Eukaryotic Cells vs. Prokaryotic Cells
description
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cells vs. Prokaryotic Cells

Eukaryotic Cells vs. Prokaryotic Cells
By Brian & David Munroe

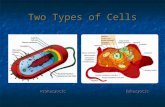
The Cells• Eukaryotic • Contains a complex structure within a membrane• Has a nucleus• Genetic material is contained within the nucleus• Large• Plant & Animal Cells• Prokaryotic• Simple singular cell• Does not have a nucleus• Genetic material can be found in the cytoplasm• Small compared to the Eukaryotes• Bacteria

Nuclear Body• Eukaryotic• Bounded by a nuclear membrane with pores connecting to the endoplasmic
reticulum • Both RNA & DNA is formed in the nucleus• The Nuclear Body is the Nucleus • Prokaryotic• Not bounded by a nuclear membrane• There is no Nucleus present• The nuclear body is called a nucleoid • The nucleoid is a the prokaryotic nuclear body, composed of a single molecule of
circular, DNA

Cell Division• Eukaryotic • The plant and animal cells divide by mitosis• Steps of mitosis are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase (PMAT)• Haploids & Diploids are divided by meiosis • Prokaryotic• Don’t divide by mitosis but binary fission • Prokaryotes are haploids so no meiosis is needed

Cytoplasmic Structures• Eukaryotic• Ribosomes • Has organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (soft & rough), Golgi
apparatus, vacuoles and lysosomes• Eukaryotes have a cytoskeleton and it contains microtubules and microfilaments• Prokaryotic• Ribosomes are also present• Prokaryotes do not have organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum,
Golgi apparatus, vacuoles, and lysosomes• contain actin proteins that are along with the cell wall, and help to cell shape

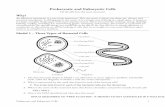
Improve this chart Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell
Vacuoles: Present Present
Cell wall: Only in plant cells (chemically simpler)
Usually chemically complexed
True Membrane bound Nucleus:
Present Absent
DNA wrapping onproteins.:
Yes No
Number of chromosomes:
More than one One--but not true chromosome: Plasmids
Nucleolus: Present Absent
Mitosis: Yes No---but has binary fission
Microtubules: Present Absent or rare
Plasma membrane with steriod:
Yes Usually no
Telomeres: Present (Linear DNA) Circular DNA doesn't need telemeres
Vesicles: Present Present
Golgi apparatus: Present Absent
cell size: 1-10um 10-100um
Lysosomes and peroxisomes:
Present Absent
Permeability of Nuclear Membrane:
Selective High
Flagella: Microscopic in size; membrane bound; usually arranged as nine doublets
Submicroscopic in size, composed of only one fiber

Movement• Eukaryotic• Have a flagella or cilia
• Prokaryotic• Have flagella• Do not have cilia

Examples• Eukaryotic• Animal cells ( Humans, lions, sloths, etc.)• Plant Cells ( Trees, flowers, grass, etc.)• Algae• Fungi (mushrooms, etc.)• Prokaryotic • Bacteria (E.coli, etc.)• Archae (methanogens, etc.)

Five Fantastic Facts1. Eukaryotes have a nucleus and Prokaryotes do not2. Eukaryotes are much more complex than Prokaryotes and much larger3. Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission and Eukaryotes reproduce through
mitosis4. Prokaryotes lack organelles 5. Genetic material in Eukaryotes is found in the nucleus and in Prokaryotes it is
found in the cytoplasm