Cell Structure & Function Module
description
Transcript of Cell Structure & Function Module

A S H L E Y J . T A Y L O RMVHS Science Department
CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONMODULE
EOCT

TWO TYPES OF CELLS
Prokaryotic Cells• Do not contain a nucleus • Do not contain membrane-
bound organelles.• Contains DNA• DNA is suspended in the
cytoplasm. • Contains Cytoplasm• Contains Cell Membrane• All prokaryotes are
microscopic • Single-celled organisms• Ex. Bacteria and Archaea
Eukaryotic Cells• Contain a nucleus • the genetic information is
stored in the nucleus• Contain membrane bound
organelles. • Contains Cytoplasm• Contains Cell Membrane• Eukaryotes may be
multicellular or single-celled organisms.
• Ex. Plants, animals, fungi.

COMPARE AND CONTRAST
Prokaryote Eukaryote

COMPARE AND CONTRAST
Prokaryote Eukaryote
• No nucleus•No organelles•Single-celled•Bacteria
• Nucleus•Organelles•Single-celled•Multicellular•Plant and Animal
• DNA•Cytoplasm•Cell Membrane

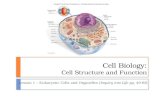
OrganellesSpecialized structures that perform cellular functions within a cell

CELL ORGANELLES
CytoskeletonFunction: Supports and Shapes the cell. Also involved in cell movement.• Microtubules - long hollow
tubes and give the cell its shape
• Intermediate filaments - give a cell its strength.
• Microfilaments - enable cells to move and divide. They play an important role in muscle cells.
NucleusFunction: Stores hereditary info in the form of DNA • Contains a nucleolus
– small dense region within responsible for the assembly of ribosomes
• Surrounded by a nuclear envelope

CELL ORGANELLES
Endoplasmic ReticulumFunction: Organelle where components of cell membrane are made and proteins are modified.• Smooth ER: Does not contain
ribosomes. Makes lipids and breaks down toxic substances.
• Rough ER: Contains ribosomes. Exports proteins from cell or sends them to the cytoplasm
RibosomeFunction: Location where proteins are made.• Made up of rRNA
(ribosomal RNA) and protein
• Can be free-roaming in cytoplasm or attached to the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum

CELL ORGANELLES
Golgi ApparatusFunction: Sac of membrane-enclosed spaces containing enzymes that process, sort, and deliver proteins.
MitochondriaFunction: Supply energy for the cell.• Site of cellular
respiration• Have their own
ribosomes and DNA

CELL ORGANELLES
ChloroplastFunction: Organelle that carries out photosynthesis. • Contains chlorophyll
( light absorbing molecule that gives plants their green color)
• Found in Plants, some Algae, and some bacteria.
Cell WallFunction: A strong rigid layer that provides protection support and shape to the cell.• Made up of cellulose• Found in Plants, Algae,
Fungi, and most bacteria.

CELL ORGANELLES
LysosomesFunction: Membrane-bound organelles that contain enzymes that defend a cell from pathogens. • Break down damaged
or worn-out cell parts
Cell MembraneFunction: A Semi-permeable barrier made up of a double layer of phospholipids that monitors the passage of materials in and out of the cell.

REINFORCEMENT ACTIVITY
USATest Prep Class Party• Navigate to USATest Prep website-
www.usatestprep.com• Click the drop down menu for EOCT and select
Biology• Watch the following video for step-by-step
directions to setup the activity for your classhttp://usatestprep.com/modules/video/video_popup.php?pop_up_help=1&id=1402

CLASS PARTY INSTRUCTIONS• Teachers• As students join the party, they will appear in the student table
• They will not be able to answer questions until you start the party• Click "Start" to begin.• There are two views we offer for projecting in front of the class.
• Stats view (default) will list percent incorrect, correct, and total complete.• Race view will animate student avatars as they move towards the finish line. A
student will cross the finish line when they get 70% correct.• Student results will update every 10 seconds.• Click "End" once all the students have answered. You will then have
the option to print the results• Students• Have students click "Join a Class Party" from the Home tab. They can
also login from their mobile-device.• Enter the code seen in the dashed box.

SOURCES
Nowicki, S. (2008). Chapter 3: Cells. In McDougal Littell Biology (pp. 70-84). Evanston, IL: McDougal Littell
www.usatestprep.com