Febrile seizures
-
Upload
csn-vittal -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
726 -
download
7
Transcript of Febrile seizures

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Febrile seizure is a seizure Febrile seizure is a seizure accompanied by fever (> 38accompanied by fever (> 3800 C) C) without CNS infection of defined without CNS infection of defined cause in infants and children 3 cause in infants and children 3
months to 6 years of age months to 6 years of age [Avg. 18 – 22 months] [Avg. 18 – 22 months]
Does not include seizures occurring during fever Does not include seizures occurring during fever in children with past H/o. afebrile seizure.in children with past H/o. afebrile seizure.
Definition:Definition:

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
“ “ a seizure occurring in childhood a seizure occurring in childhood after 1 month of age, associated with after 1 month of age, associated with
a febrile illness not caused by an a febrile illness not caused by an infection of the CNS, without infection of the CNS, without previous neonatal seizures or previous neonatal seizures or
previous unprovoked seizures”previous unprovoked seizures”
Definition: Definition: ILAEILAE

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
“ “ an event in infancy or childhood an event in infancy or childhood usually occurring between three usually occurring between three
months and five years of age, months and five years of age, associated with fever but without associated with fever but without
evidence of intracranial infection or evidence of intracranial infection or defined cause of the seizure”defined cause of the seizure”
Definition: Definition: NIH consensus statementNIH consensus statement

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
• 3 -4 % of children < 5 years3 -4 % of children < 5 years• In India – 1.8 to 10.1%In India – 1.8 to 10.1%
• More in boys More in boys
Incidence:Incidence:

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Etiology:Etiology:
• Genetic Predisposition : Genetic Predisposition : • A strong family history in siblings and A strong family history in siblings and parentsparents• Linkage studies mapped FS gene to Linkage studies mapped FS gene to chromosome chromosome 9p9p and and 8q8q13-2113-21• Autosomal dominant pattern in some Autosomal dominant pattern in some familiesfamilies

Febrile SeizuresFebrile SeizuresRisk Factors for 1Risk Factors for 1stst Episode Episode
About 50% of FS no identifiable risk factorsAbout 50% of FS no identifiable risk factors
Positive family history 1st degree or relatives – 4.5 times risk
Ante and perinatal factors Metarnal preeclampsia, infections, proteinuria Prematurity, LBW, neonatal jaundice, asphyxia,
birth injuries Immunizations
Following DPT or MMR vaccinations Infections
Human herpes virus 6 infection Miscellaneous
Iron deficiency anemia

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Infections commonly found in a child with FSInfections commonly found in a child with FS Acute Otitis MediaAcute Otitis Media UTIUTI URIURI RoseolaRoseola GI InfectionsGI Infections
Precipitating Factors:Precipitating Factors:
Fever of any cause can precipitate seizure in Fever of any cause can precipitate seizure in a predisposed child.a predisposed child.

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Usually a generalized tonic-clonicUsually a generalized tonic-clonic
And lasts for a few seconds to 10 And lasts for a few seconds to 10 minutes and is followed by a brief minutes and is followed by a brief postictal period.postictal period.
DescriptionDescription

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Simple Simple – 85 %– 85 % Complex Complex – 15 %– 15 %
Partial OnsetPartial Onset Prolonged Duration ( > 15 min.)Prolonged Duration ( > 15 min.) Multiple Attacks (>1 seizure in 24 hrs.)Multiple Attacks (>1 seizure in 24 hrs.)
Types :Types :

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Occur in typical age groupOccur in typical age group Generalized tonic clonic type Generalized tonic clonic type Last for less than 15 minLast for less than 15 min Single within 24 hrsSingle within 24 hrs
SimpleSimple ::

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Associated with Todd’s palsyAssociated with Todd’s palsy Last for more than 15 minLast for more than 15 min FocalFocal Multiple in 24hrsMultiple in 24hrs
ComplexComplex : : (about 1/3 of FSs)(about 1/3 of FSs)

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Seizure associate with fever in Seizure associate with fever in appropriate age group, appropriate age group,
Lasting more than 30 min or Lasting more than 30 min or Multiple seizures lasting 30 min Multiple seizures lasting 30 min
or more without regaining or more without regaining consciousness in betweenconsciousness in between
Febrile Status EpilepticusFebrile Status Epilepticus
About 25% of cases of SE in children are About 25% of cases of SE in children are due to febrile FSdue to febrile FS

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
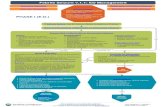
Rule out meningitis. Rule out meningitis. Lumbar puncture ?Lumbar puncture ?
Blood glucose Blood glucose HypoglycemiaHypoglycemia
Evaluation :Evaluation :
EEG – Not warrantedEEG – Not warranted Neuroimaging – not usefulNeuroimaging – not useful

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Establish clear airwaySemiprone position to prevent aspiration Monitor vital signs
Management : Management : Acute StageAcute Stage

Status EpilepsyStatus Epilepsy
Intravenous: 0.1 to 0.3 mg / kg at a rate not > 2 mg/min for a maximum of 3 doses repeated at 10 min.
Rectal: Injectable form diluted in NS by a syringe & a flexible tube at a dose of 0.3 – 0.5 mg/kg Rectal Diazepam gel : 2.5, 5, 10 mg Can be repeated after 10 min.
Intravenous: 0.1 to 0.3 mg / kg at a rate not > 2 mg/min for a maximum of 3 doses repeated at 10 min.
Rectal: Injectable form diluted in NS by a syringe & a flexible tube at a dose of 0.3 – 0.5 mg/kg Rectal Diazepam gel : 2.5, 5, 10 mg Can be repeated after 10 min.
Diazepam

Status EpilepsyStatus Epilepsy
Lorazepam
Intravenous : 0.05 to 0.10 mg / kg Rectal : Ditto Sublingual : 0.05 to 0.1 mg / kg
Intravenous : 0.05 to 0.10 mg / kg Rectal : Ditto Sublingual : 0.05 to 0.1 mg / kg

Intraosseous Intraosseous RouteRoute

Intraosseous RouteIntraosseous Route

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Tepid spongingTepid sponging AntipyreticsAntipyretics Reassurance of parentsReassurance of parents
Management :Management :

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
33% Of these 9 % have > 3 33% Of these 9 % have > 3 recurrencesrecurrences
75 % of recurrences within 75 % of recurrences within 1 year1 year
90 % of recurrences within 90 % of recurrences within 2 years2 years
Risk of Recurrence :Risk of Recurrence :

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Early age at seizure onsetEarly age at seizure onset Low temperature at the Low temperature at the
onsetonset Short duration of temp. Short duration of temp. before FSbefore FS Positive family historyPositive family history
Factors Predisposing Recurrence :Factors Predisposing Recurrence :
•Complex FS are not a predictors of recurrenceComplex FS are not a predictors of recurrence

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
9% when several risk factors +9% when several risk factors + 1% when no risk factors1% when no risk factors
Risk of Epilepsy in children with FS:Risk of Epilepsy in children with FS:
• Risk Factors:Risk Factors:
•Atypical features of seizures or Postictal periodAtypical features of seizures or Postictal period
•Positive family h/o. epilepsyPositive family h/o. epilepsy
•Initial FS before 9 mo. Of ageInitial FS before 9 mo. Of age
•Delayed developmental mile stonesDelayed developmental mile stones
•Pre-existing neurological disorderPre-existing neurological disorder

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Prolonged anticonvulsant prophylaxis Prolonged anticonvulsant prophylaxis is no longer recommended.is no longer recommended.Phenytoin and carbamazepine have Phenytoin and carbamazepine have no effect on febrile convulsionsno effect on febrile convulsionsPhenobarbitone reduces the congnitive Phenobarbitone reduces the congnitive
function in childrenfunction in childrenSodium valproate – potential risk of Sodium valproate – potential risk of hepatotoxicity in childeren < 2 yrs.hepatotoxicity in childeren < 2 yrs.
Prevention of Recurrences : Prevention of Recurrences : DontDontss

Febrile SeizuresFebrile Seizures
Evaluat the causeEvaluat the cause Early antipyreticsEarly antipyretics Oral diazepam at the onset Oral diazepam at the onset of each febrile episode of each febrile episode
0.3 mg/kg q8h0.3 mg/kg q8h
Prevention of Recurrences : Prevention of Recurrences : DoDoss

- CSN Vittal- CSN Vittal- CSN Vittal- CSN Vittal