Eukaryotic Cell Membrane. Cell Membrane Cell membrane: the flexible boundary of a cell (also called...
-
Upload
regina-helena-french -
Category
Documents
-
view
239 -
download
3
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cell Membrane. Cell Membrane Cell membrane: the flexible boundary of a cell (also called...

Eukaryotic Cell Membrane

Cell Membrane
• Cell membrane: the flexible boundary of a cell (also called a plasma membrane)
• It separates a cell from its surroundings.
• It allows nutrients to enter and waste to be removed.

Cell Membrane
• Homeostasis: maintaining a healthy balance
• The cell membrane allows some molecules into the cell and keeps others out.

Cell Membrane
• Selective permeability: allowing only certain molecules to enter and leave the cell
• Selective permeability is like a screen on a window

Cell Membrane
• What gets in?• H2O freely enters
cell• O2 in ,CO2 out• Na and Ca at
certain times in certain amounts
• Waste leaves but can’t reenter

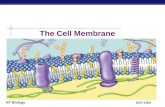
Membrane Structure
• Phospholipid: lipid with a glycerol backbone and two fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group

Membrane Structure
• The polar head is hydrophilic: it likes water
• Fatty acid tail is hydrophobic: it does not like water.
• They form a bilayer

Membrane Structure

Membrane Structure
• The cell membrane also contains proteins to help support the cell structure.
• Cholesterol to keep the fatty acid tails from sticking together

Membrane Structure
• Fluid Mosaic Model: the organization of the cell membrane.
• Fluid because it is not fixed in a particular spot
• Mosaic because of the patterns the proteins make

Membrane Structure
• Proteins in the membrane function as:
• Transport proteins: moving molecules across the membrane
• Identify chemical signals