Small Intestine
-
Upload
iamsanwar019170 -
Category
Documents
-
view
231 -
download
0
Transcript of Small Intestine
Bowel components
Dow Jones Industrial Climbing Average Closing Stock Report AwesomeDuodenum sigmoidJejunum RectumIleum Anal canalCecumAppendixcolon
Small Intestine• It extends from the pylorus to ileocaecal junctionExtent• 6 m longDivided into • Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum
Duodenum• The duodenum is the proximal part of the small intestine.• Shortest & most fixed part Course• extends from pylorus to duodo-jejunal flexure• 25 cm long• forms a C-shape, the concavity of which is occupied by the pancreas• its course can be described in 4 parts: superior, descending, horizontal,
ascending• Lies just above the level of umbilicus Opposite L1-L3
Relations:• Peritoneal Relation• Proximal 1 inch is movable which is attached to lesser omentum above &
greater omentum below• The distal 1 inch fixed. It is retroperitoneal & covered with peritoneum on
anterior aspect
Visceral Relation Posteriorly• gastroduodenal artery• common bile duct & portal vein Superiorly• epiploic foramenInferiorly• head & neck of pancreas
Perotoneal Relations:• Retroperitoneum, Fixed• Anterior part covered with Peritoneum except in middle where it is related
to colon Visceral RelationAnteriorly• Rt lobe of liver• transverse colon• Root of transverse mesocolon• Small Intestine
Posteriorly• Rt kidney• Rt. Renal vessels• Rt. Psoas majorlaterally• Rt. Edge of IVC• Rt hepatic flexureMedially• head of pancreas• bile duct
Interior of 2nd part of DuodenumMajor duodenal papilla• Is elevation present postero-medially 8 – 10 cm distal to pylorus. • Hepato-pancreatic ampulla opens at summit of papillaMinor Duodenal papilla • 6-8 cm distal to pylorus• Acessory pancreatic duct opens
Perotoneal Relations• Retroperitoneum & fixed• Covered by peritoneum anteriorly except in median plane where it is
crossed by superior mesenteric vessels & root of mesentery
Anteriorly Posteriorly Superiorly Inferiorly1. roots of
mesentry2. superior
mesenteric vessels in it
1. Rt ureter2. Rt psoas muscle3. Rt. Testicular or
Ovarian vessels4. IVC5. aorta
1. head of pancreas with uncinate process
1. coils of jejunum
Visceral Relations
4th (Ascending) Part• 2.5cm long• runs upwards & to the Lt• ends at duodeno-jejunal flexure at level of L2
Peritoneal Relations• Retroperitoneum• The terminal part is suspened by uppermost part of mesentry & is mobileVisceral RelationsAnteriorly• Transverese colon• Transverse mesocolon• Lesser sac & stomach
Posteriorly• Lt. Sympathetic chain• Lt. Renal vessels• Lt psoas muscle• Lt. Testicular vesels• Inferior mesenteric veinRt• Upper part of root of mesentery• Superior
– Body of Pancreas
Lt.• Lt Kidney, lt. Ureter
Blood Supply• Superior Pancreatoduodenal artery –Upto the opening of the bile duct• Inferior Pancreatoduodenal artery – below the opening of the bile duct
• First part gets additional supply from Right gastric artery, the supraduodenal artery of Wilkie, retroduodenal branches of gatroduodenal artey and some branches of Rt gastroepiploic artery
Blood supply of the small intestines
• The intestines are mainly supplied by the three unpaired branches of the abdominal aortas:
• Coeliac artery• Superior mesenteric artery• Inferior mesenteric artery
• The coeliac artery emerges immediately after the passage of the aorta through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm. It divides into a branch to the spleen, the lienal artery, a branch to the stomach, the left gastric artery, and into the common hepatic artery, which somewhat later becomes the right gastric artery.
• The superior mesenteric artery supplies the whole small intestine and extends branches up to the middle third of the transverse colon. Up to this point, the innervation is taken over by the vagus nerve (CN X).
• The inferior mesenteric artery is responsible for supplying blood to the left third of the transverse colon and to the sigmoid colon
Venous DrainageVeins correspond to arteries & • portal vein• superior mesenteric vein• Splenic veinThus the venous drainage is ultimately
into the portal vein
Lymphatic Drainage• Pancreaticoduodenal nodes present inside of the curve• From here to the hepatic nodes & then end in Coeliac nodeNerve Supply• Sympathetic arises from T9 & T10 spinal segments• Parasympathetic from Vagus
Jejunum & Ileum: • These parts of the small intestine extend from Duodeno Jejunal flexure to
ileocecal junction• They are suspended by mesentery & are thus free mobile• The upper 2/5 is arbitrarily designated
jejunum, there being no clear-cut distinction between the 2
Mesentery• Fan shaped fold of peritoneum which suspends the coils of jejunum & ileum
from the posterior abdominal wall
Jejunum• Lies coiled in the upper part of the
peritoneal cavity.
• Have wider lumen, thicker wall
and more red in color
WWW.SMSO.NET
Ileum• Lies coiled in the lower part of the
peritoneal cavity and in the pelvis.
• Have smaller lumen, thinner wall
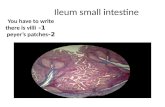
and less red in color. • Has Peyer’s Patches opposite
attachment of mesentery (antimesenteric border).
WWW.SMSO.NET
Jejunum• Mesenteric vessels form only 1
or 2 arcades with long branches passing to the jejunal wall.
• In mesentery, fat is deposited near root and is scanty (very little) near the jejunal wall.
Ileum• Mesenteric vessel form 3 to 5
arcades with numerous short branches.
• In mesentery, fat extends from the root to the ileal wall. .
Blood Supply• Branches of superior mesenteric artery Venous Drainage• The veins correspond to the branches of the sup mesenteric art• They drain mainly into the sup mesenteric vein
Aggregated Lymphatic follicles or payer’s patches • Cintains 10 – 200 follicles aggregated in circular or oval patches with size of
2-10 cm they are placed length wise along antimesentric border of intestine
Glands of Intestine• Crypts of Lieberkuhn – Mucous membrane of jejunum & Ileum
– Secrete – Digestive enzymes & mucous • Brunner’s Glands – Sub- mucosa of Duodenum
– Secretes mucous
Meckel’s Diverticulum• It is persistent proximal part of vitellointestinal duct which is present in
embryo & which normally disappears during 6th week of intrauterine life
• It occurs in 2% subject• It is 2 inch long• Situated about 2 feet proximal to ileocaecal valve, attached to
antimesenteric border of ileum• Its apex may be free or attached to umbilicus, to mesentry or to any other
abdominal structure by fibrous band