Febrile seizures
-
Upload
soundar1969 -
Category
Documents
-
view
287 -
download
2
Transcript of Febrile seizures

Seizures
Prof.Dr.P.Soundararajan

seizure is a transient occurrence of signs and symptoms resulting from abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain.

Febrile seizure; definition
• Between 6m to 60months• Fever >38oc • no CNS infection, no metabolic
imbalance• No prior febrile seizure

SFS
• GTC• <15mts• No >1 episode <24hrs• No postictal complications

CFS
• Focal• >1 episode in 24hrs• >15mts• Post ictal abnormality

• 2-5% incident• SFS; No risk of complications• CFS; 2 fold increase in morbidity

Cause
• Autosomal dominant• Many genes, • sodium channel genes
• generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+)
• severe myoclonic epilepsy of infancy

Recurrence
• <1yr age• <24hr of fever• Family h/o febrile fit or epilepsy• CFS• Male• Low serum sodium

RISK FACTOR RISK FOR SUBSEQUENT EPILEPSY
Simple febrile seizure 1%
Neurodevelopmental abnormalities 33%
Focal complex febrile seizure 29%
Family history of epilepsy 18%
Fever <1 hr before febrile seizure 11%
Complex febrile seizure, any type 6%
Recurrent febrile seizures 4%

Workup
• Thorough history & examination• LP [assess sensorium]• Prior antibiotics?

EEG
• Normal CNS; no need• Doesn’t predict epilepsy• Spikes seen during drowsy• To do >2 weeks• To know type of epilepsy• 30mts wakefulness & sleep

• Serum glucose• CT or MRI
– Status epilepticus [hippocampal atrophy]

Management • Counsel parent• Antipyretics • SFS; no drugs• CFS; Diazepam, lorazepam, midazolam• Rectal diazepam• Intranasal midazolam• Intermittent prophylaxis
– Diazepam, phenobarbitone, clobazam• Iron deficiency?

Status epilepticus
• continuous seizure activity or recurrent seizure activity without regaining of consciousness lasting for >30 min.
• impending status epilepticus ; seizures between 5 and 30 min.
• Nonconvulsive status epilepticus • Refractory status epilepticus

Causes
• 30% 1st episode SFS• CNS infection• Trauma• CVA• Metabolic imbalance• Poisoning

• Imbalance between excitation & inhibition• Increased excitability [glutamate, aspartate]
• Decreased GABA mediated inhibition• Inadequate O2 supply• Hypoxia• Cerebral edema• Ca influx into neurons• Neuronal death

Management
• A B C• Detect underlying etiology• Electrolytes, BUN, glucose• CSF study• EEG• Imaging

Drugs
• IV lorazepam• midazolam• Fosphenytoin• Phenobarbitone• Valproate• propofol, thiopentol• Isoflorane• Induced acidosis.

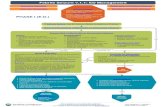
SE Protocol - 0 - 10 min
• Verify and describe seizure
• Airway - Positioning & suctioning
• O2 through mask, Attach pulse oxymeter
• NGT, BMV if needed
• Start IV / IO - IV lorazepam 0.1 mg / kg (1st dose)
• If no IV / IO, Midazolam IM 0.15 mg / kg
• Monitor HR, RR, perfusion, BP, SaO2

SE Protocol - 10 - 20 min
• Check Glucose - Dextrostix, IV dextrose
• Lab investigations
• IV lorazepam 0.1mg / kg (2nd dose)
• Monitor HR, RR, Perfusion, BP, SaO2
• BM ventilation if needed
• IV Phenytoin 20 mg / kg over 20 min. (1st dose)
• Fever reduction

SE Protocol - 40 - 50 min
• BM ventilation
• IV Phenytoin 10 mg / kg (2nd dose)
• If seizure still persists, IV Phenobarbitone
20mg / kg over 10 min.
• Intubate prior to Phenobarbitone
• Manage ICT
• Consider IV Pyridoxine if > 3 yrs old

SE Protocol - 60 min.Refractory Status Epilepticus
• Admit in PICU
• Involve Anesthetist / PICU team
• Support circulation
• Correct metabolic problems (Hypoglycemia,
Hypocalcemia, Hypomagnesemia)
• IV Midazolam infusion, Pentothal, IV Sodium
valproate

• IV Midazolam 0.15 mg / kg stat. dose
Maintenance - 1 mcg / kg / min.
• Raise / 1 mcg / kg / min. every 15 min. if seizure
persists. Maximum 20 mcg / kg / min.
• Higher the dose, need for ventilation
• After control, same rate of infusion for 24 hours
then taper by 1 mcg every 2 hours

Approach to seizure
• Assess CVS, RS status• Metabolic screen• Head examination• Eye ex• NCM• HSM• FND• EEG, imaging


Thank you