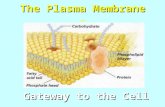
1 The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell copyright cmassengale.
-
Upload
luke-mcculloch -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
0
Transcript of 1 The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell copyright cmassengale.

1
The Plasma The Plasma MembraneMembrane -
Gateway to the CellGateway to the Cellcopyright cmassengale

2
Photograph of a Cell Photograph of a Cell MembraneMembrane
copyright cmassengale

3
Cell MembraneCell Membrane
The cell membrane is flexibleflexible and allows a unicellular organism to move
copyright cmassengale

4
HomeostasisHomeostasis
•Balanced internal condition of cells
•Also called equilibrium•Maintained by plasma
membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
copyright cmassengale

5
Functions of Plasma Functions of Plasma MembraneMembrane
Protective barrierProtective barrier
Regulate transport in & out of Regulate transport in & out of cell cell (selectively permeable)(selectively permeable)
Allow cell recognitionAllow cell recognition
Provide anchoring sites for Provide anchoring sites for filaments filaments of cytoskeletonof cytoskeleton
copyright cmassengale

6
Functions of Plasma Functions of Plasma MembraneMembrane
Provide a binding site for Provide a binding site for enzymesenzymes
Interlocking surfaces bind cells Interlocking surfaces bind cells together (junctions)together (junctions)
Contains the cytoplasm (fluid in Contains the cytoplasm (fluid in cell) cell)
copyright cmassengale

7
Cell MembraneCell Membrane
Hydrophobic molecules pass easily; hydrophilic DO NOT
The cell membrane is made of 2 layers of phospholipidphospholipids called the lipid bilayerbilayer
copyright cmassengale

8
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
Make up the cell membrane
Contains 2 fatty acid chains that are nonpolarHead is polar & contains a –PO4 group & glycerol copyright cmassengale

9copyright cmassengale

10
Polar heads are hydrophilichydrophilic “water loving”Nonpolar tails are hydrophobichydrophobic “water fearing”
Cell MembraneCell Membrane
Makes membrane “Selective” in what crosses
copyright cmassengale

11
FLUIDFLUID- because individual phospholipids and - because individual phospholipids and proteins can move around freely within the proteins can move around freely within the layer, like it’s a liquid.layer, like it’s a liquid.
MOSAICMOSAIC- because of the pattern produced by - because of the pattern produced by the scattered protein molecules when the the scattered protein molecules when the membrane is viewed from abovemembrane is viewed from above..
FLUID MOSAIC MODELFLUID MOSAIC MODEL
copyright cmassengale

12
Small molecules and larger hydrophobic molecules move through easily.e.g. O2, CO2, H2O
Semipermeable Semipermeable MembraneMembrane
copyright cmassengale

13
PhospholipidsPhospholipids
CholesterolCholesterol
Proteins-peripheral- (on the edge of the membrane)and integral- (also called intrinsic proteins, they are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer)
Membrane ComponentsMembrane Components
copyright cmassengale

14
Proteins are important Proteins are important structures in the cell structures in the cell
membranemembrane
copyright cmassengale
Glyco –means “of or relating to sugar”Glycoproteins have the carbohydrate chain (They are also called Marker Proteins) they identify the cell- they are not transport proteins.

Glycolipids are lipids with carbohydrate chains attached. Their main function is to provide energy and serve as markers for
cellular recognition.
copyright cmassengale 15

What is the difference between glyco-proteins and glyco-lipids?
Glycoproteins are NOT energy storage molecules, they function in cell-cell recognition pathways. (They are
marker proteins.)
Glycolipids are energy storage molecules and they also those function in recognition, mostly in vesicle
trafficking pathways inside the cell, not in recognition between different cells.
They both have carbohydrate chains(This will not be on your test.)
copyright cmassengale 16

Cell membrane components
copyright cmassengale 17

18
SolubilitySolubility•Materials
that are soluble in lipids can pass through the cell membrane easily
copyright cmassengale

19
Ions, hydrophilic molecules larger than water, and large molecules such as proteins do not move through the membrane on their own.
Semipermeable Semipermeable MembraneMembrane
copyright cmassengale

20
Types of Transport Types of Transport Across Cell Across Cell MembranesMembranes
copyright cmassengale

21
Simple DiffusionSimple Diffusion
• Requires NONO energy
• Molecules move from area of HIGH HIGH to LOWto LOW concentration
copyright cmassengale

22
DIFFUSIONDIFFUSION
Diffusion is a PASSIVEPASSIVE process which means no energy is used to make the molecules move, they have a natural KINETIC ENERGY
copyright cmassengale

23
Diffusion of LiquidsDiffusion of Liquids
copyright cmassengale

24
Diffusion through a Diffusion through a MembraneMembrane
Cell membrane
Solute moves DOWN concentration gradient (HIGH to LOW)copyright cmassengale

25
OsmosisOsmosis• Diffusion of Diffusion of
waterwater across a across a membranemembrane
• Moves fromMoves from HIGH water HIGH water potentialpotential (low (low solute) tosolute) to LOW LOW water potentialwater potential (high solute)(high solute)
Diffusion across a membrane
Semipermeable
membrane
copyright cmassengale

26
Diffusion of HDiffusion of H22O Across O Across A MembraneA Membrane
High H2O potentialLow solute concentration
Low H2O potentialHigh solute concentration
copyright cmassengale

27
Cell in Isotonic SolutionCell in Isotonic Solution
CELLCELL
10% NaCL90% H2O
10% NaCL
90% H2O
What is the direction of water movement?The cell is at _______________.equilibrium
ENVIRONMENTENVIRONMENT
NO NET NO NET MOVEMENMOVEMENTT
copyright cmassengale

28
Cell in Hypotonic Cell in Hypotonic SolutionSolution
CELLCELL
10% NaCL90% H2O
20% NaCL
80% H2O
What is the direction of water movement? copyright cmassengale

29
Cell in Hypertonic Cell in Hypertonic SolutionSolution
CELLCELL
15% NaCL85% H2O
5% NaCL95% H2O
What is the direction of water movement?
ENVIRONMENTENVIRONMENT
copyright cmassengale

30
Cells in SolutionsCells in Solutions
copyright cmassengale

31
Isotonic Solution
NO NET MOVEMENT OF
H2O (equal amounts entering
& leaving)
Hypotonic Solution
CYTOLYSIS
Hypertonic Solution
PLASMOLYSIS
copyright cmassengale

32
Cytolysis & PlasmolysisCytolysis & Plasmolysis
Cytolysis Plasmolysis
copyright cmassengale

33
Osmosis in Red Blood Osmosis in Red Blood CellsCells
IsotonicIsotonic Hypotonic
Hypertoniccopyright cmassengale

34
hypotonic hypertonic isotonic
hypertonic isotonic hypotonic
copyright cmassengale

35
Three Forms of Transport Across the MembraneThree Forms of Transport Across the Membrane
copyright cmassengale

36
Passive Passive TransportTransport
Simple DiffusionSimple Diffusion
Doesn’tDoesn’t require require energyenergy
Moves Moves high to lowhigh to low concentrationconcentration Example: Example: OxygenOxygen or or waterwater diffusing into a diffusing into a cell and cell and carbon carbon dioxidedioxide diffusing out diffusing out.
copyright cmassengale

37
Passive Passive TransportTransport
Facilitated diffusion
Doesn’t require energy
Uses transport proteins to move high to low concentrationExamples: Examples: GlucoseGlucose or or amino acidsamino acids moving moving from blood into a from blood into a cell.cell.
copyright cmassengale

38
Proteins Are Critical to Proteins Are Critical to Membrane FunctionMembrane Function
copyright cmassengale

39
Types of Transport Types of Transport ProteinsProteins
• Channel proteins are embedded in the cell membrane & have a pore for materials to cross
• Receptor or carrier proteins can change shape to move material from one side of the membrane to the other
copyright cmassengale

40
Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion
Molecules will randomly move Molecules will randomly move through the through the porespores in in Channel Channel ProteinsProteins..
copyright cmassengale

41
Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion
• SomeSome Carrier Carrier proteinsproteins do not do not extend through the extend through the membrane.membrane.
• They They bond and bond and drag moleculesdrag molecules through the lipid through the lipid bilayer and release bilayer and release them on the them on the opposite side.opposite side.
copyright cmassengale

42
Receptor or Carrier Receptor or Carrier ProteinsProteins
• Other carrier Other carrier proteins proteins change shapechange shape to move to move materials materials across the cell across the cell membranemembrane
copyright cmassengale

43
Active TransportActive Transport
Requires energy or ATP
Moves materials from LOW to HIGH concentration
AGAINST concentration gradient
copyright cmassengale

44
Active transportActive transportExamples:
Pumping Na+ (sodium ions) out and K+ (potassium ions) in against strong concentration gradients.
Called Na+-K+ Pump
Helps muscle cells contract.copyright cmassengale

45
Sodium-Potassium Pump & Sodium-Potassium Pump & Transport Protein- Transport Protein-
Active Transport using ATPActive Transport using ATP pumping against the gradient.
3 Na+ pumped in for every 2 K+ pumped out; creates a membrane potential.
copyright cmassengale

46
Moving the “Big Stuff”Moving the “Big Stuff”
Molecules are Molecules are moved outmoved out of the cell by of the cell by vesiclesvesicles that that fusefuse with the plasma membrane. with the plasma membrane.
ExocytosExocytosisis-
moving things out.
This is how many This is how many hormoneshormones are secreted and how are secreted and how nerve cellsnerve cells communicate with one another communicate with one another.
copyright cmassengale

47
ExocytosisExocytosisExocytic Exocytic vesicle vesicle immediately immediately after fusion after fusion with plasma with plasma membrane.membrane.
copyright cmassengale

48
Moving the “Big Moving the “Big Stuff”Stuff”Large molecules move materials into the Large molecules move materials into the
cell by one of cell by one of three forms of endocytosisthree forms of endocytosis.
copyright cmassengale

49
PinocytosisPinocytosis
Most Most commoncommon form of endocytosis form of endocytosis. Takes in Takes in dissolveddissolved molecules as a molecules as a vesiclevesicle.
copyright cmassengale

50
PinocytosisPinocytosis
• Cell forms an Cell forms an indentionindention
• Materials Materials dissolve in dissolve in waterwater to be to be brought into brought into cellcell
• Called Called “Cell “Cell Drinking”Drinking”
copyright cmassengale

51
Example of Example of PinocytosisPinocytosispinocytic vesicles forming mature transport vesicle
Transport across a capillary cell (blue).copyright cmassengale

52
Receptor-Mediated EndocytosisReceptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Some Some integral proteinsintegral proteins have have receptorsreceptors on their surface to on their surface to recognize & take in recognize & take in hormones, hormones, cholesterolcholesterol, etc., etc.
copyright cmassengale

53
Receptor-Mediated EndocytosisReceptor-Mediated Endocytosis
copyright cmassengale

54
Endocytosis – Phagocytosis Endocytosis – Phagocytosis
Used to Used to engulf large particlesengulf large particles such such as food, as food, bacteriabacteria, etc. into vesicles, etc. into vesicles
Called Called “Cell Eating”“Cell Eating”copyright cmassengale

55
Phagocytosis About to OccurPhagocytosis About to Occur
copyright cmassengale

56
PhagocytoPhagocytosissis - Capture of a Yeast Cell (yellow) by Membrane Extensions of an Immune System Cell (blue)
copyright cmassengale

57
ExocytosisExocytosis The opposite of endocytosis is exocytosis. The opposite of endocytosis is exocytosis. Large moleculesLarge molecules that are manufactured in that are manufactured in
the cell are the cell are releasedreleased through the cell through the cell membranemembrane..
Inside Cell Cell environment
copyright cmassengale

58copyright cmassengale
Now go to classzone.com and go to Ch 3 1.) Go to Research Center and watch the Animations on Active Transport2.)Watch the Ch 3 Animations – on “Cell Structures” and“Get through a cell membrane” 2.)Take the Section Quizzes














![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)