Lufukuja G.1 The cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the...
-
Upload
shanna-parker -
Category
Documents
-
view
226 -
download
0
Transcript of Lufukuja G.1 The cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane The cell membrane (also known as the...

Lufukuja G. 1
The cell (plasma) membrane

The cell membrane
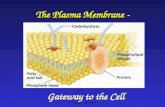
• The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane, which is present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells
• The cell membrane is selectively permeable and works as a barrier between the inner and outer surface of a cell
2Lufukuja G.

Function of Plasma Membrane• It separates the contents of the cell from its outside
environment and it regulates what enters and exits the cell.• Plasma membrane plays a vital role in protecting the
integrity of the interior of the cell by allowing only selected substances into the cell and keeping other substances out.
• It also serves as a base of attachment for the cytoskeleton in some organisms and the cell wall in others. Thus the cell membrane supports the cell and helps in maintaining the shape of the cell.
• The cell membrane is primarily composed of proteins and lipids. While lipids help to give membranes their flexibility and proteins monitor and maintain the cell's chemical climate and assist in the transfer of molecules across the membrane.
• The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, which allows only selected molecules to diffuse across the membrane
Lufukuja G. 3

Plasma Membrane Structure• It is the phospholipids bilayer.• Plasma membrane is an amphipathic, which
contains both hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
• It is a fluid mosaic of lipids, proteins and carbohydrate.
• It is lipid bilayer, which contains -two layers of phospholipids, phosphate head is polar (water loving), fatty acid tails non-polar (water fearing) and the proteins embedded in membrane.
4Lufukuja G.

Lufukuja G. 5

The cell transport mechanisms• Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process in which cells
absorb molecules by engulfing them.• Endocytosis is a pathway for internalizing solid particles
("cell eating" or phagocytosis), small molecules and ions ("cell drinking" or pinocytosis), and macromolecules. Endocytosis requires energy and is thus a form of active transport.
6Lufukuja G.

Lufukuja G. 7

The cell transport …• Exocytosis: Exocytosis occurs in various cells to remove
undigested residues of substances brought in by endocytosis, to secrete substances such as hormones and enzymes, and to transport a substance completely across a cellular barrier eg. Exocrine glands
8Lufukuja G.

The cell transport …• Exocrine glands secrete their products through a duct onto
an outer surface of the body. Secretion is directly onto the apical surface– Apocrine glands; Holocrine glands and Merocrine
glands
9Lufukuja G.

The cell transport …• Apocrine glands a portion of the secreting cell's body is lost during
secretion. e.g. mammary gland, sweat gland of arm pit, pubic region, skin around anus, lips, nipples.
10Lufukuja G.

The cell transport …• Holocrine glands the entire cell disintegrates to secrete its substances
(e.g., sebaceous glands) sebaceous.
11Lufukuja G.

The cell transport …• Merocrine glands cells secrete their substances by exocytosis (e.g.,
mucous and serous glands). Also called "eccrine". e.g. the sweat gland, goblet cells, salivary gland, tear gland, intestinal glands.
12Lufukuja G.

Transport Proteins and Carrier Proteins
G.LUFUKUJA 13

Transport protein/ Carrier proteins
• Carrier proteins facilitate the diffusion of different molecules, while channel proteins are involved in the movement of ions, small molecules, or macromolecules, such as another protein, across a biological membrane
Lufukuja G. 14

Carrier proteins…• Na+-K+ pump: A carrier protein is involved and it
pumps Na + out of the cell and K + into the cell. It requires ATP to maintain this pump, where the concentration of Na + outside the cell is 10-20 times that in the cell, and likewise concentration of K + in the cell is 10-20 times its concentration outside the cell.
15Lufukuja G.

CYTOPLASMIC ORGANELLES
Lufukuja G. 16

Cytoplasmic cell Organelles• Membrane bound organelles that are generally found in eukaryotic
cells are rough ER, smooth ER, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, plastids and lysosomes
• Non-membrane bound organelles, which generally do not contain membranes, are ribosomes, cytoskeletal structures, centrioles, cilia, and flagella
17G.LUFUKUJA

Cytoskeleton…• Microfilaments - Any of the minute contractile protein
fibers, actin, located throughout the cytoplasm of cells and functioning primarily in maintaining the shape and structural integrity of a cell; they may contribute to changes in cell shape in those cells capable of changing their shape.
• Microtubules - The cylindrical hollow cytoskeletal protein complexes (structures) which are distributed throughout the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells, providing structural support and assisting in cellular locomotion, internal transport and forming the spindle apparatus at cell
• Centrioles - The two cylindrical, non-membrane bound cell organelles. Centrioles are involved in the organization of the mitotic spindle and in the completion of cytokinesis
Lufukuja G. 18

Endoplasmic Reticulum• Endoplasmic reticulum - A complex membrane-
bound cell organelle which consists of a network of interconnected membranous channels and compartments (cisternae) of various shapes which are continuous with both the nuclear envelope and the Golgi apparatus located within the cytoplasm of cells which are involved in the synthesis, modification, and transport of cellular materials.
19G.LUFUKUJA

Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough ER )…
• Rough ER - A cell organelle with a network of membranous channels and compartments (cisternae) of various shapes which are continuous with both the nuclear envelope and the Golgi apparatus; it always has ribosomes which are attached to the cytoplasmic face of the channels which synthesize proteins for storage in vesicles and perhaps export from the cell.
Lufukuja G. 20

Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER )…
• Smooth ER - A cell organelle with a network of membranous channels and compartments (cisternae) of various shapes which are continuous with both the nuclear envelope and the Golgi apparatus; ribosomes are not attached to the cytoplasmic face of the channels.
• It synthesizes lipids, phospholipids, and steroids. Cells which secrete these products, such as those in the testes, ovaries, and skin oil glands have a great amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
Lufukuja G. 21

Endoplasmic Reticulum (Smooth ER )…
• Metabolism of carbohydrates • It also carries out the metabolism of
carbohydrates, drug detoxification (they have enzymes cytochrome P-450 which is involved in detoxification of drugs)

Golgi apparatus• The Golgi apparatus is an integral in modifying,
sorting, and packaging these macromolecules for cell secretion (exocytosis) or use within the cell.
• It primarily modifies proteins delivered from the rough endoplasmic reticulum, but is also involved in the transport of lipids around the cell, and the creation of lysosomes.
•
23G.LUFUKUJA

Golgi apparatus…• The GA is involved in the synthesis of lipoproteins and
proteoglycans (sulphated mucopolysaccharides).• Production of mucopolysccharides is particularly prominent
in mucus secreting cells such as Goblet cells.
24G.LUFUKUJA

Ribosomes • Ribosomes are made up of 35% ribosomal
protein and the 65% ribosomal RNA (rRNA).• There are more than 50 different proteins
that unite with rRNA to form a ribosome. • The formation of ribosomes begins in the
cytosol where all cell proteins are synthesized.
25G.LUFUKUJA

Mitochondria• The mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a
membrane bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells
27G.LUFUKUJA

Inheritance of mitochondrial DNA
• About 99% of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) are inherited from the mother, but about 0.1-1% of persons mitochondria can be inherited from the father.
• The reason for such a low percentage from the father is that the mitochondria of the spermaotozoa are normally thrown out during fertilization.
• It is therefore possible to tress the uterine (maternal) lineage far back in time. Unlike the nuclear DNA which changes by 50% in each offspring.
28G.LUFUKUJA

Lysosomes • Is the membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles
which contain various hydrolytic enzymes (proteases, lipases, nucleotidases, etc.,
• Synthesized at the rER and packaged by the Golgi apparatus) which function in intracellular digestion by merging with a phagosome and are suspected of contributing to aging when they become "leaky;"
• Lysosomes are often large enough to be seen in the light microscope; they are especially prominent in leukocytes, and liver and kidney cells.
Lufukuja G. 29

Peroxisomes • Peroxisomes contain oxidative enzymes, such as
catalase, D-amino acid oxidase, and uric acid oxidase. • However the last enzyme is absent in humans, explaining
the disease known as gout, caused by the accumulation of uric acid
Lufukuja G. 31

G.LUFUKUJA 32
The Nucleus

Nucleus• The nucleus is the largest cellular organelle in
animal cells• It contains most of the cell's genetic material,
organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes
• The genes within these chromosomes are the cell's nuclear genome
G.LUFUKUJA 33
The following are the components of the nucleus
Nuclear laminsNucleoplasmNucleolusChromatinRibosomes

Nuclear envelope• A nuclear membrane, also known as the nuclear
envelope, nucleolemma, is the double lipid bilayer membrane which surrounds the genetic material and nucleolus in eukaryotic cells.
• During the G2 phase of interphase, the nuclear membrane increases its surface area and doubles its number of nuclear pore complexes. The nuclear membrane must break down during the prometaphase state of mitosis to allow the mitotic spindle fibers to access the chromosomes inside.
G.LUFUKUJA 34

G.LUFUKUJA 35

Nucleolus • The nucleolus is the nuclear subdomain that assembles
ribosomal subunits in eukaryotic cells. Ribosome assembly begins with transcription of pre‐rRNA.
• The pre‐rRNA is modified and processed into rRNA with the aid of non‐ribosomal proteins and small nucleolar RNAs.
• The nucleolus has numerous other functions including assembly of signal recognition particles, modification of transfer RNAs and sensing cellular stress
G.LUFUKUJA 36

Genetic materials• The terms chromatin and chromosomes are used in
relation to genetic materials that are present in the nucleus. Chromatin and chromosomes are similar structures in the sense that they are made up of DNA and histone proteins.
• The use of these terms is based on morphological appearance of genetic materials.
G.LUFUKUJA 37

Chromosome and chromatin• The nucleus of a non-dividing cell contains
chromatin; they are responsible for giving the nucleus a characteristic appearance of electron dense materials under the electron microscope.
• There are two types of Chromatin; heterochromatin (condensed) and euchromatin (extended) forms
• Euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. 92% of the human genome is euchromat
• Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA, which comes in different varieties. These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive and facultative heterochromatin.
G.LUFUKUJA 38

Constitutive and facultative heterochromatin
• The genes contained within the constitutive heterochromatin are poorly expressed.
• For example, all human chromosomes 1, 9, 16, and the Y-chromosome contain large regions of constitutive heterochromatin.
• In most organisms, constitutive heterochromatin occurs around the chromosome centromere and near telomeres
G.LUFUKUJA 39

Facultative heterochromatin
• Facultative heterochromatin: contains DNA sequences that are not transcribed in one cell but may be transcribed in other cells. An example of facultative heterochromatin is X-chromosome: one X chromosome is packed in facultative heterochromatin and does not transcribe, while the other X chromosome is packaged in euchromatin and transcribed
G.LUFUKUJA 40

Centromere• The centromere (centro- + -mere) is the part of a
chromosome that links sister chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore
• The chromosomes can be metacentric, subcentric, acrocentric and telocentric
G.LUFUKUJA 41

Karyotyping• A karyotype is the number and appearance of
chromosomes in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell. • Karyotyping involves: Counting the number of
chromosomes & Looking for structural changes in chromosomes
G.LUFUKUJA 42
Certain abnormalities can be identified through the number or arrangement of the chromosomes. Therefore useful for detecting genetic diseases

Examples of Genetic diseases• Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), is a genetic
condition in which a person has 47chromosomes instead of the usual 46. Down syndrome occurs when there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. Thus known as Trisomy 21. The extra chromosome causes problems and interferes with normal development of the body and brain
G.LUFUKUJA 43

Genetic diseases…• The most common types of autosomal trisomy that survive
to birth in humans are:• Trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome)• Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)• Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)• Trisomy of sex chromosomes can also occur and include:• XXX (Triple X syndrome)• XXY (Klinefelter syndrome)• XYY
G.LUFUKUJA 44