Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 3
description
Transcript of Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 3

Major Endocrine Glands – Abdominopelvic - 3

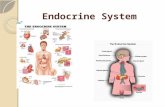
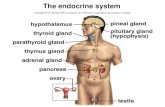
Endocrine Glands


Gonads The testes contain two types of cells that secrete
hormones:1. Interstitial cells
2. Sustentacular cells

Interstitial CellsMake androgens:
The main androgen is testosterne.
In addition to developing secondary sex characteristics, testosterone affect CNS
development in the hypothalamic nuclei that influences sexual behaviors.


Sustentacular Cells
Direct the differentiation and physical maturation of sperm.

Feedback
Both types of cells are affected by the release of FSH from the anterior pituitary.
However, when the FSH blood levels rise, cells secrete inhibin.
Inhibin then stops (inhibits) the release of FSH.

Gonads The ovaries contain two types of cells/structure that
secrete hormones:1. Ovarian cells
2. Corpus luteum

Ovarian Cells
Make estrogens when stimulated by FSH and LH:
The main estrogen is estradiol.
Developed secondary sex characteristics and helps prime the uterus for pregnancy.


Corpus Luteum
At ovulation, an immature oocyte is released.
The remaining follicle cells form the corpus luteum.
This structure releases estrogens and progestins – the primary progestin is progesterone.
The exposure to estrogens and progesterone prepares the uterus for zygote implantation.


Feedback
Similar to the testes, ovaries are influenced by the release of FSH from the anterior
pituitary.
However, when the FSH blood levels rise, cells secrete inhibin.
Inhibin then stops (inhibits) the release of FSH.

Non-Endocrine Gland Hormones
Stomach Small intestine
Heart (atrial natriuretic peptide)Kidneys
Adipose tissue Placenta

Functions regulated by the Endocrine System
GrowthHealing
Water balance & Blood PressureCalcium MetabolismEnergy Metabolism
StressRegulation of other Endocrine
Organs

Growth
Growth hormone-releasing hormoneHuman growth hormone (hGH)
Thyrotropin (TSH)Thyroxine & triiodothyronine
Calcitonin Somatostatin (GHIH)

Healing
Growth hormone-releasing hormoneHuman growth hormone (hGH)
Thyrotropin (TSH)Thyroxine & triiodothyronine
Calcitonin Glucagon, InsulinErythropoietin

Water Balance & Blood Pressure
ADHAldosterone
Angiotensin IIAtrial natriuretic H.
Epinephrine

Calcium Metabolism
CalcitoninParathyroid H. (PTH)Estrogens/androgens
Growth hormone

Energy Metabolism
Thyroxine & triiodothyronineThyroid-stimulating hormone
Epinephrine & norepinephrineInsulin
GlucagonAdrenocorticotropic hormone
Cortisol

Stress
Epinephrine Norepinephrine
ACTHCortisol
T3 & T4 - maybe?

Endocrine DiseasesCushing's Syndrome
AcromegalyPheochromocytoma
GlucagonomaSomatostatinomaDiabetes mellitusDiabetes insipidus
Hyperthyroidism (Graves disease)Hypothyroidism (Goiter)
Hypothyroidism (Cretinism in babies)Hypothyroidism (Myxedema) Achondroplasia (Dwarfism)
GigantismSADS (Seasonal Affective Disorder):