Day 11- Eukaryotic Cell Parts
Transcript of Day 11- Eukaryotic Cell Parts

LECTURE PRESENTATIONSFor CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION
Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Lectures byErin Barley
Kathleen Fitzpatrick
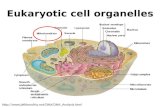
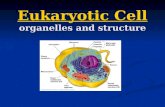
A Tour of the Cell
Chapter 6

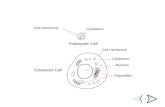
The endomembrane system regulates protein traffic and performs metabolic functions in the cell
• Components of the endomembrane system– Nuclear envelope– Endoplasmic reticulum– Golgi apparatus– Lysosomes– Vacuoles– Plasma membrane
• These components are either continuous or connected via transfer by vesicles
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.

Figure 6.11 Smooth ER
Rough ER
ER lumen
CisternaeRibosomes
Smooth ERTransport vesicle
Transitional ER
Rough ER 200 nm
Nuclearenvelope


Figure 6.12
cis face(“receiving” side ofGolgi apparatus)
trans face(“shipping” side ofGolgi apparatus)
0.1 m
TEM of Golgi apparatus
Cisternae

Figure 6.15-3
Smooth ER
Nucleus
Rough ER
Plasmamembrane
cis Golgi
trans Golgi

A pancreatic beta cell produces and secrete insulin (a protein hormone).
Trace the pathway of production and export of this protein from the nucleus to the blood stream.
Describe what happens at each stop along its way.

Brefeldin A is an antibiotic produced by fungal organisms.
It interferes with transport from the ER to the Golgi apparatus (by blocking receiving end of the Golgi), leading to proteins accumulating inside the ER.
What are the immediate and long-term consequences of this antibiotic on cell structure and function?

Concept 6.5: Mitochondria and chloroplasts change energy from one form to another
• Mitochondria are the sites of cellular respiration
• Chloroplasts are the sites of photosynthesis
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.

• Mitochondria and chloroplasts have similarities with bacteria
– Enveloped by a double membrane– Contain free ribosomes and circular DNA
molecules– Grow and reproduce somewhat
independently in cells
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
The Evolutionary Origins of Mitochondria and Chloroplasts

Figure 6.17
Intermembrane space
Outermembrane
DNA
Innermembrane
Cristae
Matrix
Freeribosomesin themitochondrialmatrix
(a) Diagram and TEM of mitochondrion (b) Network of mitochondria in a protistcell (LM)
0.1 m
MitochondrialDNA
Nuclear DNA
Mitochondria
10 m

Figure 6.18
RibosomesStroma
Inner and outermembranes
Granum
1 mIntermembrane spaceThylakoid
(a) Diagram and TEM of chloroplast (b) Chloroplasts in an algal cell
Chloroplasts(red)
50 m
DNA

• The Endosymbiont theory – An early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed
a nonphotosynthetic prokaryotic cell, which formed an endosymbiont relationship with its host
– The host cell and endosymbiont merged into a single organism, a eukaryotic cell with a mitochondrion
– At least one of these cells may have taken up a photosynthetic prokaryote, becoming the ancestor of cells that contain chloroplasts
© 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.

NucleusEndoplasmicreticulum
Nuclear envelope
Ancestor ofeukaryotic cells(host cell)
Engulfing of oxygen-using nonphotosyntheticprokaryote, whichbecomes a mitochondrion
Mitochondrion
Nonphotosyntheticeukaryote
Mitochondrion
At leastone cell
Photosynthetic eukaryote
Engulfing ofphotosyntheticprokaryote
Chloroplast
Figure 6.16

Figure 6.UN01a
Nucleus
(ER)

Figure 6.UN01c

carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic acids
Always contain P
Generally contain no P*
Always contain N
Generally contain no N
Frequently contain S
Generally contain no S
Functional group
Polar or Nonpolar?
Hydrophobic or Hydrophilic
Found in all proteins
Found in many proteins
Found in many lipids
—OH
—CH2
—COOH
—NH2
—SH
—PO4

Compare and contrast the two molecules below using the following criteria :A.the arrangement of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atomsB.the types of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atomsC.the number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atomsD. the number of covalent bondsE. Functional role in cell

The functional group of the amino acid threonine is -OH. The functional group of the amino acid valine is methyl. Where would you expect to find these amino acids in globular protein in aqueous solution? Draw a picture