Cell Basics - Weebly · Cell Basics. Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or...
Transcript of Cell Basics - Weebly · Cell Basics. Two Basic Cell Types All cells are either prokaryotic or...

Cell Basics

Two Basic Cell Types
All cells are either
prokaryoticor
eukaryotic

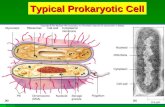
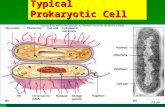
Prokaryotic Cells
a.k.a. Bacteria

Typical bacteria cell
Prokaryotes, which includes all bacteria. They are the simplest cellular organisms. They have genetic material but no nucleus.

• Unicellular
• No membrane bound organelles –therefore, not many specialized functions.
Bacteria!
Prokaryotic cells

Cell Membrane
• Regulates what goes in and out of the cell (selective).
• Composed of lipids and proteins.

DNA
• Genetic Material of the cell
• Generally small and circular
• Made of monomers called nucleotides.

Cytoplasm
• Cytoplasm is a clear,
jelly-like fluid that
fills the cell

Ribosomes
• Make proteins.

Cytoskeleton
• A network of protein structures that determines cell shape

Cell wall
• Helps support, protect and maintain the shape of the cell

Flagella
• Tail-like structure that helps bacteria move (MOTILITY)
• Flagella are also found on some eukaryotic cells.
• For example, some protists have flagella. So do sperm cells!

Pilli
• Hair-like structure that helps bacteria stick to surfaces

Capsule
• A sticky outer protective covering that allows bacteria to adhere to surfaces
• Increases their ability to cause disease

Name the structures of this bacterium.
1. 5.
2. 6.
3. 7.
4.

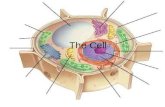
Eukaryotic Cells
a.k.a. Plant, Animal, Fungi, Protista

• Complex cells that contain a nucleusand many membrane-bound organelles with specialized functions.
• Animal or plant cells. (also includes fungi and protists)
Eukaryotic cells

Nucleus
• Controls activities of the cell and holds the genetic information (DNA)
• Surrounded by the nuclear membrane/envelope
• the “control center” of the cell

DNA
• Genetic Material of the cell
• Contained within the Nucleus
• Made of monomers called nucleotides.

Nucleolus
• Located in the center of the nucleus.
• Site of ribosome production.

Plasma or Cell Membrane
• Regulates what goes in and out of the cell (selective).
• Composed of lipids and proteins.

Lets quickly examine the structure and function of the cell membrane:
Which of the following animals do you think can pass easily through this opening? Why?

Cytoplasm
• Cytoplasm is a clear,
jelly-like fluid that
fills the cell

Ribosomes
• Make proteins.
• Found throughout the cell and on rough ER.

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• System of internal membranes that transport proteins and other substances through the cell.
• 2 Kinds:
–Rough ER: transports proteins that are made by ribosomes attached to it
–Smooth ER: helps make new lipids and helps to break down toxic substances such as alcohol• Has no ribosomes attached to it

Which picture best depicts the function of the ER?
• The ER is referred to as the highway of the cell since it transports molecules, such as proteins, throughout the cell.

Golgi Apparatus
• Flattened, membrane-bound sacs that serve as the packaging and distribution center of the cell.
– They modify the proteins that travel from the
ER in vesicles (small, membrane-bound sacs)
before they are released to serve their function.

Which picture best depicts the function of the golgi apparatus?
• The Golgi is sometimes referred to
as the post officesince it modifies and packages proteins before they are shipped to their rightful destination

• Releases energy from organic compounds to make ATP (energy)
• “Powerhouse” of the cell
Fact: Mitochondria contain their own DNA and ribosomes to make their own proteins. Who do you inherit your mitochondrial DNA from?
• Your mother –it’s found within the egg and the father only donates his DNA (23 chromosomes)
Mitochondria

Mitochondria
• Look at the mitochondrial DNA and determine whether it looks like picture a or b.

Mitochondrial DNA similar to Prokaryotic (bacterial) DNA?
• This fact supports the widely accepted theory that mitochondria were once primitive prokaryotes!

Which picture best depicts the function of the Mitochondria?
TXU supplies electricity to many houses and businesses in Dallas just as the mitochondria supplies energy for it’s cell

Based on your knowledge of mitochondria, which of the following cells would contain a greater number
of mitochondria?
• Muscle cells require large amounts of energy in order to perform functions and therefore require a larger number of mitochondria

Mitochondria Quick Write

Lysosomes
• Specialized vesicles that contain digestive enzymes
– Function by digesting and recycling the cell’s used components (carbs, proteins, lipids and old organelles)

Which picture best depicts the function of the lysosome?
• Both contain digestive enzymes and both help to breakdown particles

Lysosomes Quick Write

Cytoskeleton
• A network of protein structures that determines cell shape
• Provides supportfor organelles and pathways for cell movement.

Some structures are found in plant cells but not animal cells…

Cell wall
• Helps support, protect and maintain the shape of the cell

Chloroplasts
• Use light energy to make carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water (photosynthesis).

• Just like mitochondria, chloroplasts contain their own DNA and are also thought to be descendents of ancient prokaryotic cells

“Large” Central Vacuole
• Stores water and may contain many substances, including ions, nutrients, and wastes
• Largest organelle found in plants
• When full of water, the cell becomes rigid (turgor pressure)
• FYI: Small vacuoles are found
in animal cells.

Flagella
• Tail-like structure that helps cells move (MOTILITY)
• Flagella are also found on some eukaryotic cells.
• For example, some protists have flagella. So do sperm cells!Sponges and flagella

Cell Membrane
Mitochondria
Chloroplast
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Nucleus
Lysosome
Golgi Body
Vacuole
Ribosome
Cell Wall
Cell Organelles
• Animal • Plant

Different Types of Cells
• Prokaryotic • Eukaryoticno nucleus
protists, fungi, plants, animalsonly in bacteria
small
small ribosomeslarger ribosomes
very small
organellesno organelles
nucleusno nucleus
small ribosomes
organellesno organelles
nucleus
protists, fungi, plants,
animals
only in bacteria
small 2-1000µmvery small 1-10µm
larger ribosomes

Homework on pages 23- 24

Watch ME!!!Watch ME!!!Watch ME!!!Watch ME!!!
Watch Me Whip!!
Watch Me NAE-NAE!!