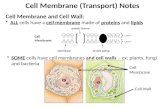
The Cell Membrane. What is the cell membrane? AKA: Plasma membrane AKA: Plasma membrane The boundary...
-
Upload
maximillian-charles -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
0
Transcript of The Cell Membrane. What is the cell membrane? AKA: Plasma membrane AKA: Plasma membrane The boundary...

The Cell Membra
ne

What is the cell membrane?
AKA: Plasma membrane The boundary between the cell and
the environmentDoes every cell have a cell membrane?
1. Yes, Each and every cell has a cell membrane.

Cell membranes help maintain homeostasis, what is that?
Cel
ls b
reat
hing
Cel
ls g
ettin
g bl
ood t.
..
Cel
ls m
aint
ainin
g in...
Cel
ls re
produc
ing
0% 0%0%0%
1. Cells breathing2. Cells getting
blood to them3. Cells
maintaining internal conditions
4. Cells reproducing
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28

The cell membrane allows nutrients to come into the
cell1. Cell membranes help to
maintain homeostasis1. Examples: Controls amounts of
glucose, amino acids, lipids

Cell Membranes are…
Fluid Mosaic Selectively Permeable Phospholipid Bilayers
Huh??? Let’s break it down…

Selectively Permeable…
What does selective mean? What does Permeable mean?

Cell membranes are SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE…
-the cell membrane lets some molecules in and keeps others out

Phospholipid Bilayer…
Phospholipids make it up It has TWO (bi) LAYERS
Just as a bicycle has two tires…the bilayer has two layers

Structure of the Cell Membrane
What does the cell membrane look like up close?
Notice the 2 layers!Lets look at one
of these structures up
close

Structure of Cell Membrane
A.Phospholipids1. Phosphate head
a. Polarb. Hydrophilicc. Make up the outer borders of
the membrane

2 Fatty acid tails (lipids=fats, oils, etc)
a. Nonpolarb. Hydrophobicc. Make up the
inner part of the membrane

Structure of Phospholipid

The phospholipids arrange Themselves in a very specific way

The key is…Polar vs. NonpolarPolar: positive and negative ends
(b/c electrons are not shared equally)
1. Example: WaterNonpolar: does not have
oppositely charged ends (atoms share electrons equally)
Which of the above is hydrophilic? Hydrophobic?

So…Why are the phospholipids arranged tail to tail? a. Water is inside and outside the
cell b. Phosphate group is hydrophilic
(polar) end1. Attracts water
c. Fatty acid tail end is hydrophobic (nonpolar)
1. Repels water

Thus we get the bilayer of phospholipids…
2 layers of phospholipids make up a cell membrane
Remember polar heads and nonpolar tails

Arrangement of phospholipids “tail to tail” due to water inside & outside the cell

Arrangement of cell surface proteins

Cell Membrane Structure

Let’s Begin to Build Our Membrane!
1. Take 1 bag with materials for you & your partner
2. You are going to build your phospholipids firsta. Marshmallows represent your
phosphate headb. Toothpicks represent your fatty acid
tails1. Break these in half. Please
include unsaturated fatty acid tails.
c. Make sure to line up the phospholipid bilayer correctly! Think polar & nonpolar!

When something is hydrophilic, it…
Has
a c
hemic
al m
ake.
.
Has
a c
hemic
al m
ake.
.
0%
100%1. Has a chemical
makeup that likes to be around water
2. Has a chemical makeup that does not like to be around water

Where would you expect to find water in this cell
membrane?
Her
e H
ere
12%
88%1. Here2. Here

Structure of Cell Membrane (cont.)
C.Cholesterol1. Helps to
stabilize the phospholipids and keep them from sticking together

Building Time!1. Now let’s add your cholesterol
into the membrane2. Use the gummy bears that are in
your bags to represent the cholesterol
a. Be sure to place them correctlyb. Check with your teacher once your
group has completed this
3. We will stop here for today. Please put your group’s name on the bag and put your phospholipids and cholesterols back in bag

Bell Work
1. Please put the parts of the cell membrane that we built yesterday back together
a. Phospholipid bilayerb. Cholesterols

Structure of the Cell Membrane (cont.)
D. Proteins: Help regulate which molecules enter and which molecules leave a cell.

1. Types of proteins in the cell membrane
a. Carrier Protein1. Use energy to help needed
substances or waste materials to move through the cell membrane which would otherwise be too big (or polar).

Let’s Build It!
Take your Pretzel out of the bag. This will represent the carrier
protein. Keeping in mind what we just talked
about in class, think of a way you can turn this into what a carrier protein is.

Types of proteins (cont.)b. Channel or Pore protein
1. Hydrophilic channel – allows lipid insoluble substances to pass in and out of cell.
2. Does NOT REQUIRE ENERGY!!!

Let’s Build It!
1. Take the Twizzler out of your bag.
2. This represents the channel protein.
3. You will need to split this in half in order to represent both sides of the channel.

Arrangement of cell surface proteins

Structure of Cell Membrane (cont.)
E. Nonpolar interior zone- true barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings
1. Many polar particles like sugars, proteins, ions, & most cell wastes cannot cross this zone b/c they are repelled by the nonpolar region

IV.) Fluid Mosaic Model of Cell Membrane
A. Lipid bilayer is not strong & firm like a hard shell, but it is fluid like a soap bubble
1. Often called a fluid mosaic model
B. Individual phospholipids, arranged side by side, float within the bilayer
1. Cholesterol prevents phospholipids from sticking together

Cell Membrane Structure Overview

Honors Only

Types of proteins (cont.)
c. Glycoproteins1. Protein with what
macromolecule attached to it?Carbohydrate
2. Functions for cell to cell recognition

Let’s Build It!
1. Take the Pretzel Stick out. 2. This will represent the “glyco” part
of the glycoprotein.3. Also take out the large Gum Drop.4. This will represent the protein part
of the glycoprotein

Types of proteins (cont.)
d. Receptor Protein1. These have binding sites for
molecules such as hormones or substrates to bind to

Let’s Build It!
Take your Fruit Gum Drop out of the bag.
This will represent your receptor protein.
You will need to use your fingers to “carve out” the active site for this receptor protein

Types of proteins (cont.)
e. Enzymatic Protein1. Catalyze specific reactions
along the inside of the cell membrane

Let’s Build It!
Take a scrap sheet of paper and cut out a Pac-Man Shape
Put this cut-out into your membrane Which way would the protein fit into the
membrane? What would fit into Pac-Man’s mouth?