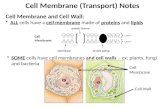
Unit B: Cell structure. Animal cell Liver Cell Cell membrane.
-
Upload
ella-roberts -
Category
Documents
-
view
239 -
download
3
Transcript of Unit B: Cell structure. Animal cell Liver Cell Cell membrane.

Unit B: Cell structure

Animal cell

Liver Cell

Cell membrane

Nucleus

Nucleus

Nuclear pores

FUNCTIONS OF NUCLEUS:
• Nuclear membrane/envelope bilayer, separates and contains nuclear contents (DNA).
• Nuclear pores: allow mRNA out of nucleus, nucleotides, nutrients & enzymes in. They are made from protein.
• Chromatin: Protein & DNA; form chromosomes when cell divides.
• Nucleolus:contains rRNA and Ribosomal proteins.

The Endoplasmic Reticulum: ER
• Rough E.R.
• Studded with ribosomes
• Site of protein synthesis for proteins meant for export
• Phospholipids made here
• Smooth E.R.
• Detoxifies poisons (found in liver cells)
• Synthesize steroids


Endoplasmic Reticulum

Endoplasmic reticulum

Ribosomes

Function of Ribosomes
• Made from two protein subunits and rRNA
• Some are free, found alone in cytoplasm
• Others are attached to the RER• Translation of mRNA into
polypeptides or PROTEIN SYNTHESIS!

Ribosome structure:

Mitochondria

Function of Mitochondria:
• Cellular Respiration converts energy in Glucose to ATP
• C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + 38 ATP
• Found in large numbers in energetic cells (sperm cells, muscles etc.)

Golgi apparatus
Looks like a series of flattened sacules.
Appears close to the cell membrane.

Golgi•Packages, modifies and stores molecules.
•Forms transport or secretory vesicles
•Involved in export of proteins through exocytosis.
•Draw diagram page 2 in green book exocytosi.ram

Lysosomes

Lysosomes:
• Contain hydrolytic enzymes (help to perform hydrolysis) for digesting molecules.
• These special vacuoles merge with another molecule containing vacuole for cell digestion.
• Called “suicide sacs”, contents could destroy cell!

Microtubules, cytoskeleton

Cytoskeleton
• Many protein filaments (actin filaments and microtubules) help organize and anchor cell parts.

cilia

Cilia and flagella microtubule arrangement 9+2

Function of cilia and flagella:
Cilia:
•Line the respiratory passages and sweep mucus upwards.
•Line the oviducts to transport ovum to uterus
•Flagella: Propel sperm
towards the ovum.