Cell Structure: Organelles EQ: How are plant and animal cells alike and different?
-
Upload
morris-copeland -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of Cell Structure: Organelles EQ: How are plant and animal cells alike and different?
Cells
• Cells are everywhere. Even though most cells cannot be seen with the naked eye, they make up every living thing.
• Your body contains trillions of cells.
Common Cell Traits
• Living cells are dynamic and have several things in common
• They are all the smallest unit that is capable of carrying on life functions
• They all have a cell membrane surrounding it and are filled with a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm.
• They all have ribosomes and DNA
Cell Types
Prokaryotic
• An organism that is made of a single cell
• No nucleus• They have a cell wall• Bacteria, Archea
Cell Types
Eukaryotic
• Have a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.
• Anything not considered bacteria or archea are eukaryotic
• Plants, animals, Fungi
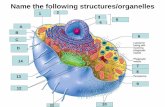
Cell Organelles
• Within a eukaryotic cell, there are structures called organelles.
• Each organelle has its own specific job to do.• Analogy: City
• Organelles are interdependent
Cell Wall
• Found only in plant cells• The outer layer of a plant
cell, it is strong, and made of cellulose.
• It supports and protects the plant.
• It allows water and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the cell.
• “Wall of the City”
Cell Membrane
• Found in both plant and animal cells.
• Gives support and protection to the cell.
• Controls movement of materials in and out of the cell.
• Barrier between the cell and its environment
• Maintains homeostasis• “Gatekeeper”
Cytoplasm
• Found in both plant and animal cells
• Not a true organelle• Jelly-like material found
inside the cell membrane.• It supports and protects the
organelles.• Chemical reactions necessary
to cell function occur here.• “Ground”
Vacuole
• Found in plant cells• They are fluid-filled
sacs.• They support the cell• They store water• They store digestive
enzymes• “Storage Tank”
Chloroplast
• Found in plants only• Green, oval, usually
contains chlorophyll.• Traps energy from the
sun to make food for the plant (photosynthesis)
• “Food Producer”
Nucleus
• Found in both plant and animal cells
• The control center of the cell
• Contains the DNA• “City Hall”
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• Found in both plant and animal cells
• Extending from the nucleus to the cell membrane, it is a series of folded membranes
• Processes substances • Moves substances • Rough ER makes proteins• Smooth ER make lipids and
break down toxins• “Transportation Center”
Ribosomes
• Found in plant and animal cells
• Smallest organelle• Most common organelle• They are small bodies that
are either free floating or attached to the ER
• Make proteins• “Assembly Line”
Mitochondria
• Found in both plant and animal cells
• Bean-shaped with inner membranes
• Breaks down sugar molecules
• The broken down sugars are use for cellular respiration
• Results in ATP (energy)• “Power Plant”
Lysosome
• Found mainly in animal cells.
• Small, round and membrane-bound
• Protects the cell from foreign invaders
• Destroy worn out organelles
• Gets rid of the waste• “Sewer System”
Golgi Complex
• Found in plant and animal cells.
• Packages and distributes proteins and other materials out of the cell
• “Packaging Factory”• Vesicles: “Packages”
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-zafJKbMPA8&safety_mode=true&persist_safety_mode=1
Plant Cell Animal Cell
But while most machines have many parts….
• Some organisms exist as a single cell.• Other organisms have many --- even trillions of cells• Most cells are smaller than the period at the end of a
sentence in your Science book.• Yet, every cell in every organism performs all the
processes (transportation, protein production, waste disposal, etc) of life.
• ARE THERE ANY ADVANTAGES TO BEING MULTICELLUAR????
YES!!!! There are many benefits of being multicellular!
• “Multi” means “many”
• We are multicellular• Multicellular
organisms grow by making new cells, not by making their cells larger.
Benefits of being multicellular
• Larger size• While many multicellular
organisms are small, they are larger than single-celled organisms
• Larger organisms usually have fewer predators.
• Larger predators can eat a wider variety of prey
Benefits of being multicellular
• Longer Life• The life span of a
multicellular organism is not limited to the life span of any single cell
• One cell = dead when cell dies
• Multicells = longer life
Benefits of being multicellular
• Specialization• Each type of cell has a
particular job.• This specialization
makes the organism more efficient.
• Cardiac muscle cells
Cells Working Togetherhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODfJjMaQmvA
Organelles Make Cells
• As you know, organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and Golgi complex make up cells.
Cells make up tissues
• A tissue is a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job.
• Animals have four basic types of tissues
• Nerve tissue: reacts to stimuli • Muscle tissue: contract and move
bones or muscle• Connective tissue: provides a
framework and support for other tissues
• Protective (Epithelial) tissue: provides protection (skin)
Cells Make up Tissues
• Plants have three basic types of tissues
• Transport (Vascular) tissue: move water and nutrients
• Protective (Dermal) tissue: helps plant retain water and protects
• Ground tissue: photosynthesis
Tissues make organs
• A structure made up of two or more tissues working together to perform a specific job is called an organ.
Tissues make organs
• Your heart is an organ• Mostly made of cardiac
tissue , but also contains nerve tissues and the tissues of your blood vessels.
• They all work together to make your heart pump blood through your body
Tissues make organs
• Your stomach is also an organ• Muscle tissue makes food move
in and through your stomach.• Special tissues make the
chemicals that digest your food.• Connective tissues hold your
stomach together• Nerve tissues carry the message
to your brain to signal hunger or “fullness”.
Organs Make Systems
• A group of organs working together to perform a particular function is called an organ system
• Each organ system has a specific job to do
• Digestive System: break down food into smaller particles
• Stomach• Intestines
Systems make Organisms
• All organ systems together make up an organism.
• Anything that can perform life processes by itself is an organism.
• Can be one-celled (unicellular)
• Can be many celled (multicellular)
Structure and Function
Structure
• The arrangement of parts in an organism
• The shape of the part• Materials the part is made
of• Lungs: large, spongy sac
Function
• The job that part does
• Lungs: bring air to the body
Levels of Organization
• Organelles make up cells• Cells make up tissues• Tissues make up organs• Organs make up organ systems• Systems make up organisms
Organelles Cells Tissues Organs Systems Organism
• OCTOSO• Organelles, Cells, Tissues, Organs, Systems, Organism
• http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODfJjMaQmvA