Cell organisation in plants
description
Transcript of Cell organisation in plants

WHAT IS THE FUNCTION OF:FLOWERSTEMLEAFROOTS
WHAT ARE THE CELLS INSIDE THOSE PARTS OF PLANT?

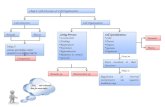
Cell organisation in plants

TISSUES 1. Meristematic tissues
2. Permanent tissues
Small cells – thin walls, large nuclei, dense cytoplasm and no vacuole
Young, cell divide actively but not undergo differentiation
at the tips of roots
Epidermal tissues
Ground tissues
Vascular tissues

Permanent tissues
1.Epidermal tissue• Outermost layer – covers the stems, leaves
and roots of young plants.• Flat and has large vacuole• Wall - covered with cuticle• Root – has root hairs• Chloroplast – guard cells

Epidermal tissue

Permanent tissue
2. Ground tissue• parenchyma – thin primary walls and large vacuole ; store sugar and starch ; gives support and shape to herbaceous plants.(leaf)• collenchyma – unevenly thickened cell walls; supports non-woody plants, young stems and petioles.(stem)• sclerenchyma – cell walls uniformly thickened by lignin and may be dead; give support and mechanical strength.(root)

Parenchyma tissue

Collenchyma tissue
Thickened cell wall

Sclerenchyma tissue

Vascular tissue


Organs and systems in plants

Regulating the internal environmentDefinitionWhy need to maintain an optimal
internal environment?Factors that affect the internal
environment?Homeostasis??
- system that regulates its internal environment so as to maintain a stable, constant condition

Homeostasis