Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 2
description
Transcript of Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 2

Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 2

Endocrine Glands


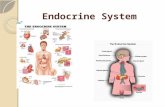
PancreasThis organ is found between the inferior
portion of the stomach and a curve of the small intestine.
Has two functions:(1) Exocrine
(2) Endocrine

PancreasExocrine:
The majority of the pancreas contains acini – cluster of glandular cells.
The acini cells release digestive enzymes that travel through secretory ducts to the digestive tract.

PancreasEndocrine:
A small number of cells are known as
pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans
(LAN-ger-hanz)
Contain 4 types of cells and each secretes a type of hormone.


Alpha CellsThe alpha cells secrete glucagon.
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels by
(1) increasing the breakdown of glycogen and
(2) increasing the release of glucose from the liver.

Alpha Cells

Beta CellsThe beta cells secrete insulin.
Insulin decreases blood glucose levels by
(1) increasing the rate of glucose uptake and utilization by most body cells
(2) increasing glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscles and liver.

Beta Cells

Beta Cells


Delta CellsThe delta cells secrete a
hormone-inhibiting hormone (GH-IH) or somatostatin.
(1) GH-IH suppresses the release of glucagon and insulin and
(2) slows the rate of food absorption and enzyme secretion in the digestive tract.

F CellsThe F cells secrete a
pancreatic polypeptide (PP).
(1) PP inhibits gallbladder contractions and
(2) regulates the production of some enzymes

Pancreatic DisordersHyposecretion of insulin:
EX – Diabetes Mellitus
(1) Genetic abnormalities, injuries, immune disorders, and hormonal inbalances
(2) Mutations resulting in inadequate insulin production
(3) Abnormal insulin molecules are made
(4) Defective protein receptors

Diabetes Mellitus
Two types of DM exist:
(1) Type I (insulin-dependent or juvenile onset)
(2) Type 2 (non-insulin dependent)

Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1Body destroys beta cells – autoimmune disorder
Approximately 10% of individuals are Type 1.
Seen in childhood and adolescence and sometimes referred to as juvenile onset diabetes.
Symptoms: retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, circulatory problems, and early heart attacks
Tx: Insulin injections

Diabetes Mellitus



Diabetes Mellitus: Type 2Body cells do not appropriately respond to
hormones
Beta cells deteriorate and produce less insulin.
Seen in all ages – most common form of disease.
Symptoms: untreated retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, circulatory problems, and early
heart attacks
Tx: Diet, exercise and medicine


Diabetes Mellitus