in:• Animal CellsAnimal Cells
Function:Function:• Contain digestive enzymesContain digestive enzymes• Digest and recycle used cell partsDigest and recycle used cell parts• Rapid breakdown of protein, nucleic acids, lipids Rapid breakdown of protein, nucleic acids, lipids
and carbohydratesand carbohydrates
Structure:Structure:• Membrane bound structureMembrane bound structure

MitochondriaMitochondria
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Break down food molecules into energy for use by Break down food molecules into energy for use by
the body the body • ““Power house” of the cellPower house” of the cell
Structure:Structure:• Oval shaped with folded internal membrane Oval shaped with folded internal membrane
(increases surface area)(increases surface area)


ChloroplastsChloroplasts
Found in:Found in:• Plants cells Plants cells • Algae (plant-like protists)Algae (plant-like protists)Function:Function:• Site of photosynthesisSite of photosynthesis• Converts energy of the sun into chemical energy Converts energy of the sun into chemical energy
(glucose)(glucose)Structure:Structure:• Oval shaped with stacked internal membranes Oval shaped with stacked internal membranes
(increase surface area)(increase surface area)


CytoskeletonCytoskeleton
Found in:Found in:• Plant & Animal CellsPlant & Animal Cells
Function:Function:• Thin protein fiber “scaffold” that protects the Thin protein fiber “scaffold” that protects the
organelles and give cells their shapeorganelles and give cells their shape
Structure:Structure:• Made of microtubules and microfilamentsMade of microtubules and microfilaments

Cell LocomotionCell Locomotion• Both of the following are found in animal cellsBoth of the following are found in animal cells• FlagellaFlagella
• Long projections that move with a whiplike Long projections that move with a whiplike motionmotion
• Usually only one or two per cellUsually only one or two per cell
• CiliaCilia• Short hairlike projections that beat in a Short hairlike projections that beat in a
coordinated wavecoordinated wave• Usually quite numerousUsually quite numerous