Gastro intestinal fistula
-
Upload
mario-ruano -
Category
Documents
-
view
741 -
download
2
Transcript of Gastro intestinal fistula

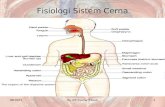
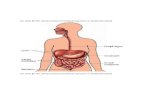
Gastro-Intestinal Fistula
Hashmi

• Fistulas are abnormal communications between two epithelial-lined surfaces
• Gastrointestinal (GI) fistulas represent abnormal ductlike communications between the gut and another epithelial-lined surface– organ system– skin surface
– GI tract itself

• The majority of external (cutaneous) fistulas represent a complication of recent abdominal surgery
• The leading causes of internal fistulas– Crohn disease– Diverticulitis– Malignancy– Complication of treatment

• F – Foreign Body• R – Radiation• I – IBD / Infection• E – Epithelialized tract• N – Neoplasm
• D – Distal Obstruction• S – Segment (>2cm)

• High output fistula are from upper GI tract
• High-output GI fistula discharge more than 500ml/day
• High-output pancreatic fistula is one which produces more than 200 ml/day
• High output fistula– more serious metabolic disturbances– higher mortality rates

• Spontaneous closure– bowel continuity is maintained– no abscess– adjacent bowel is healthy– no distal obstruction– fistula tract is not epithelialized– not more than 2 cm in length– bowel defect is less than 1 cm in diameter
• Least likely to close with non-operative therapy– gastric– lateral duodenal– ligament of Treitz– ileal fistula

• Nutritional Support– Minerals, vitamins, electrolytes
– Caloric intake (35-45 cal/kg/day)– Protein (1.5-1.75 gm/kg/day)– TPN

• Recognition and Stabilization– fluid resuscitation, electrolytes, acid/base balance,
control of sepsis, local wound care, nutritional support
• Investigation and Assessment– radiological– source, nature of tract, bowel continuity, obstruction,
adjacent bowel, abscess
• Definitive Treatment– somatostatin and nutritional support, surgical
resection +/- diversion