fisiologi ginjal
-
Upload
andrimencit -
Category
Documents
-
view
26 -
download
0
description
Transcript of fisiologi ginjal
I.FUNGSI GINJAL :1.Mengatur keseimbangan air dan ion
inorganik2.Mengeluarkan end produc metabolisme3.Mengeluarkan benda asing4.Glukoneogenesis5.Memproduksi hormon / Enzim :
-Erythopoetin-Renin / Enzim angiotensin- 1-25 Dihydroxi vitamin D
PRINSIP DASAR FISIOLOGI PRINSIP DASAR FISIOLOGI GINJALGINJAL
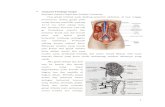
II.Struktur Ginjal Dan Sistim urinarius-Organ retrperitoneal-Terdiri atas cortex dan Medula-Ginjal terdiri atas 1 million Nefron-1 nefron terdiri atas :
-Renal Corpuscle :=glomerulus=Capsul Bowman
-Tubulus proximal-Ansa Henle-Tubuli distal-duktus koligentes
FIGURE 16–2Basic structure of a nephron. (a) Anatomical organization. The macula densa is not a distinct segment but a plaque of cells inthe ascending loop of Henle where the loop passes between the arterioles supplying its renal corpuscle of origin. The outerarea of the kidney is called the cortex and the inner the medulla. The black arrows indicate the direction of urine flow.(b) Consecutive segments of the nephron. All segments in the screened area are parts of the renal tubule; the terms to theright of the brackets are commonly used for several consecutive segments.
Ada 3 tahap dalam ginjal Ada 3 tahap dalam ginjal untuk membentuk urinuntuk membentuk urinFiltrasi glomerulusReabsorpsiSekresi Di ginjal
Terakhir.. Ekskresi keluar tubuh
◦Ekskresi ke luar melalui pelvis – uretra (miksi)
FIGURE 16–3(a) Anatomy of the renal corpuscle. Brown lines in the capillary loops indicate space between adjoining podocytes. (b) Crosssection of the three corpuscular membranes—capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and epithelium (podocytes) ofBowman’s capsule. For simplicity, glomerular mesangial cells are not shown in this figure.
Section of a human kidney. For clarity, the nephron illustratedto show nephron orientation is not to scale—its outline wouldnot be clearly visible without a microscope. The outer kidney,which contains all the renal corpuscles, is the cortex, and theinner kidney is the medulla. Note that in the medulla, the loopsof Henle and the collecting ducts run parallel to each other.The medullary collecting ducts drain into the renal pelvis.
Anatomy of the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
FIGURE 16–4
FIGURE 16–5
III.Proses dasar pada Ginjal :◦1.Glomerulu filtrasi◦2.Reabsorbsi tubuli ◦3.Sekresi tubuli• Pembentukan urin hasil Filtrasi gromeruli,
Reabsorbsi dan Sekresi Tubuli :-Pembentukan urin =filtrasi
=Reabsorbsi=Sekresi
The three basic components of renal function. This figure isto illustrate only the directions of reabsorption and secretion,not specific sites or order of occurrence. Depending on theparticular substance, reabsorption and secretion can occur atvarious sites along the tubule.
FIGURE 16–6
.Kecepatan ekresi urinGFR – Reabsorbsi + Sekresi
. FILTRASI : -terjadi melalui
memb.glomerulus -Komposisi filtrat = plasma
kecualitampa proten dan sel.
Rabsorbsi glukosa: @glikosa difiltrasi glomerulus-Reabso- bsi Tub proks---Trans aktif @Transfort maksimum 375 mgr/menit @Biasanya terjadi bersamaan dengan NaREABSORBSI Na: @65 % reabs Na di Tub proks/25 % di HenleREABSORBSI KLORIDA:aktif/pasif biasanya Bersamaan dengan Na:(65% tub proks/25 %
Henle/10 % diantara tub distal-kolligen
REABSORBSI KALIUM: -50% diserap di tub prksimal/40 % pars
ascnden L/H /10 % dukt koligenREABSORBSI ASAM AMINO: -semua asam amino direabsorbsi tub
proksimaREABSORBSI PROTEIN PLASMA: -<<< protein yang filtrasi di glomerulus -Reabsorbsi di tubuli proksimalREABSORBSI UREA:hasil akhir metabolisProtei di hepar.(50 % tub proksimal/40 %
urea menetap filtratdiekresikan
REABSORBSI BIKARBONAT: @tubuli proksimal-aktif(Duk koligent<)FUNGSI ENDOKRIN GINJAL: @Renin @1-25 dihidroksi vitamin D3minerali- sasi tulang @eritropoitin--merupakan respon da-
ri iskhemia ginjal berfungsi pembentukan sel-sel darah merah
V.Konsep Clearance Ginjal-Kemampuan ginjal membersihkan
plasma darah dari suatu zat persatuan waktu
- Cs = Us x VPs
Bahan yang dipergunakan :
◦Inulin◦PAH◦Creatinin◦Iotalamat radioaktif
FIGURE 16–7Renal handling of three hypothetical substances X, Y, and Z. X is filtered and secreted but not reabsorbed. Y is filtered, and afraction is then reabsorbed. Z is filtered and completely reabsorbed.
FIGURE 16–8Forces involved in glomerular filtration. The symbol denotes the osmotic force due to the presence of protein inglomerular capillary plasma.
FIGURE 16–10Example of renal handling of inulin, a substance that isfiltered by the renal corpuscles but is neither reabsorbed norsecreted by the tubule. Therefore, the mass of inulinexcreted per unit time is equal to the mass filtered duringthe same time period, and as explained in the text, theclearance of inulin is equal to the glomerular filtration rate.
Blader fillsCereberal
CortexStrech reseptor
Parasymphatetic nerve
Bladder
Internal urethral Sphinter mecanically open when
bladder contraction
Bladder contraction
Motor neuron to external sphinter
External urethara sphinter remains
closed when motor neuron is stimulated
No Urination
External urethral sphinter open when
motor neuron inhibition
Urination
Voluntery controlReflex control
+
+
+
+-
Micturation