Objectives To learn the structure of the cell membrane To learn how structure and function of the...
-
Upload
nelson-chandler -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
4
Transcript of Objectives To learn the structure of the cell membrane To learn how structure and function of the...

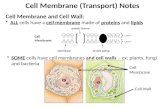
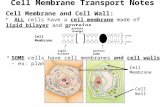
Cell membrane and transport
Objectives To learn the structure of the cell
membrane To learn how structure and function of
the cell membrane are linked To learn about different forms of
transport across the cell wall.

Cell Membrane Cell is bound by a fluid membrane It regulates movement of chemicals in
and out of the cell; It is involved in recognition and
identification It facilitates the function of the cell It protects the cell It keeps the cell together It interacts with the membranes of other
cells

Cell membrane http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ow
Egqrq51zY

Structure of the cell membrane

What it comprised of 1 A phospholipid bilayer which allows
the passage of lipids across the membrane
2. Bilayer of phospholipid molecules with water loving heads on the inner and outer surface and water hating tails pointing into the membrane.
We describe our understanding of it as the ‘Singer and Nicholson’ fluid mosaic model.

Inclusions Included in the phospholipid bilayer are: Integral proteins (carrier proteins) Peripheral proteins Cholesterol Carbohydrate chains Glycolipids (lipids with attached
carbohydrate chains) Glycoproteins (proteins with attached
carbohydrate chains) These inclusions can move around the fluid
phospholipid bilayer.

Carbohydrate chains Carbohydrate chains Give the cell a sugar coat or
glycocalyx which protects the cell. These carbohydrate chains are
unique to individuals, tissue types and blood groups.
They are what our immune system uses to recognise our cells and invading ones.

Fluidity Allows rapid movement of carrier
proteins around; Gives flexibility to cells, so e.g. your
nerve cells don’t crack when you bend.
Membrane proteins move freely. Has been demonstrated by merging
human and mouse cells. In 40 minutes membrane proteins from two cells completely mixed.

Proteins Channel proteins: allow molecules to
move across the membrane through a channel;
Carrier proteins: combine with chemicals to transport them across the membrane;
Cell recognition proteins are glycoproteins which allow us to recognise our own cells and invaders and therefore facilitate an immune response.

More proteins Receptor proteins: Have a shape that
allows one type of molecule to bind to it.
Once the molecule is bound to it, it changes shape altering the properties of the cell.
E.g. insulin binding to liver cells causes them to store sugar.
Enzymatic proteins carry out metabolic functions.

Plenary activity 1. make a model of the plasma
membrane 2. Explain how your model shows its
different parts and functions 3. Marking rubric same as for cell
model.

Movement of substances Known as cell transport covers the
movement of substances in and out of the cell membrane.
Will include both the different types of transport
And the structure and function of the cell membrane

Diffusion E.g. H2O, CO2 and O2 in and out of the cell. What is diffusion? http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H7QsD
s8ZRMI
Across the cell membrane it is helped by protein
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OV4PgZDRTQw
This is called facilitated diffusion An idea of random particle movement:
http://ccl.northwestern.edu/netlogo/models/DLA

Key points about diffusion 1. It happens because of the natural
movement of the particles of liquids and gases;
2. It does not need an organism to use energy;
3. It can only happen down a concentration gradient from higher to lower concentrations;
4. Across cell membranes it is assisted by carrier proteins.

Osmosis The diffusion of water across a semi-
permeable membrane; http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdiJtDRJQE
c Important in enabling plant cells to absorb
water to maintain their turgor pressure; Results in dilution of the solution Water moves from weak solutions where
there is lots of water to strong solutions where there is less water.
Does not require energy Does require semi-permeable membrane.

Investigating in lab

Key terms Hypotonic solution is weaker than the
solution in the cell; Isotonic solution is equal to that in the cell; Hypertonic solution is stronger than that in
the cell; Lysed means split Turgid means full and firm Flaccid means limp, droopy Plasmolysed means cell membrane and
contents have shrunk away from the cell wall in plants.

Facilitated transport This does not require energy All chemicals pass down a concentration
gradient. It is necessary for the transport of materials like
glucose and some amino acids across the cell membrane because they are not lipid soluble;
It uses carrier molecules which are proteins crossing the cell membrane
Each carrier molecule is specific to one molecule to be transported
http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/membrane-channels Open this simulation and try to show what is happening in a cell in different osmotic conditions

Active transport This does require energy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ST
zOiRqzzL4 To summarise both facilitated and
active transport. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Z
FqOvxXg9M&NR=1

Active: Endocytosis endocytosis & exocyctosis are ways to
transport large molecules across a membrane
In some cases, receptor sites on the surface of the cell bond with the large molecule
Endocytosis takes in material from the cell by pockets or in-foldings of the cell membrane itself • this happens by phagocytosis (solids) &
pinocytosis (liquids)

See how this works!

Active: Exocytosis release of large amounts of material
from the cell• The membrane of the vacuole surrounding
the material joins with the cell membrane, forcing the contents out of the cell. Large amounts of water may be removed from a
cell in this way.

Active: Phagocytosis type of endocytosis this means “eating cell” cytoplasm surrounds a particle &
package it within a food vacuole next, the cell engulfs it (surrounds it)
• Amoebas use this to take in their food this uses A LOT of energy= form of
active transport http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_A
ASYGG7mrw&feature=related

Active: Pinocytosis the taking up liquid from a cell’s
surrounding environment tiny pockets form along the cell
membrane, fill with liquid, and pinch off to form vacuoles within the cell
vitamins, nutrients and hormones may be absorbed into a cell using pinocytosis

Example of how it works The sodium potassium pump. http://
www.youtube.com/watch?v=GTHWig1vOnY
Watch the video and write your own voice over. You may work in pairs. Submit video with your voice over recorded.

Video Time!

Homework: Structure and function of the plasma membrane
Describe the structure of the plasma membrane. Say how its structure affects the transport of materials across it. Think about how chemicals are imported and exported from the
cell. Describe how the structure of the cell membrane allows other
functions. You must also describe the types of transport and say which parts
of the cell membrane they use and how they actually occur. Give examples of each.
¼ of a mark to be deducted for each mistake spelling technical words up to 2 marks
½ marks deducted for each time sentences are not correctly separated with punctuation or joined appropriately and meaningfully – up to 2 marks.
All information must be referenced. You may quote sections of articles but must show this with quotation marks and you must reference the information in the text. Minimum length 1000 words.
You must include labeled diagrams (2 marks). Content 14 marks (total 20marks)