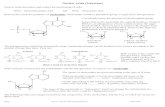
Lecture 21 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and...
-
date post
15-Jan-2016 -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Lecture 21 Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular growth and...

Lecture 21 Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids are molecules that store information for cellular
growth and reproduction;deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are large molecules consisting of long chains of monomers called nucleotides

The bases in DNA and RNA are pyrimidines C, T, and U and purines A and G
In DNA, the bases are A: T
G: C
In RNA, U replaces T
The sugars are :

A nucleotide is formed when a sugar combines with a base and phosphate

Adding phosphate groups to AMP forms the diphosphate ADP and the triphosphate ATP.

The primary structure of RNA and DNA is the sequence of the four nucleotides A-T-G-C in DNA and A-U-G-C in RNA
The nucleotides are combined in the sequence:
phosphate-sugar-phosphate sugar - ... attached at the 3’ and 5’ locations of the sugar

An example of a partial structure of RNA

In DNA, the amount of A always equals the amount of T; G equals the amount of C

The DNA structure is a double helix that consists of two strands of nucleotides that form a double helix structure like a spiral stair case;DNA has hydrogen bonds between the bases A–T and G–C;DNA has bases along one strand that complement the bases along the other

When DNA unravels into a single strand, a duplicate copy of the departed strand can be reproduced

In RNA uracil replaces thymine

RNA has several types:Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to the ribosome to make the protein.Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up 2/3 of ribosomes where protein synthesis takes place.
The sequence in DNA is transmitted to messenger RNA

Each tRNA has a triplet called an anticodon that complements a codon on mRNA;bonds to a specific amino acid at the acceptor stem;there is a transfer tRNA for every amino acid
aminoacid attached here
tRNA binds to -A-A-A on mRNA here which was TTT in DNA

Where you see UUU, the DNA must have read AAA; UUC was AAG

The activation of tRNAoccurs when a synthetase uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to attach an amino acid to a specific tRNA
each tRNA uses a triplet called an anticodon to complement a codon on mRNA
For the initiation of protein synthesis,an mRNA attaches to a ribosomethe start codon (AUG) binds to a tRNA with methionine the second codon attaches to a tRNA with the next amino acid a peptide bond forms between the adjacent amino acids at the first and second codons

How is it known that for example, UUU or UUC only codes for phenylalanine
If a synthetic mRNA with only the UUU is used, the protein that is synthesized is polyphenylalanine even though all other tRNA’s are present


Phenyketonuria results when phenylalanine cannot be converted to tyrosine due to the lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase
large amounts of phenylalanine and phenylpyruvate lead to mental retardation
A mutationalters the nucleotide sequence in DNAresults from mutagens such as radiation and chemicalsproduces one or more incorrect codons in the corresponding mRNAproduces a protein that incorporates one or more incorrect amino acidscauses genetic diseases that produce defective proteins and enzymes

Hemoglobin is made up of 2 and 2 chains. Each carries a heme which contains the Fe+
gene DNA code
... ATG-GTG-CAC-CTG-ACT-CCT-GAG-GAG-AAG-TCT-GCC
normal chain:Val- His- Leu- Thr - Pro – Glu -Glu - Lys - Ser - Ala
... ATG-GTG-CAC-CTG-ACT-CCT-GTG-GAG-AAG-TCT-GCCmissense Val- His- Leu- Thr - Pro - Val -Glu - Lys - Ser - Alamutation: the sickle cell mutation
... ATG-GTG-CAC-CTG-ACT-CCT-GAG-GAG-TAG-TCT-GCCVal- His- Leu- Thr - Pro – Glu -Glu - STOP
nonsense mutation resulting in thalassemia
... ATG-GTG-CAC-CTG-ACC-CTG-AGG-AGA-AGT-CTG-CC...
Val- His- Leu- Thr - Leu– Arg -Arg - Ser - Leu ...
frameshift mutation also resulting in thalassemia

Genetic diseases result from a mutation which results in a defective enzyme.