Membrane Notes, Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Structure: A) Integral/transmembrane protein: Doorway for...
-
Upload
annabel-sanders -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Membrane Notes, Chapter 4 Cell Membrane Structure: A) Integral/transmembrane protein: Doorway for...

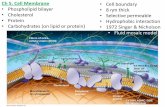
Membrane Notes , Chapter 4
Cell Membrane Structure: A) Integral/transmembrane
protein: Doorway for molecules to enter to cell
B) Peripheral protein: Cytoskeleton anchor
C) Phospholipid bilayer: Cell boundary, regulates entry to cell.

Cell Membrane Structure Cont’d D) Phospholipid Head: Hydrophilic
Head E) Phospholipid Tail: Hydrophobic, can
be saturated, (membrane more solid because packed closer together) or unsaturated (membrane more fluid because don’t pack tightly together)
F) Cholesterol: Prevents membrane from solidifying

Cell Membrane Structure Cont”d G) Sugars: Helps as an ID tag for
the cell H) Skip I) Skip J) Cytoskeleton fibers: Cell
Structure

Cell membrane

Fluid Mosaic Model Fluid: All the “stuff” moves around
with in the cell membrane. Mosaic: Membrane made up of
lots of different parts.

Transport Across Membranes A) Passive Transport 1. Diffusion a) particles can move either way
across the membrane, depending on the concentration
b) size restrictions: large molecules will not pass (WNP), charged ions WNP, small stuff will pass!

Transport Across Membrane Cont’d 1) Diffusion 2) Osmosis: Diffusion of
water. 3) Facilitated Diffusion:
Some molecules require proteins to help them through the membrane (Down their concentration gradient* . Hi to LOW!)
*Concentration gradient: A difference between concentrations in a space.

Diffusion Review

Osmosis Review: Blue=SoluteRed=Water

Transport Across Membrane Cont”d Types of facilitated Diffusion
Proteins: 1) carrier proteins* 2) Tunnel Proteins: Open tunnels
that allow passages

Are these proteins exhibiting examples of passive transport?

Transport across Membrane Cont’d B. Active Transport 1) Sodium Potassium Pump: In
order for neurons to work, we have to move sodium and potassium to a particular side of the membrane- not necessarily from an area of high to low concentration! Pumps used to move particles. ATP required to force particles through.

Transporting Across Membrane: Active Transport cont’d 1. Sodium Potassium Pump 2. Bulk Transport a)Endocytosis (IN) Types: ^Pinocytosis: Cell “drinking” ^Phagocytosis: Cell “eating” ^Receptor mediated endocytosis Specific in terms of what food
particles will fuse with lysosomes to digest food
material.

Transport Across Cell Membrane (bulk transport continued)
a) Endocytosis b) Exocytosis (OUT) Protein carriers:
^Sodium/Potassium Pump ^Coupled
Transport ^ Proton Pump

Review of Endocytosis

Review of Exocytosis