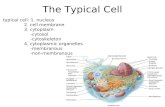
CELL: Structure & Function. Objectives: – Explain why a cell is like a tiny factory. – List,...
-
Upload
elvin-phillip-rich -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
1
Transcript of CELL: Structure & Function. Objectives: – Explain why a cell is like a tiny factory. – List,...
Objectives:
– Explain why a cell is like a tiny factory.
– List, label, and describe the functions of the parts of a typical eukaryotic animal cell.
– Explain how a cell conducts all the processes of living things, just on a smaller scale.
What You Need To Run A Factory
• building• supports/ internal framework• control center• blueprints• power plant• raw materials• machines/ workers• assembly line• packing centers• packing/ boxes• trucks/ shipping vehicles• waste disposal
Prokaryotic
• Do not have structures surrounded by membranes
• Few internal structures• 1-celled organisms,
Bacteria
http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/prokaryotic_cells.html
Eukaryotic• Contain organelles surrounded by membranes• Most living organisms
Plant Animal
http://library.thinkquest.org/C004535/eukaryotic_cells.html
Cell/Plasma Membrane“Building”
• Outer membrane of cell that controls nutrient and waster material movement in and out of the cell
• Double layer of lipid & protein separating cell from its environments
• All cells have one
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Cell Wall
• Most commonly found in plant cells & bacteria
• Supports & protects cells
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Nucleus“control center”
• Controls the cell’s actions• Contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA).• Surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear
envelope/membrane• Has a dense region called the nucleolus where ribosomes are
formed.
© Glencoe Biology 2007
Chromatin“blueprints”
• Located in the nucleus• Composed of nucleic acids
(DNA)• Condenses into chromosomes
during cell division• Contain instructions for traits
& characteristics Chromosomes during early cell division – 10,000x
Cytoskeleton“supports & internal framework”
• A network of protein fibers (microfilaments) and tubes (microtubules) extending throughout the cell.– Provides a framework for the cell.– Helps transport materials.– Anchors the organelles.– Functions in cell movement
© G
lencoe Biology 2007
• Organelles that manufacture proteins• Composed of RNA and protein• Not bound by a membrane.• Some float free in the cytoplasm while others are
attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Ribosomes- “machines/ workers”
Electron Micrograph of ribosomes. The ribosomes operate in chains when translating a mRNA.
Copyright © Daniel Kunkel
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Golgi Apparatus“packing plant”
• A series of flat, membrane-bound sacs that sorts, modifies, packages, and distributes molecules into sacs called vesicles.
© Glencoe Biology 2007
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
Lysosomes“waste disposal”
• Special vesicles that contain powerful digestive enzymes that can break down large molecules and old organelles.
• Cell breaks down if lysosome explodes
© G
lenc
oe B
iolo
gy 2
007
http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html
The Discovery of the Cell-1665: Robert Hooke used an early compound microscope to look at
a thin slice of cork, a plant material.
-Cork looked like thousands of tiny, empty chambers…“cells”
Idea: The cell is the basic unit of life basic
The Discovery of the Cell
• Anton van Leeuwenhoek: used a single-lens microscope to observe pond water and other things.
• The microscope revealed a world of tiny living organisms.
Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells
Cells are the smallest working units of all living things
All cells come from preexisting cells through cell division