Cell structure and function (Eukaryotic cells)
description
Transcript of Cell structure and function (Eukaryotic cells)

Cell structure and function(Eukaryotic cells)
Standard 4 Key idea 1 Major understanding 1.2f,
1.2g, 1.2i, and 1.2j
Notes: This power point presentation is made by Eunah Kim.

Bell Ringer questionWrite down things inside a cell you al-
ready know.

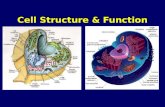
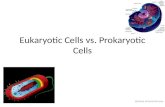
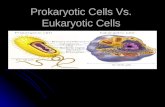
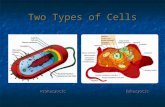
Organelles of a cell 1. Plasma membrane: the outer membrane of the cell2. Cytoplasm
Things inside the cytoplasm: a. Centrioleb. Ribosomec. Mitochondriond. Vacuole
e. Endoplasmic reticulum f. Golgi complex g Lysosome h. Chloroplast (only for plants)3. Nucleus Things inside the nucleus: DNA

http://amoebamike.wordpress.com/2009/11/06/the-cell/

Activity Label each organelle and write its
function on the cell diagram booklet.

Special organelles• Mitochondria: found in all eukaryotic cells
(both in plant cells and animal cells)Function: extraction of energy from nutrients
through cellular respiration (chemical res-piration). Power house of a cell.
http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/mitochondria/mitochondria.html

Special organelles• Chloroplast: found only in plant and
algae cells Function: photosynthesis/ contains
chlorophylls
http://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/plant-cells-chloroplasts-and-cell-walls-14053956

Cell wall: found primarily in plants.Function: provides support and protec-
tion.
http://geneticssuite.net/node/11

Cellular communication• How do cells communicate with each
other? Receptor molecules (proteins embed-
ded in the plasma membrane) play an important role in the interactions. between cells.
http://www.ftmguide.org/hormonebasics.html

Cellular communication con’t
Receptor molecules recognize specific hormones or neurotransmitters and deliver the information to the interior of the cell.
Two types of agents of cellular com-munication:
1) Hormones i.e.) growth hormone2) Neurotransmitters i.e.) acetylcholine

Cellular communication con’t1) Hormones
i.e.) growth hormoneChemicals that are secreted by en-
docrine glands and delivered through the blood to affect target cells.
2) Neurotransmitters i.e.) acetylcholine Chemicals that are secreted from one
neuron cell and carry the impulse to the next neuron.

Sample questions
Regents June 2008 #10(2)

Regents Jan 2013 #5
(1)

Exit ticket1. Write two organelles that are only
found in plants.
2. Write those organelles’ functions.