Striated muscle tissue x 400 Muscle histology Notice the fine ‘stripes’ or striations along each...
-
Upload
juliet-cox -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
2
Transcript of Striated muscle tissue x 400 Muscle histology Notice the fine ‘stripes’ or striations along each...
Striated muscle tissuex 400
Muscle histology
Notice the fine ‘stripes’ or striations along each muscle cell.
Skeletal muscle cells (fibres) are long, cylindrical and multinucleate
peripheralmultiple nuclei
myofibrils
cell membrane(=sarcolemma)
cytoplasm(=sarcoplasm)
cross-striations(alternating lightand dark bands)
Characteristicbanding pattern
due to thearrangement of
the myofilamentsMYOFIBRIL
T.E.M. showing ‘light’ ‘I’ bands made of Actin
And broader ‘dark’ ‘A’ bands made of Myosin
‘A’ Band‘I’ Band
MYOSIN
ACTIN
Z LINEZ LINE
Myofilaments
A singlemyofibril
SARCOMERE
SARCOMERE
myofilaments insidethe myofibril do notextend the entire lengthof the MYOFIBRILS butare arranged in repeatingunits called SARCOMERES Thin actin
filamentThick myosinfilament withcross bridges
Actin and myosin are protein molecules that form the myofilaments
Each thin filament is a strand of actin molecules twisted into
a helix
THIN ACTIN FILAMENT
THICK MYOSIN FILAMENTEach thick filament consists ofabout 200 molecules of the protein
myosin
Each myosin molecule is a longfibrous protein with a ‘head’ at one end.
Myosinmolecule
Myosinhead
Each actin molecule has amyosin-binding site where myosin
heads can attach
Myosin ‘heads’ attach to theactin molecules and form cross-bridges
Under a light microscope the striated nature of skeletal muscle can be observed
This is seen as a regular alternation of light and dark bandsThis banding pattern is due to the arrangement of the thick and thin filaments
within the myofibrilsDark bands (A bands) appear where thick myosin filaments are located
A BANDLight bands (I bands) appear where there are thin filaments only
I BANDI BANDThe edges of the Abands are very darkas thick and thinfilaments are presenttogether
The centre of theA band containsthick filaments onlyand is slightly lighter (H Zone)
HZONE
Across the middleof each I-band isa dark line called the Z line: The sectionof myofibril betweenthese Z lines is the SARCOMERE
SARCOMERE
z z
This electron micrograph of a longitudinalsection of skeletal muscle shows the
myofibrils and Z-lines of the sarcomeres(magnification X75 000)
Z line
Z line
I BAND
A BAND
H ZONE No overlap
Myofibrils extendalong the entire length of the muscle cell
A network of smoothendoplasmic reticulum(sarcoplasmic reticulum)surrounds each myofibril
Cisternae or sacsof the sarcoplasmicreticulum where calciumions are stored
Sarcoplasm containedwithin the musclecell
The sarcolemmais the outerlimiting membraneof the muscle cell
Transverse T-tubulesextend inwardsacross the musclecell from thesarcolemma
Mitochondria extendin rows throughoutthe sarcoplasmproviding the energyfor muscle contraction
Following the arrivalof a nerve impulse
at the neuromuscularjunction, a wave of
depolarisation spreadsthroughout the
sarcolemmaand inwards via thetransverse tubules
The inward spreadof the impulsedepolarises thesarcoplasmic
reticulum
The inward spreadof depolarisation
triggers the releaseof calcium ions
from the sarcoplasmicreticulum Calcium ion
concentrationsin the vicinity
of the thin filamentsincrease
Bindingsites Myosin
head
Calcium ions now bind to TROPONIN
TROPONIN
CalciumIon
TROPONIN changes shape allowing TROPOMYOSIN to moveaway from the myosin binding sites
Bindingsites Myosin
head
The myosin binding sites on the actin molecules are EXPOSED
Myosin heads make contact with the actin filaments
Calcium ions now bind to TROPONIN
TROPONIN changes shape allowing TROPOMYOSIN to moveaway from the myosin binding sites
Bindingsites Myosin
head
The myosin binding sites on the actin molecules are EXPOSED
Myosin heads make contact with the actin filaments
Calcium ions now bind to TROPONIN
TROPONIN changes shape allowing TROPOMYOSIN to moveaway from the myosin binding sites
ZZ
Sarcomere Shortens
THE SLIDING FILAMENT MECHANISMIS TRIGGERED INTO ACTION AND MUSCLE
CONTRACTION TAKES PLACE
Notice that it is the H-Band which shortens
Both the below are very good simulations of the slilding filament muscle contractionhttp://www.sci.sdsu.edu/movies/actin_myosin_gif.html
http://msjensen.education.umn.edu/1135/Links/Animations/Flash/0008-swf_sarcomere_shor.swf
Good animation of pairs of muscle contracting: http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio105/muscles.htm
An excellent animation on structure and function of muscle: http://entochem.tamu.edu/MuscleStrucContractswf/index.html
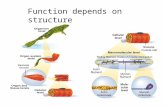
WHOLEMUSCLE
MAGNIFY
MAGNIFYMuscle consists of bundlesof very long cells calledmuscle fibres
Muscle fibres are very long, cylindrical cells containing many nuclei (multinucleate). The nucleiare located at the periphery of thecell just underneath the cellmembraneMuscle cells show cross-striationscomposed of alternating light anddark bands
Each myofibril is composed of aregular arrangement of myofilamentsknown as the thick and thin filamentsZ Z
THIN ACTIN FILAMENT
THICK MYOSIN FILAMENT
SARCOMERE
MYOFIBRIL
Each muscle fibrecontains numerousmyofibrils
MAGNIFY