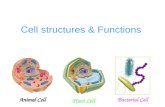
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. Essential Question What are the functions of the major cell structures?
Cell structures and functions
-
Upload
joevani007 -
Category
Education
-
view
261 -
download
0
Transcript of Cell structures and functions

Cell Structures and Functions
Presented by: Joevani S. Peñol

1. Plasma MembraneOutermost component of the
cell. Encloses the cytoplasm and
forms the boundary between material inside and materials outside the cell.

Structure of the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is a double layer (bilayer) of proteins and phospholipids and is fluid rather than solid.
This can be interpreted by the fluid mosaic model developed by Jonathan Singer and Garth Nicolson in 1972.


Function of the Plasma Membrane Regulate material moving into and
out of the cell. Separate the internal and external
part of the cell. Provide a large surface area on which
specific chemical reactions can occur.

Functions of the Plasma Membrane
Separate cells from one another.
Site for the receptors containing
specific cell identification markers
that differentiate one cell type
from the other.

2. Cytoplasm
Semifluid enclosed within plasma
membranes and are consist of
organelles, cytosol and other
structures.

Animal Cell

Function of the CytoplasmDissolves substances and
houses organelles and vesicles.

3. NucleusControl center of the cell.Contains nucleolus and DNA.

4. Endoplasmic Reticuluman extensive membranous
network continuous with the outer nuclear membrane.
Contains series of channels and is storage unit for enzymes and other proteins.

Endoplasmic Reticulum

2 Types of ERRough Endoplasmic ReticulumSmooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum

Rough Endoplasmic ReticulumAttached to it is the
ribosomes.

Microscopic view of Rough ER

Smooth Endoplasmic ReticulumSite for lipid production,
detoxification of a wide variety of organic molecules and storage of calcium ions in muscle cells.
Don’t have ribosomes attached on it.

Microscopic View of the Smooth ER

5. Golgi ApparatusCollection of membranes
associated physically and functionally with the ER in the cytoplasm.
Named after Camillio Golgi, 1998.

StructureComposed of flattened stacks of
membrane bound cisternae

Function Sorts, packages, and secretes proteins
and lipids.

Golgi Apparatus/Golgi Bodies

6. Mitochondrion
Double-membrane bound organelles that are spherical to elongate in shape.
Powerhouse of the cell. Contains its own DNA.


7. Lysosomes Membrane bound spherical
organelles that contain enzymes called acid hydrolases, which are capable of digesting organic molecules under acidic conditions.

Microscopic view of the Lysosome


8. Centrioles Located within microtubule-
organizing center. Contains nine triplet microtubules Forms basal body of cilia and flagella. Function in mitotic spindle fiber
formation.


Microscopic view of the Centriole

9. ChloroplastFound only in plant cellsSite of photosynthesis.Contains its own DNA.

Chloroplast

10. RibosomesSite of protein synthesis.

11. Cilia/FlagellaThreadlike processes.Move small particles past
fixed cells and are a major form of locomotion in some cells.

Cilia and Flagella

12. Vacuoles Membrane surrounded, often
large sac in the cytoplasm.Storage site of food and other
compounds, also pump water out of a cell.


13. CytoskeletonInterconnecting microfilament
and microtubules; flexible cellular framework.
Assist in cell movement; provides support; site for binding of specific enzymes.

Cytoskeleton

14. PeroxisomesSmall membrane bound
vesicles containing enzymes that break down fatty acids, amino acids, and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).


15. Cell WallRigid (up to many
micrometers in thickness) and gives plant cells a very defined shape.
Composed of cellulose fiber, polysaccharides, and proteins.

Function
1. Cell stability2. Determines its shape,3. Influences its development,
protects the cell against pathogens
4. Counterbalances the osmotic pressure.

StructureComposed of primary and secondary cell
walls.

References http://www.phschool.com/science/biolog
y_place/biocoach/cells/intro.html http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/301not
es1.htm http://www.uic.edu/classes/bios/bios100/
summer2002/lect05.htm