Eukaryotic Cells Workbook
-
Upload
rossbiology -
Category
Education
-
view
3.025 -
download
1
Transcript of Eukaryotic Cells Workbook

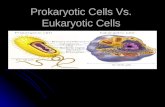
Eukaryotic Cells
All cells are self-contained units. They are surrounded by a membrane and have a nuclear area at some stage in their existence.
Prokaryotic cells were probably the first forms of life on earth (Pro = before, Karyo = nucleus). They include the kingdom Bacteria (& Archaea) and do not have membrane-enclosed organelles.
Approximately 1.5 million years ago eukaryotic cells appeared (Eu = true). Eukaryotes have a membrane-enclosed nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles. They include the kingdoms Animalia, Plantae and Fungi (& Protista).
You need to know the ultrastructure of general plant and animal eukaryotic cells and their organelles, along with the function of these organelles.
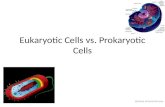
Overview of an animal cell
Drawing of a generalised animal cell combining all of the most common structures found in animal cells (no cell actually looks like this). Some of the labels are slightly different to what you are used to – please add the following labels to this drawing and the next: Cell Membrane, Golgi Body.

Overview of a plant cell
Revision & Extension – Plant & Animal Cells
Complete the following table of the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells:
Similarities Differences

Eukaryotic Organelles
1. Plant cell wall
What are plant cell walls composed of? How is this substance formed?
How does the structure and composition of the cell wall allow it to fulfil its role effectively?
What function do the plasmodesmata (singular plasmodesma) provide? How does their structure assist this function?
Location:
Size:
Function:

2. Cell surface membrane
Cell membranes are described as having a fluid mosaic structure. Describe what this means. What are they composed of?
How does this structure allow the cell surface membrane to complete its function?
What other components of a eukaryotic cell involve a membrane?
Location:
Size:
Function:

3. The nucleus (membrane-bound)
The nucleus consists of various structures; list each of them along with their function.
How is the overall structure of the nucleus suited to its function?
In what ways does the nucleus change during cell division?
Location:
Size:
Function:

4. Mitochondria (membrane-bound)
Describe the structure and features of the mitochondrion.
Which of the features described are not shown on the diagram?
In what ways are the features of mitochondria suited to their function?
What is the ‘endosymbiotic theory’?
Location:
Size:
Function:

5. Chloroplast (membrane-bound)
List the structures present in the chloroplast and for each explain how its structure is related to its function.
Which features does the chloroplast share with the mitochondrion? Why are these features shared?
Location:
Size:
Function:

6. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) – rough &smooth (membrane-bound)
Smooth ERDescribe the features of the smooth ER.
How are these features related to the function of the smooth ER?
Rough ERDescribe the features of the rough ER.
Location:
Size:
Function:

How are these features related to the function of the rough ER?
7. Ribosomes
Describe the role of ribosomes. How is their location related to their function?
Location:
Size:
Function:

8. Golgi body (membrane bound)
Describe the functions of the Golgi body.
Outline the features of the Golgi body which assist these functions.
What are lysosomes?
Location:
Size:
Function:

9. Additional featuresIf you’re finished, make very brief notes on the structure and functions of these structures.
Peroxisome
Central Vacuole
Tonoplast
Centriole
Microfilaments & Microtubules
Flagellum

Additional notes