Endocrine System and Endocrine Glands
-
Upload
ebrahim-saruvaan -
Category
Education
-
view
1.124 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Endocrine System and Endocrine Glands

By: SaruVaan, ShaHuma, ShaNiya, ShaMila, SaNa, and IffathEndocrine System
Biology

Brief IntroductionENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Vertebrate hormones regulate such diverse activities as; Growth Development Reproduction Metabolic Rate Fluid Balance Blood Homeostasis And Coping with stress
Hormones Regulations
21
Hormones are Regulated by the Glands
In this Presentation, Mainly we are going to explain about the Classical Human Endocrine glands

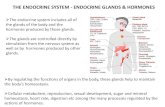
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Hypothalamus
Pituitary glands
1
2
3
4
5
6
Pineal gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid glands
Thymus gland
Adrenal gland
Pancreas
Testes
7
8
9
Ovary10

Your Logo
Controls an immense amount of our bodily functions.
Located in the middle of the base of the brain and encapsulates the ventricle portion of the third ventricle.
Hypothalamus

Your Logo
• Located in the center of the skull.
• the size of the Pituitary gland is about the size of a pea.
• Important link between the nervous system and the endocrine system and releases many hormones which affect
• Growth• sexual development• metabolism• system of reproduction
• . The pituitary gland has two distinct parts, the anterior and the posterior lobes.
• This gland was once believed to be the main controlling gland of the body.
• The pituitary gland then makes hormones of its own in answer to the body's needs.
Pituitary gland

the "third eye" by ancient people. The pineal does contain a complete map of the
visual field of the eyes, and it plays several significant roles in human functioning.
center for the production of the hormone melatonin.
regulates daily body rhythms, most notably the day/night cycle, prevents jet lag, is implicated in seasonal affective disorder, coordinates fertility, and allows for deep restful sleep patterns
Connect to the brain and nerves system through a complex network of bidirectionnel links.
Pineal gland

Shaped like a butterfly.
and usually weighs less than one ounce.
The thyroid cartilage covers the larynx and produces the prominence on the neck known as the "Adam's Apple".
Controls the rate at which the body produces energy from nutrients.
If the body does not get enough iodine, the thyroid gland cannot produce a proper amount of hormones for this conversion process.
Thyroid gland

small endocrine glands in the neck that produce parathyroid hormone.
Humans have four parathyroid glands. located in variable manner on the
posterior surface of the thyroid gland, or, in rare cases, within the thyroid gland itself or in the chest (mediastinum) or even the thymus.
control the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones.
Parathyroid gland

Forms in a part of the immune system.
It is situated in the upper part of the chest.
made up of two lobes that join in front of
function is to transform lymphocytes (white blood cells developed in the bone marrow) into T-cells (cells developed in the thymus)
The thymus enlarges from about the 12th week of gestation until puberty.
transported to various lymph glands.
play an important part in fighting infections and disease.
Thymus gland

found on top of both of the kidneys.
The center of the adrenal consists of the medulla which produces epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Adrenal gland

• pancreas has two main functions: • to produce pancreatic
endocrine hormones, which help regulate many aspects of our metabolism
• to produce pancreatic digestive enzymes
Pancreas

o produce a female hormone and it called as estrogen.
o store female sex cells, or “ova.”
Ovary

Testes is male gonads.Suspended within a sac of skin called the Scromtum.It is composed of seminiferous tubles.It have two main function: Formation, Developmet and
excretion of sperm. The secretion of testosteron.
Testes

Conclusion
Hormones are Regulated by the Glands
Growth Development Reproduction Metabolic Rate Fluid Balance Blood Homeostasis And Coping with stress
Endocrine system is the system of glands that produce endocrine secretions that help to control bodily metabolic activity

THANK YOU!
Your Logo