Objectives: 4(A) Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4(B) Investigate and explain...
-
Upload
elmer-anthony -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
3
Transcript of Objectives: 4(A) Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. 4(B) Investigate and explain...

7.3 Structures and Organelles
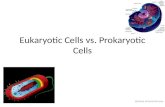
Objectives:• 4(A) Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.• 4(B) Investigate and explain cellular processes, including
homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules.



Cytoplasm and Cytoskeleton

The environment enclosed by the plasma membrane is a semifluid material called cytoplasm. In prokaryotes, all the chemical
processes of the cell take place directly in the cytoplasm.
In eukaryotes, these cell processes take place within organelles in the cytoplasm.

The cytoskeleton is a supporting network of long, thin protein fibers that form a framework for the cell and provide an anchor for organelles. Microtubules are long, hollow protein
cylinders that form a rigid skeleton for the cell and assist in moving substances within the cell.
Microfilaments are thin protein threads that help give the cell shape and enable part or the entire cell to move.

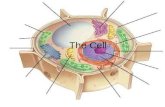
Cell Structures

The nucleus Contains most of the cell’s DNA, which
stores information used to make proteins that determine a cell’s growth, function, and reproduction.
Surrounded by a double membrane called a nuclear envelope.

Ribosomes Organelles that manufacture proteins.▪ Not membrane-bound like other organelles.▪ Produced inside the nucleus in the nucleolus.

Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) A membrane system of folded sacs and
interconnected channels that serves as the site for protein and lipid synthesis.
Two types: rough ER and smooth ER

Golgi apparatus A flattened stack of membranes that
modifies, sorts, and packages proteins. Proteins are packaged into sacs called
vesicles, which can fuse to the plasma membrane and release the proteins to the environment.

Lysosome Are vesicles that contain substances that
digest excess or worn-out organelles and food particles.
Also digest bacteria and viruses that invade the cell.

Centrioles Organelles made of microtubules that
function during cell division. Located in the cytoplasm.

Mitochondria Convert food particles into usable
energy. Have an outer membrane and a highly
folded inner membrane that provides surface area for breaking the bonds in sugar molecules.


Vacuoles A membrane bound sac used for
temporary storage Store food, enzymes, or waste. Found only in plant cells.

Chloroplasts Found in plant cells and some other
eukaryotes. Capture light and convert it into
chemical energy during photosynthesis. Contain multiple small disks called
thylakoids, which contain the light capturing pigment chlorophyll.

Cell Wall Found in plant cells. A thick rigid, mesh of fibers that
surround the outside of the plasma membrane.▪ Protects the cell ad gives it structure.▪ Made from a carbohydrate called cellulose.

Cilia and Flagella Cilia are short, numerous projections
that look like hair.▪ Move in tandem like oars in a rowboat.
Flagella are longer and less numerous than cilia.▪ Move with a whip-like motion.
Both are made of microtubules.


Comparing Cells
Features plant cells have that animal cells generally do not: Chloroplasts/chlorophyll Vacuoles Cell walls

Organelles at Work
An understanding of different organelles allows for an understanding of cellular processes.
Example: Protein synthesis: Begins in the nucleus with information contained in
DNA. RNA and ribosomes leave the nucleus and produce
a protein on the ER. Proteins produced in the ER are sent to the Golding
apparatus for packaging. Packaged proteins are delivered to other organelles
where they serve a variety of functions.