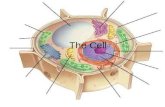
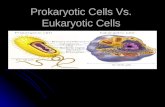
Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic
description
Transcript of Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic

1

2
Eukaryotic Eukaryotic vs. vs.
ProkaryoticProkaryotic

3
Charts and Charts and Tables Tables

4
Comparing Comparing OrganismsOrganisms

5
EvolutionEvolution

6
MiscellaneMiscellaneous ous

7
Type Subject Type Subject Six HereSix Here

8
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500
$100
$200
$300
$400
$500

9
The bacteria that live in The bacteria that live in the bodies of giant the bodies of giant tubeworms and the tubeworms and the giant white clams are giant white clams are classified asclassified asA.A. eukaryotes eukaryotes B.B. prokaryotes prokaryotes C.C. plants plants D.D. fungi fungi

10
B. ProkaryotesB. Prokaryotes

11
• Scientists have recently Scientists have recently discovered a new species that discovered a new species that lives attached to the side of a lives attached to the side of a tree. An organism from this tree. An organism from this new speciesnew species•• is multicellular is multicellular •• has cell walls has cell walls •• has vascular tissues has vascular tissues •• makes its own food makes its own food •• has structures that absorb has structures that absorb moisture from the air moisture from the air

12
Which of these terms Which of these terms best describes this new best describes this new organism?organism?A.A. omnivore omnivore B.B. eukaryote eukaryote C.C. herbivore herbivore D.D. prokaryote prokaryote

13
A cell is observed through a A cell is observed through a microscope. The cell is found to microscope. The cell is found to have a cell wall, a cell have a cell wall, a cell membrane, and numerous membrane, and numerous ribosomes. The cell does not ribosomes. The cell does not have a nucleus. This cell is most have a nucleus. This cell is most likely from alikely from aA.A. bacterium bacterium B.B. fungus fungus C.C. plant plant D.D. protist protist

14
A. BacteriumA. Bacterium

15
Prokaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells possess all of the possess all of the following exceptfollowing exceptA.A. cell membrane cell membrane B.B. ribosomes ribosomes C.C. cell wall cell wall D.D. nuclear membrane nuclear membrane

16
D. Nuclear D. Nuclear membranemembrane

17
There are several There are several differences between plant differences between plant cells and animal cells. What cells and animal cells. What organelle is found only in organelle is found only in plant cells?plant cells?A.A. Golgi BodiesGolgi BodiesB.B. Rough Endoplasmic Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumReticulumC.C. RibosomesRibosomesD.D. ChloroplastsChloroplasts

18
D. ChloroplastsD. Chloroplasts

19
According to the data According to the data above, the unknown above, the unknown bacteria are most closely bacteria are most closely related to which related to which species?species?

20
Species IVSpecies IV

21
According to the table, According to the table, which of these which of these vertebrates are most vertebrates are most closely related?closely related?

22
Birds and Birds and theropod theropod dinosaursdinosaurs

23
Based on this Based on this information, which two information, which two species are most closely species are most closely related?related?

24
the red panda the red panda and the raccoon and the raccoon

25
To which kingdom do To which kingdom do flowering plants flowering plants belong?belong?

26
Kingdom 2Kingdom 2

27
Based on the Based on the information in the information in the table, which group table, which group contains humans?contains humans?

28
Group 5Group 5

29
A 125-million-year-old small A 125-million-year-old small mammal skeleton was recently mammal skeleton was recently discovered in China. The role discovered in China. The role of this small mammal in its of this small mammal in its ecosystem can best be ecosystem can best be determined by comparing its determined by comparing its skeleton to skeleton to A.A. ancient small mammal ancient small mammal skeletons skeletons B.B. modern small mammal modern small mammal skeletons skeletons C.C. modern small mammal DNA modern small mammal DNA
D.D. ancient small mammal DNA ancient small mammal DNA

30
B.B.modern small modern small mammal mammal
skeletons skeletons

31
A researcher is studying A researcher is studying raccoons and skunks. She raccoons and skunks. She wants to find out how wants to find out how closely these two mammals closely these two mammals are related. Which of these are related. Which of these characteristics would be characteristics would be best for her to study? best for her to study? A.A. sequences of DNA sequences of DNA B.B. reproductive habits reproductive habits C.C. movement of RNA movement of RNA D.D. physical appearancephysical appearance

32
A.A.sequences of sequences of DNA DNA

33
A scientist wants to determine A scientist wants to determine how closely two organisms are how closely two organisms are related. Which of these would related. Which of these would provide the best evidence of a provide the best evidence of a close relationship?close relationship?A. They look the sameA. They look the sameB. They move the same wayB. They move the same wayC. They have similar C. They have similar organellesorganellesD. They have similar DNA D. They have similar DNA sequencesequence

34
D. They have D. They have similar DNA similar DNA sequencesequence

35
Which of these characteristics Which of these characteristics would provide the best would provide the best evidence to determine if evidence to determine if menhaden and striped bass menhaden and striped bass are closely related?are closely related?A.A. They are both cold-blooded. They are both cold-blooded. B.B. They occupy the same trophic They occupy the same trophic level. level. C.C. They both live in coastal They both live in coastal waters. waters. D.D. They have similar DNA They have similar DNA sequences. sequences.

36
D.D. They have They have similar DNA similar DNA sequences. sequences.

37
Which of the Which of the vertebrate skulls vertebrate skulls shown to the left is shown to the left is probably most probably most closely related to closely related to modern birds modern birds shown above? shown above?
A.
B.
C.
D.

38

39
Scientists have found many Scientists have found many similarities in the proteins of similarities in the proteins of turtles and sharks. These turtles and sharks. These similarities suggest that similarities suggest that turtles and sharksturtles and sharksA.A. have stopped evolving have stopped evolving B.B. have a common ancestor have a common ancestor C.C. have all the same DNA have all the same DNA sequences sequences D.D. have the same number of have the same number of chromosomes chromosomes

40
B.B.have a have a common common ancestor ancestor

41
Which of these structures are Which of these structures are the best evidence of an the best evidence of an evolutionary relationship?evolutionary relationship?A.A. bat wing and bee wing bat wing and bee wing B.B. bat lower jaw and whale lower bat lower jaw and whale lower jaw jaw C.C. whale flipper and bee wing whale flipper and bee wing D.D. bat wing and whale flipper bat wing and whale flipper

42
D.D. bat wing and bat wing and whale flipper whale flipper

43
Which of these explains why the Which of these explains why the skeletal structures of the seal's skeletal structures of the seal's flipper and the monkey's arm are flipper and the monkey's arm are similar?similar?A.A. Seals and monkeys have a common Seals and monkeys have a common ancestor. ancestor. B.B. Seals and monkeys have identical Seals and monkeys have identical DNA sequences. DNA sequences. C.C. All of the same genetic mutations All of the same genetic mutations occurred in seals and monkeys. occurred in seals and monkeys. D.D. All of the same vitamins are used for All of the same vitamins are used for bone formation in seals and monkeys. bone formation in seals and monkeys.

44
A.A.Seals and Seals and monkeys have a monkeys have a
common common ancestor. ancestor.

45
Students conducted an experiment to test the Students conducted an experiment to test the effect of antibiotics on bacteria. They placed effect of antibiotics on bacteria. They placed bacteria in a petri dish that contained agar bacteria in a petri dish that contained agar treated with an antibiotic. Only one of the treated with an antibiotic. Only one of the bacterial colonies survived.bacterial colonies survived.
Which of these statements best explains why Which of these statements best explains why only one colony survived?only one colony survived?
A.The bacteria in the colonies competed for survival. A.The bacteria in the colonies competed for survival. B.There was only enough food in the dish for some of B.There was only enough food in the dish for some of the bacteria to survive. the bacteria to survive. C.There was not enough antibiotic in the dish to kill all C.There was not enough antibiotic in the dish to kill all the bacteria. the bacteria. D.The bacteria in the surviving colony had genetic D.The bacteria in the surviving colony had genetic variations that allowed them to survive.variations that allowed them to survive.

46
D. The bacteria in D. The bacteria in the surviving the surviving
colony had genetic colony had genetic variations that variations that
allowed them to allowed them to survive.survive.

47
The leafy sea dragon is a type of fish that The leafy sea dragon is a type of fish that lives in the ocean near Southern Australia. lives in the ocean near Southern Australia. The leaf-like fins and appendages that The leaf-like fins and appendages that hang from its body look like kelp, a type of hang from its body look like kelp, a type of brown algae founds in its habitat. This brown algae founds in its habitat. This leaf-like appendage help protect the leafy leaf-like appendage help protect the leafy sea dragon from predators.sea dragon from predators.
The leafy sea dragon’s leaf-like fins and The leafy sea dragon’s leaf-like fins and appendage can best be described as:appendage can best be described as:A. AdaptationA. AdaptationB. GenotypeB. GenotypeC. CloneC. CloneD. AlleleD. Allele

48
A. AdaptationA. Adaptation

49
Which cell structure Which cell structure contains molecules contains molecules that direct cell that direct cell activities?activities?A.A. nucleus nucleus B.B. ribosome ribosome C.C. mitochondrion mitochondrion D.D. chloroplastchloroplast

50
A.A.nucleus nucleus

51
Which of these is not a use Which of these is not a use for DNA fingerprinting?for DNA fingerprinting?A.A. to determine how to determine how individuals are related individuals are related B.B. to make messenger RNA to make messenger RNA C.C. to determine a genetic to determine a genetic sequence sequence D.D. to study inherited diseases to study inherited diseases

52
B.B.to make to make messenger RNA messenger RNA

53
Coyotes and gray wolves have a Coyotes and gray wolves have a high degree of relatedness. high degree of relatedness. Which of these best describes Which of these best describes why the two species are closely why the two species are closely related?related?A.A. They have similar behaviors. They have similar behaviors.
B.B. They have a common They have a common ancestor. ancestor. C.C. They feed on the same types They feed on the same types of food. of food. D.D. They are found in the same They are found in the same habitat. habitat.

54
B.B.They have a They have a common common
ancestor. ancestor.

55
Students working in a biology Students working in a biology laboratory use many tools. Which laboratory use many tools. Which task is correctly paired with the task is correctly paired with the appropriate tool?appropriate tool?A.A. grouping organisms—Punnett grouping organisms—Punnett square square B.B. determining genotypes—determining genotypes—microscope microscope C.C. discovering mutations—discovering mutations—classification key classification key D.D. determining relatedness—determining relatedness—electrophoresis gel electrophoresis gel

56
D.D. determining determining relatedness—relatedness—
electrophoresis gel electrophoresis gel

57
Organisms 2 and 4 belong to Group B of the below Organisms 2 and 4 belong to Group B of the below classification chart. Which of these could be used to classification chart. Which of these could be used to place these two organisms into two groups, Group B1 place these two organisms into two groups, Group B1 and Group B2?and Group B2?A. Type of feetA. Type of feetB. Number of legsB. Number of legsC. Presence of beaksC. Presence of beaksD. Presence of wingsD. Presence of wings
1.Wings Go to 2No wings Group A2.Feathers Group BNo Feathers Go to 33.Two legs Group CSix legs Group D
1 (Bat) 2 (Duck) 3(Frog)
4 (Bird) 5 (butterfly)

58
A. Type of feetA. Type of feet