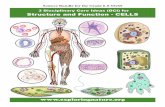
Cells Objective: To learn the structure and function of typical human cells.
Cell Structure and Function Discovering Cells Overview Cells are basic units of structure and...
-
Upload
lawrence-atkinson -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell Structure and Function Discovering Cells Overview Cells are basic units of structure and...

CELLS UNIT Cell Structure and Function

Section One Discovering Cells

Overview
• Cells are basic units of structure and function in living things.
• This means that cells form the parts or an organism and carry out all of the an organism’s processes, or functions.

Cells and Structure
• The structures of living things are determined by the variety of ways in which cells are put together.
• Examples:• A tall tree consists of cells arranged to form a
high trunk and leafy branch.• A red newt’s cells form a body with a head
and four legs.

Cells and Functions
An organisms functions are processes that enable it to stay alive and reproduce.
Examples:Obtaining oxygen Getting rid of wasteGrowing Obtaining food

Many and Small
One square centimeter of your skin’s surface contains approx. 100,000 cells.

First Observations of Cells
The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover and lean about cells.
A microscope is an instrument that makes small objects look smaller.

Robert Hooke
One of the first people to observe cells was the English scientist and inventor Robert Hooke.
Hooke used his microscope to observe a thin slice of cork.Cork is made from trees
To Hooke the empty spaces looked like empty rooms, which is where we get the word cell –meaning “small rooms”

Hooke and Cork Cells

Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch businessman who sold cloth. In his spare time he build simple microscopes.
Leeuwenhoek looked at samples from lake water, scrapings from teeth, and rain water.
When looking at the samples he say cells and some of these cells moved.\
He called these moving organisms animalcules meaning “little animals”

Leeuwenhoek and cells

The Cell Theory Three scientists
helped develop the cell theory.
The cell theory is a widely accepted explanation of the relationship between cells and living cells.

The Cell Theory
The cell theory states the following:All living things are composed of cells.Cells are the basic units of structure and
function in living things All cells are produced from other cells.

The Cell Theory The cell theory
applies to every living thing no matter how big or small.
https://www.brainpop.com/health/bodysystems/cells/

TYPES OF ORGANISMS
Unicellular Organismsvs.
Multicellular Organisms

What makes a living thing different from a nonliving thing?
A living things uses energy! Any individual form of life that uses
energy to carry out its activities is an organism.
Most organisms move. All organisms get water and other
materials from the environment.

Characteristics of Living Things
Living things have these characteristics: organization the ability to develop and grow the ability to respond to the environment the ability to reproduce

Needs of Life
Organisms cannot carry out the activities that characterize life without a few necessities: EnergyMaterialsLiving space.

What is an Organism?
Definition:
Organism – anything that can live on its own

Unicellular Organisms

Unicellular Organisms
Definition:Unicellular organism – an organism made of
only one cell
Information:These organism are very small and need to be
seen with a microscope.

Unicellular:Common Names Microscopic Organisms
Microorganisms
Really small living things

Examples of Unicellular Organisms
Amoeba
Bacteria
Protozoa
Unicellular algae
Unicellular fungi
Unicellular yeasts
Paramecium

Images of Unicellular Organisms

Multicellular Organisms

Multicellular Organisms
Definition:Multicellular organism – an organism made of
two or more cells
Information:These organisms are able to be seen with the
naked eye.These organisms need all parts of itself to
survive.

Common Names Many – celled organisms Eukaryotic organisms Mammals Birds Reptile Fish Many others…

Examples of Multicellular Organisms
Humans
Cats
Dogs
Insects
Birds
Flowers
Mold
Trees

Images of Multicellular Organisms

Looking Inside Cells Section Two

Looking Inside Cell Cells are basic units of structure and function in
living things.
There are even small structures inside a cell. These tiny structures are called organelles.
Organelles carry out specific functions within the cell.
https://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/cellstructures/

Looking Inside the Cell
Each organelle has a different function inside the cell.

Cell Wall
Description:The cell wall is a rigid layer of nonliving
materials that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Job:A plant’s cell wall helps to protect and
support the cell. Type of Cell:
Plant Only

Cell Wall
Animal cell Plant cell

Cell Wall
Additional Information:The cell wall is made mostly of a strong
material called cellulose.
The cell wall is tough and strong but ○ Water can pass through ○ Oxygen can pass through

Cell Membrane
Description:In cells with cell walls, the cell membrane is
located just inside the cell wall. In other cells, the cell membrane forms the outside boundary that separates the cell from its environment.
Job:The cell membrane controls what
substances come into and go out of the cell.

Cell Membrane
Type of Cell:Plant and Animal Cells
Additional Information:Everything that the cell needs from food to
oxygen pass through the cell membrane.
The cell membrane prevents harmful materials from entering the cell

Cell Membrane

Nucleus Description:
A large oval structure in the center of the cell. Job:
The “brain of the cell”. Controls the activities of the cell
Types of Cell:Animal and Plant Cell
Additional Information:There are several parts that make up the
nucleus

Nucleus

Nuclear Envelope
Description:A membrane that surrounds the nucleus.
Covered in pores Job:
Protects the nucleus and allows materials to pass in and out through the pores
Types of Cells:Plant and animal cells

Chromatin
Description: Thin strand floating in the nucleus
Job:Contain genetic material that are the
instructions for directing the cell’s functions Type of Cell:
Plant and animal cells

Nucleolus
Description:A small circular structure that is located in
the nucleus Job:
Produces the ribosomes of the cell Type of Cell:
Plant and animal cell

All Parts of the Nucleus

Cytoplasm
Description:The region between the cell membrane and
the nucleus. Made of a clear gel-like fluid. Job:
Cytoplasm is responsible for giving a cell its shape, keeps organelles in their place.
Types of Cells:Plant and animal cells

Cytoplasm

Mitochondria
Description:Rod shaped structure
Job:Known as the “powerhouse” of the cell
because they convert energy into food molecules to energy the cell can use to carry out its functions
Types of Cells:Plant and Animals

Mitochondria

Endoplasmic Reticulum
Description:A maze of passageways that surround the
nucleus Job:
Carries proteins and other materials from one part of the cell to another
Types of Cells:Plants and Animal Cell

Endoplasmic Reticulum

Ribosomes
Description:Small, grain-like bodies that attach to the
Endoplasmic Reticulum Job:
Produce proteins Types of Cells:
Animal and Plant cells

Golgi Bodies
Description:Flattened sacs and tubes
Job:Receive proteins and other newly formed
materials from the endoplasmic reticulum, package them, and distribute them to the other parts of cells
Types of Cells:Plant and Animal Cells

Golgi Bodies

Chloroplasts
Description:Large green structures that float in the
cytoplasm. It is what makes the leaves green.
Job:Capture the energy from sunlight and use it
to produce food for the cell. Types of Cells
Animal cells

Chloroplasts

Vacuoles
Description:Large water filled sac floating in the
cytoplasm. Plants have one large one. Some animal cells have several some ones
Job: The storage areas of the cells. Stores food,
water, and waste. Types of Cells
Animal and plants cells

Vacuoles

Lysosomes
Description:Small, round structures that contain
chemicals Job:
Break down materials in the cell. ○ Food○ Old parts of the cell
Types of Cells Animal and Plant cells

Lysosomes

The Cell in its Environment
Section Four

The Cell in its Environment
All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment.
The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which means that some substances can pass through the membrane while others cannot.

The Cell in its Environment
Cells must let things enter and leave. Oxygen, food molecules, and waste
products all must pass through the cell membrane.

The Cell in its Environment
Substances that can move into and out of a cell do so by one of three methods:Diffusion Osmosis Active transport

Diffusion
Diffusion is the main method by which small molecules move across the cell membrane.
Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
https://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/passivetransport/

What Causes Diffusion?
Molecules are always moving and bumping into one another.
The more molecules there are in an area, the more collisions there will be.
Eventually they will spread evenly throughout the area.

Diffusion

Osmosis
Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
Cells cannot function properly without adequate water, many cellular processes depend on osmosis

Osmosis and Diffusion
In osmosis, water molecules move by diffusion from an area where they are highly concentrated through the cell membrane to an area where they are less concentrated.
Osmosis is simply diffusion for water

Effects of Osmosis
There are three effects of osmosis:Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic

Hypertonic Hypertonic osmosis:
Low water concentration outside of the cell
Water moves out of the cell during osmosis

Isotonic
Isotonic osmosis:Normal Cell Concentration of water inside the cell is the
same as outside.

Hypotonic Hypotonic Osmosis:
High water concentration outside the cell.
During osmosis, water moves into the cell.

Passive Transport
For a cell moving materials through the cell membrane by diffusion and osmosis require no energy.
The movement of dissolved material through a cell membrane without using cellular energy is called passive transport

Active Transport
What if a cell has to take in a substance that is present in a higher concentration inside the cell than outside?
The cell would have to move the molecules in the opposite direction than they naturally move by diffusion.

Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy.
Active transport uses the cell’s energy while passive transport does not.
https://www.brainpop.com/science/cellularlifeandgenetics/activetransport/

Active Transport vs. Passive Transport

Types of Active Transport
Transport proteins:Transport proteins in the cell membrane
“pick up” molecules outside the cell and carry them inside the cell ○ Calcium ○ Potassium ○ Sodium


Types of Active Transport
Transport by engulfing:The cell membrane surrounds and engulfs,
or encloses, a particle.Once the particle is engulfed, the cell
membrane wraps around the particle and forms a vacuole within the cell.


Specialized Cells
Plants and animals contain many cells.
In a many-celled organism, the cells are often quite different from one another and are specialized to preform specific functions.

Specialized Cells
Red Blood Cells Nerve Cells

Levels Of Organization

The levels of organization from simplest to most complex are:
Cells Tissues Organs System Organism

Levels of Organization

Cells The basic unit of structure and
function in the human body Though all cells perform the
processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well.
Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells.

Tissues A group of specialized cells
that work together to perform the same function.
There are four basic types of tissue in the human body:

Tissues
1. Nerve tissue – carries impulses back and forth to the brain from the body

Three types of muscle tissue
Muscle tissue – (cardiac, smooth, skeletal) contract and shorten, making body parts move
Skeletal
Cardiac
Smooth

3. Epithelial tissue – covers the surfaces of the body, inside (as lining and /or covering of internal organs) and outside (as layer of skin)

4. Connective tissue – connects all parts of the body and provides support (for example tendons, ligaments, cartilage).

Organs A group of two or more different types
of tissue that work together to perform a specific function.
The task is generally more complex than that of the tissue.
For example, the heart is made of muscle and connective tissues which functions to pump blood throughout the body.


Systems A group of two or more organs that work
together to perform a specific function. Each organ system has its own function but the
systems work together and depend on one another.
There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory, and skeletal.


The Digestive SystemPurpose: to convert food particles into simpler micromolecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
Major Organs and their Functions:
Mouth – to chew and grind up food
-- saliva also begins the chemical breakdown
Esophagus – pipe connecting mouth to stomach
Stomach – secretes an extraordinarily strong acid (pH = 2) that leads to breakdown of food

Pancreas – produces the hormone insulin that regulates blood sugar levels
-- also help neutralize stomach acid
Liver – produces bile, which breaks down fats in foods
Gallbladder – pouch-like organ that stores bile for future use
Small Intestine – after digestion is complete, the chyme enters the small intestine where it is absorbed into the bloodstream
-- the chyme is propelled along by folded surfaces called villi, on the intestine
Large Intestine – removes water from the chyme and gets the waste ready for excretion

The Digestive System

The Excretory System
Purpose: to rid the body of wastes, including excess water and salts
Major Organs and Their Functions
Kidneys – the main organs of the excretory system
-- waste-laden blood enters the kidney and the kidney filters out urea, excess water and other waste products, which eventually travel out of the kidney as
urine
-- eventually they travel through the ureter to the urinary bladder
Rectum – solid (food) waste travels out of the body through the rectum
Skin – sweat glands remove excess water and salts from the body
Lungs – expel the waste gas carbon dioxide

The Excretory System

The Respiratory SystemPurpose: to provide the body with a fresh supply of oxygen for cellular respiration and remove the waste product carbon dioxide
Major Organs and Their Functions
Nose – internal entry and exit point for air
Pharynx – serves as a passage way for both air and food at the back of the throat
Larynx – your “voicebox”, as air passes over your vocal chords, you speak
Trachea – the “windpipe”, or what connects your pharynx to your lungs

Bronchi – the two large passageways that lead from the trachea to your lungs (one for each lung)
The diaphragm is the muscle that causes you to breath

Image of the Respiratory System

The Circulatory SystemPurpose: to deliver oxygenated blood to the various cells and organ systems in your body so they can undergo cellular respiration
Major Organs and Their Functions
Heart – the major muscle of the circulatory system
-- pumps blood through its four chambers (two ventricles and two atria)
-- pumps deoxygenated blood into the lungs, where it gets oxygenated, returned to the heart, and then pumped out through the aorta to the rest of the body
-- valve regulate the flow of blood between the chambers

Arteries – carry blood away from the heart and to the major organs of the body
Veins – carry blood back to the heart away from the major organs of the body
Capillaries – small blood vessels where gas exchange occurs
Blood – the cells that flow through the circulatory system
Spleen – helps to filter out toxins in the blood

Image of the Circulatory System

The Nervous SystemPurpose: to coordinate the body’s response to changes in its internal and external environment
Major Organs and Their Functions
Brain – control center of the body, where all processes are relayed through
Spinal Cord – sends instructions from the brain to the rest of the body and vice versa
Nerves – conduct impulses to muscle cells throughout the body

Diagram of a Nerve Cell

The Muscular SystemPurpose: works with the skeletal and nervous system to produce movement, also helps to circulate blood through the human body
-- muscle cells are fibrous
-- muscle contractions can be voluntary or involuntary
Major Muscles in the Human Body
-- biceps -- triceps -- deltoids
-- glutes -- hamstrings

The Muscular System