CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CELLS COMPARING modeling relating Make up/comprise Cell structure and...
-
Upload
jason-gallagher -
Category
Documents
-
view
225 -
download
0
Transcript of CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CELLS COMPARING modeling relating Make up/comprise Cell structure and...
CELLS- STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
CELLS
COMPARING
modeling relating
Make up/comprise
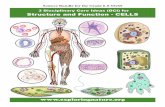
Cell structure and function
Viruses, bacteria, plant and animal cells
Cell structure
Organelle function & cell function
Organisms in a variety of ways
What is a cell???A cell is the structural and functional unit of all living things
Some organisms are unicellular (bacteria, protists)
Some organisms are multicellular (plants, animals, fungi)
Amount of cells in the human body= 100,000,000,000,000 (100 trillion!)
Scientist Involved in Cell TheoryHooke-coined the word “cell”von Leeuwenhoek- lens grinder; made
microscopes;discovered microscopic organisms in pond
water (animacules)Schleiden-botanist (all plants made of
cells)Schwann-zoologist (all animals made of
cells)Virchow-all cells produce more cells
Microscopes Used to View CellsCompound light
microscope- magnifies UP TO 1500 X
Electron Microscopes- magnify up to 1,000,000 X
Images differ Greatly
2-D image of RBCs in blood vessel (Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
Image of RBCs from Compound Light Microscope (40x)
3-D image of RBCs (Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
Types of CellsPROKARYOTESNo nucleus, no
membrane bound organelles
Archaebacteria & Eubacteria
EUKARYOTESNucleus, membrane-
bound organellesProtists, fungi,
plants, animals Humans have 200
types of cells (60 BILLION)
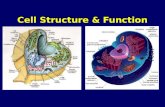
Organelles Cell membrane, nucleus, nucleolusCytoplasm, Ribosomes, Golgi apparatusEndoplasmic Reticulum, LysosomemitochondriaPlastids- (CHLOROPLASTS & LEUCOPLASTS)
PLANTS ONLYCell wall- PLANTS (cellulose), FUNGI (chitin), &
SOME PROTISTS ONLYCENTRIOLES-ANIMALS ONLYCilia=hair-like structures; Flagella = tail-like
structures
: COMMON TO EUKARYOTES
A cell’s structure is directly related to its function
1. Nerve cells have long, thin projections that enable them to communicate with other nerve cells.2. Respiratory tract lining cells have cilia, which have the job of trapping viruses and bacteria.3. Intestinal lining cells have projections called microvilli, which enable them to absorb the most nutrients possible
FOR EXAMPLE:
4. Fallopian tube lining cells: have cilia that beat, moving fluid and causing egg cell to move through tube toward uterus
5. SpermatozoaSperm cells have
a long, thin flagellum, that enables them to move through the mucus and fluid of the female reproductive tract
6. Sickle Cell Anemia: genetic disorder, mutation causes red blood cells to have a different shape- can’t do their job efficiently!
1. Take in nutrients2. Export wastes3. Take in gases (oxygen or carbon dioxide)4. Release gases (oxygen or carbon dioxide)5. Convert nutrients into energy6. Hundreds of specialized jobs that keep you alive!
WHAT DO CELLS DO?
Proposed 200 years AFTER Hooke coined the term cell
All living things made of cellsCells are the basic unit of structure
and function in living thingsAll cells come from other cells
CELL THEORY