Cell Structure & Function. Eukaryotic Cells … an introductory video.
-
Upload
franklin-skinner -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell Structure & Function. Eukaryotic Cells … an introductory video.

Cell Structure & FunctionCell Structure & Function

Eukaryotic Cells … an introductory video

Living Things & Cells The cell is the basic unit of
structure & function of all living things.
The cell is the smallest unit of life that can still carry on all life processes.
Both unicellular (one celled) and multicellular (many celled) organisms are composed of cells

History:History:
Before the 17th century, no one knew cells existed
In the early 17th century microscopes were invented & cells were seen for the 1st time

Anton Von Leeuwenhoek, a Dutchman, made the 1st hand-held microscope & viewed microscopic organisms in water & bacteria from his teeth
In 1665, an English scientist named Robert Hooke made an improved microscope and viewed thin slices of cork viewing plant cell walls
Hooke named what he saw "cells"

In 1831, Scottish botanist Robert Brown used the word nucleus to describe the dark, central globule.
(The word nucleus is Latin for little nut.)
In the 1830’s, Matthias Schleiden (German botanist
studying plants) & Theodore Schwann (German zoologist studying animals) stated that all living things were made of cells
In 1855, German scientist Rudolf Virchow stated that cells only arise from pre-existing cells

The Cell Theory The Cell Theory
The combined work of Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow is
known as The Cell Theory:1) All living things are made of one or more cells
2) Cells are the basic unit of structure & function
in organisms
3) Cells come only from the reproduction of
existing cells

Cell DiversityCell Diversity Not all cells are alike Cells differ in size, shape, and function

Cell SizeCell Size: : Most cells measured in
micrometers (10-6)
The female egg cell is the largest cell in the body & can be seen without a microscope (ostrich egg is the largest known cell)
A group of bacteria called mycoplasmas are the smallest known cells
Nerve cells, although microscopically thin, can be very long (some up to 6 feet in giraffes)

Cell Size AnalysisCell Size Analysis

Why are cells small ?Why are cells small ?Surface Area Volume SA:Vol Ratio
(L x H x 6) (L x H x W)1
2
4
1 x 1 x 6 = 6 1 x 1 x 1 = 1 6:1 (6)
2 x 2 x 6 = 24 2 x 2 x 2 = 8 24:8 or 3:1 (3)
4 x 4 x 6 = 96 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 96:64 or 3:2 (1.5)

Assume Oxygen is the substance moving Assume Oxygen is the substance moving across through the membrane …across through the membrane …
What % of each cell What % of each cell would not receive would not receive oxygen ?oxygen ?
About 80%: This cell probably will not survive
About 5%: This cell should survive
Large Large CellCell
Small CellSmall Cell

Cells are small because:Cells are small because: Cells need surface area in order to
exchange materials across their membrane
Cell are limited by the surface area to volume ratio
Smaller cells have a much higher ratio As cells grow, the amount of surface area
becomes too small to allow materials to enter & leave the cell quickly enough

Cell Shape/FunctionCell Shape/Function Cells come in a variety of shapes, & the Cells come in a variety of shapes, & the
shape helps determine the function of the shape helps determine the function of the cellcell
Remember: Remember: Function dictates shapeFunction dictates shape ! !

Blood CellsBlood Cells
NORMAL = ROUND
SICKLE CELL
Blood CellsBlood Cells are round – travel through small are round – travel through small vessels (sickle cell anemia problem)vessels (sickle cell anemia problem)

Nerve CellsNerve Cells
Nerve CellsNerve Cells are long and thin – transmit are long and thin – transmit nerve impulses across long distancesnerve impulses across long distances

Skin CellsSkin CellsSkin Cells are squared – provide a wall-like barrier when linked together

Muscle CellsMuscle Cells
Muscle CellsMuscle Cells are tapered – provide for are tapered – provide for contraction allowing movement contraction allowing movement

Cell Organelles: Cell Organelles: A Cell Component that PERFORMS
SPECIFIC FUNCTIONS FOR THE CELL.
“Little Organs”
Just as the organs of a multicellular organism carry out the organisms life functions, the organelles of a cell maintain the life of the cell.

1.1. CELL MEMBRANE /CELL MEMBRANE /PLASMA MEMBRANEPLASMA MEMBRANE
Entire cell is Surrounded by A THIN MEMBRANE
The Cell Membrane is a complex barrier separating the cell from it's external environment.
This "Selectively Permeable" Membrane regulates what passes into and out of the cell.

Cell membranes are made mostly of phospholipid molecules.
The phospholipids are arranged into two layers called a lipid bilayer.
The hydrophilic phosphate “heads” face the watery fluids inside and outside the cell.
The hydrophobic lipid “tails” are sandwiched inside the bilayer.
In addition, other structures, like proteins are embedded into the lipid bilayer and serve various functions.

Phospholipid Phospholipid BilayerBilayer

The The Fluid Mosaic ModelFluid Mosaic Model of cell membranes of cell membranes Membranes are fluid
and have the consistency of vegetable oil.
The lipids and proteins of the cell membrane are always in motion.
Phospholipids are able to drift across the membrane, changing places with their neighbor.
Proteins in and on the membrane form patterns, or MOSAICS.

2. 2. CYTOPLASM:CYTOPLASM: Everything between the cell membrane and
the nucleus is the cell’s CYTOPLASM.
Cytoplasm consists of two main components: CYTOSOL and ORGANELLES.
CYTOSOL is a colloid mixture that consists mostly of water, along with proteins, carbohydrates, salts, minerals and other organic molecules.
Cytoplasm is always in constant motion = Cytoplasmic Streaming or Brownian Motion

3. 3. ENDOPLASMIC ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER):RETICULUM (ER):
The ER is an extensive network of membranes connects different parts of the cell and usually connects the nuclear envelope to the cell membrane.
The ER functions primarily as an intracellular highway, a path along which molecules move from one part of the cell to another.


Rough vs. Smooth ERRough vs. Smooth ERRough ER is studded with
ribosomes and processes proteins to be exported from the cell.
Smooth ER is NOT covered with ribosomes and processes lipids and carbohydrates. The Smooth ER is involved in the synthesis of steroids in gland cells, the regulation of calcium levels in muscle cells, and the breakdown of toxic substances by liver cells.

4. 4. RIBOSOMESRIBOSOMES:: Ribosomes are the
site of protein synthesis in a cell.
They are the most numerous organelles in almost all cells.
Some are free in the cytoplasm; others line the membranes of rough endoplasmic reticulum.

5. 5. GOLGI APPARATUSGOLGI APPARATUS: : The Golgi Apparatus
is a system of membranes made of flattened sac-like structures and is involved in the processing, packaging and secreting of materials in the cell.
Vesicles (packages of chemicals) bud off at the edges.

6. 6. MITOCHONDRIAMITOCHONDRIA::
Mitochondria are found scattered throughout the cytoplasm, and are relatively large, bean-shaped organelles
The “powerhouse" of the cell: Site of cellular respiration and the production of ATP. ATP is the molecule that most cells use as their main energy currency.

Mitochondria is surrounded by two membranes
The inner membrane has many folds, known as cristae. The cristae greatly increases the surface area of the inner membrane, providing more space for the chemical reactions to occur (more ATP).
Mitochondria have their own DNA, and new mitochondria arise only when existing ones grow and divide.

7. 7. LYSOSOMESLYSOSOMES Lysosomes are small
spherical organelles that enclose digestive enzymes within a single membrane.
Lysosomes are the site of food digestion in the cell
Lysosomes are formed from pieces of the golgi that break off.
Common in animal, fungi, and protist cells, but rare in plant cells

8. 8. NucleusNucleus The nucleus is often the
most prominent structure within a eukaryotic cell
The nucleus is the control center of the cell.
The nucleus is surrounded by a double layer membrane called the nuclear envelope (has nuclear pores)

The nucleus contains DNA, the hereditary material of the cell.
The DNA is in the form of a long strand called chromatin (cell not dividing)
During cell division, chromatin strands coil and condense into thick structures called chromosomes

9. 9. NucleolusNucleolus
Most nuclei contain at least one nucleolus (plural = nucleoli)
The nucleolus produces (synthesizes) ribosomes.

10. Cytoskeleton In animal cells, an internal framework
called the cytoskeleton maintains the three-dimensional shape of the cell, participates in the movement of organelles within the cytosol, and helps the cell “move”.
Composed of microfilaments and microtubules.

MicrofilamentsMicrofilamentsMicrofilaments are NOT
HOLLOW and have a structure that resembles ROPE
Microfilaments can CONTRACT, causing movement.

Microtubules Microtubules are HOLLOW TUBES like plumbing pipes. They are the largest strands of the cytoskeleton

Microtubules have three functions:Microtubules have three functions:
A. Maintain shape of cell and hold organelles in place.
B. To serve as tracks for organelles and molecules to move along within the cell.
C. When the cell is about to divide, two short cylinders of microtubules at right angles known as centrioles create bundles of microtubules known as SPINDLE FIBERS.

11.11. CiliaCilia Short, hair-like
projections.
Often numerous

12.12. FlagellaFlagellaLong, whip=like
projections
Often singular, but not always

Cilia & FlagellaCilia & Flagella Unicellular organisms such as Paramecium and Euglena use Cilia and Flagella to move through water.
Sperm use flagella to swim to the egg.
In Humans, beating Cilia line parts of the respiratory system, moving dust particles and bacteria away from the lungs.

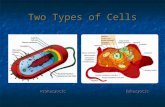
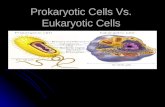
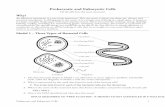
Types of CellsTypes of CellsProkaryotic
– Have NO membrane bound nucleus
– Have FEW membrane bound organelles
– All bacteria are prokaryotic

Eukaryotic
– Have a membrane bound nucleus
– Have many organelles
– All protists, fungi, plants and animal cells


Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells
– Have a cell wall made of cellulose
– Typically have one central vacuole (food & water storage)
– Contain plastids Chloroplasts: sites
of photosynthesis Contains
chlorophyll (green)
– Typically square-like in shape

Animal Cells
– No cell wall
– Many small vacuoles (food storage)
– No chloroplasts
– Typically round


Inside a Plant Cell