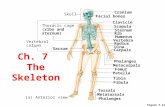
Chapter 11 Cranium Part 1. Cranial Bones Skull = __________ and ________ bones Cranium (8 bones) –...
-
Upload
hailey-buss -
Category
Documents
-
view
232 -
download
0
Transcript of Chapter 11 Cranium Part 1. Cranial Bones Skull = __________ and ________ bones Cranium (8 bones) –...
Cranial Bones
• Skull = __________ and ________ bones
• Cranium (8 bones)– Area that surrounds and protects the brain.– ____________ (Skull Cap)– Floor
Frontal Bone
• ____________ (Vertical) Portion– Forehead
• ___________ (Horizontal) Portion– Superior Orbits
Frontal BoneSquamous
• ___________– Area between eyebrows
• _____________ Groove– Depression above eyebrows
• ______________margin– Superior rim of orbit
• _____________ ridge (Arch)– Ridge beneath eyebrow
Frontal BoneOrbital
• _____________plate– Superior portion of each orbit
• _______________ Notch– Separates orbital plate
• Articulates with 4 cranial bones– Right and left parietals, sphenoid, _________
Parietal Bones
• Forms the __________calvarium.
• Articulates with 5 cranial bones – Frontal, occipital, temporal, sphenoid, parietal
Occipital Bone
• ___________portion of the calvarium.
• Squamous Portion
• _______________Protuberance (Inion)– Prominent bump on the back of head.
Occipital
• ____________Magnum– Hole for spinal cord
• _______________ condyles– Articulating surface on each side of foramen
magnum.
• Articulates with 6 bones– 2 parietals, 2 temporals, sphenoid, ________
Temporal Squamous Portion
• Vertical aspect and very thin.
• _______________– Articulates with Zygoma– ____________
Temporal Petrous Portion
• Houses hearing and equilibrium
• _______________– Petrous Ridges
• _______________Meatus– Opening for the nerves of hearing and equilibrium
• ________________
Sphenoid
• Centrally located. Anchors all 7 cranial bones.
• _______________(Turk’s Saddle)– Houses _______________– __________sellae – Posterior wall of sella– _____ – Depression posterior to dorsum sella. – Posterior clinoid – Anterior clinoid
Sphenoid
• ___________ Wings– Anterior clinoid
• ___________ Wings – Forms portion of floor and walls of cranium
Sphenoid
• Lateral ______________– Lateral downward projections
• Medial ________________– Medial downward projections
• ___________ hamuli– Process off of medial pterygoid
Sphenoid Optic Components
• Optic __________ (Chiasm) – Groove between Anterior body and lesser wings
• Optic ___________– Hole between anterior body and lesser wings
• Superior ______________– Space lateral to optic foramen between lesser and
greater wings
Ethmoid Bone
• Small bone lying primarily below floor of cranium.
• Articulates with 2 cranial bones.
• ____________– Horizontal portion
• ____________– Superior projection from cribriform plate into frontal
bone
More Ethmoid
• _________________ plate– Downward projection forms nasal septum
• Lateral _____________ (masses)– Suspend from cribiform
• Nasal ___________(Turbinates)– Downward projection from labyrinth
Sutures
• Areas of cranial fusion– Synarthrodial
• __________ suture– Fuses Parietal to Frontal bone
• ___________suture– Fuses right and left Parietal
• __________suture– Fuses Parietal to Occipital
• __________ suture– Fuses Parietal to Temporal