Lesson 8: Cell Structure and Functions
description
Transcript of Lesson 8: Cell Structure and Functions

AP Biology 2008-2009
Lesson 8:Cell Structure and Functions
The Building Blocksof Life
eu – true pro – beforeelle – small bi – twocyto – cell lys – to splitchloro - green

The Cell Theory
1. All living things are made of cells.2. New cells come from cells.3. Cells are the basic units of structure and function
of living things.
May the CODE be with you!
1. ALTMC2. NCFC3. CBUSFLT

bacteriacells
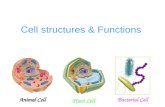
bacteriacellsTypes of cells
animal cellsanimal cells plant cellsplant cells
Prokaryote- no organelles
Eukaryotes- organelles

Cell size comparison
Bacterial cell
Animal cell
micron = micrometer = 1/1,000,000 meter diameter of human hair = ~20 microns
most bacteria 1-10 microns
eukaryotic cells 10-100 microns

Model Animal Cell
Organelles = structures inside a cell that perform specific functions required by the cell.

Cells need power to live! Making energy
to fuel daily life & growth, the cell must… take in food & digest it take in oxygen (O2)
make ATP remove waste
organelles that do this work… cell membrane lysosomes vacuoles & vesicles mitochondria
ATP

Cell MEMBRANE Function
separates cell from outside controls what enters or leaves cell
O2,CO2, food, H2O, nutrients, waste recognizes signals from other cells
allows communication between cells
Structure double layer of fat
phospholipid bilayer receptor molecules
proteins
lipid “tail”
phosphate“head”

Membrane• cell boundary• controls passage• communicates
Cytoplasm = jelly-like filling that holds organelles

Vacuoles & vesicles Function
Transports material in cell
storage Structure
membrane sacsmall food
particle
vacuole
digesting food inside cell

Food & water storage
plant cellsplant cells
contractilevacuole
contractilevacuole
animal cellsanimal cells
central vacuole central vacuole
food vacuoles food vacuoles

cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage

Lysosomes
small foodparticle
vacuole
digesting food
lysosomes
Function digest food clean up & recycle
digest broken organelles
Structure membrane sac of
digestive enzymes
digesting brokenorganelles

lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage

Function make ATP energy from cellular respiration
sugar + O2 ATP fuels the work of life
Structure double membrane
Mitochondria
in both animal & plant cellsin both animal & plant cells
ATP

lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage
mitochondriamake ATP energy from sugar + O2

Mitochondria make energy from sugar + O2
cellular respiration sugar + O2 ATP
Chloroplasts make energy + sugar from sunlight
photosynthesis
sunlight + CO2 ATP & sugar ATP = active energy sugar = stored energy
build leaves & roots & fruit out of the sugars
Plants make energy two ways!
ATP
sugar
ATP

Mitochondria are in both cells!!
animal cellsanimal cells plant cellsplant cells
mitochondriamitochondria
Chloroplast/plastidChloroplast/plastid

When things go bad… Diseases of lysosomes are fatal
digestive enzyme not working in lysosome picks up food, but can’t digest it
lysosomes fill up with undigested material grow larger & larger until disrupts cell &
organ function example:
Tay-Sachs diseasebuild up undigested fat in brain cells

But sometimes cells need to die… Lysosomes can be used to kill cells when
they are supposed to be destroyed some cells have to die for proper
development in an organism ex: tadpole tail gets re-absorbed when it turns
into a frog ex: getting rid of webbing between your fingers
during fetal development “auto-destruct” process
lysosomes break open and kill cell cell “suicide”

Fetal development
15 weeks
6 weeks
syndactyly

Chloroplasts sun energy ATP & sugars photosynthesis
+ water + energy glucose + oxygencarbondioxide
6CO2 6H2O C6H12O6 6O2light
energy + ++
ATP

The Great ENERGY Circle of Life
sun
ATP
Photosynthesis
Respiration
O2glucosesugarCO2 H2O+ +
plants
animals & plants

central vacuolestorage: food, water or waste
mitochondriamake ATP in cellular respiration
chloroplastmake ATP & sugars in photosynthesis
cell wallsupport
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signalslysosomedigestion & clean up
cytoplasm

Cells need workers (proteins)! Making proteins
to run daily life & growth, the cell must… read genes (DNA) build proteins
structural proteins (muscle fibers, hair, skin, claws) enzymes (speed up chemical reactions) signals (hormones) & receptors
organelles that make proteins… nucleus ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Golgi apparatus

Proteins do all the work!
cellsDNA proteins
one of the major job of cells is to make proteins,because…
one of the major job of cells is to make proteins,because…
proteins do all the work!proteins do all the work!
signals
structure
enzymes
receptors

Nucleus Function
control center of cell protects DNA
instructions for building proteins
Structure nuclear membrane nucleolus
ribosome factory chromosomes
DNA

lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage
mitochondriamake ATP energy from sugar + O2
nucleusprotects DNAcontrols cell
chromosomesDNA

Ribosomes on ER
Ribosomes Function
protein factories read instructions to build proteins from DNA
Structure 2 subunits some free in cytoplasm some attached to ER
largesubunit
smallsubunit

lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage
mitochondriamake ATP energy from sugar + O2
nucleusprotects DNAcontrols cell
ribosomesbuilds proteins

Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
part of protein factory helps complete the
proteins makes membranes
Structure rough ER
ribosomes attached works on proteins
smooth ER makes membranes

lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage
mitochondriamake ATP energy from sugar + O2
nucleusprotects DNAcontrols cell
ribosomesbuilds proteins
ERhelps finish proteinsmakes membranes

transport vesicles
vesiclescarrying proteins
Function finishes, sorts, labels & ships proteins
like UPS headquarters shipping & receiving department
ships proteins in vesicles “UPS trucks”
Structure membrane sacs
Golgi Apparatus

DNA
RNA
ribosomes
endoplasmicreticulum
vesicle
Golgi apparatus
vesicle
proteinon its way!
protein finishedprotein
Making Proteins
TO:
TO:
TO:
TO:
nucleus

cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
cytoplasmjelly-like material holding organelles in place
vacuole & vesiclestransport inside cellsstorage
mitochondriamake ATP energy from sugar + O2
nucleusprotects DNAcontrols cell
ribosomesbuilds proteins
ERhelps finish proteinsmakes membranes
Golgi apparatusfinishes, packages & ships proteins
lysosomefood digestiongarbage disposal &recycling

central vacuolestorage: food, water or waste
mitochondriamake ATP in cellular respiration
chloroplastmake ATP & sugars in photosynthesis
cell wallsupport
cell membranecell boundarycontrols movementof materials in & out
recognizes signals
Golgi apparatusfinish & ship proteins
nucleuscontrol cellprotects DNA
endoplasmic reticulumprocesses proteinsmakes membranes
lysosomedigestion & clean up
cytoplasm
ribosomesmake proteins

TEST TIPS!
Before the test, use flash cards to help you study. Prepare cards about items that are difficult for you. Review the
cards in random order.

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz1. Which structure is responsible for
making proteins?A. Mitochondria
B. Ribosomes
C. Endoplasmic reticulum
D. Vacuoles

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
2. Ribosomes are made in theA. nucleus
B. nucleolus
C. rough endoplasmic reticulum
D. smooth endoplasmic reticulum

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
3. Which structure controls what enters and leaves the cell?
A. nucleus
B. cell membrane
C. vacuoles
D. smooth endoplasmic reticulum

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
4. In what structure would you find digestive enzymes?
A. ribosomes
B. lysosomes
C. golgi apparatus
D. vacuoles

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
5. Which structure has the ability to communicate with other cells?
A. nucleus
B. lysosomes
C. cell membrane
D. ribosomes

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
6. Which organelle provides the ATP energy for an animal cell?
A. mitochondria
B. chloroplast
C. rough endoplasmic reticulum
D. golgi apparatus

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
7. When proteins are complete, they go to which organelle for packaging?
A. golgi apparatus
B. ribosomes
C. vesicles
D. smooth endoplasmic reticulum

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
8. Plants can make energy in two ways. Which organelles are used in plants for making energy?
A. mitochondria and ribosomes
B. chloroplasts only
C. mitochondria and chloroplasts
D. mitochondria only

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
9. Which organelle holds large amounts of water to provide structure for a plant cell?
A. vesicle
B. central vacuole
C. cell wall
D. cell membrane

Cell Structures and Functions Quiz
10. In a plant cell where would you find chromosomes?A. nucleus
B. nucleolus
C. nuclear envelope
D. chloroplasts