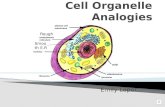
Cell organelle power point notes
-
Upload
shaunabristol -
Category
Education
-
view
1.439 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Cell organelle power point notes

1
Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum
Vacuole
Nucleolus Mitochondria
Cell Wall
Cytoplasm Golgi Body Chloroplast
Cell membrane
Lysosome Ribsomes

2
NucleusThe “brain” of the cell
Controls all of the cellular activities
DNA is inside the nucleus

3
CHROMOSOMES-
Chromosomes –
carry the information that determines what traits a living thing will have
are found inside the nucleus
Nucleus

4
NUCLEOLUS
The dark area in the nucleus
Like a tiny nucleus inside the nucleus.

CYTOPLASMCytoplasm- everything inside the cell
membrane & outside of the nucleus except the cell’s nucleus
5
cytoplasm

6
CELL MEMBRANE
holds the cell together
keeps all of the pieces (like the organelles and the cytoplasm) inside the cell
controls what goes in and out of the cell
Example: like a big plastic bag with tiny holes in it

7
Endoplasmic Reticulum known as the “ER”
it is an organelle inside the cell that ismade up of membranes that are in the CYTOPLASM of the cell
There are two different Smooth ERRough ER

8
Smooth ER
Main function is to collect, maintain & transport things
Shaped slightly tubular
Creates steroids
Stores Ions for the cell to keep nutrients balanced

9
Rough ER It has bumps all over it giving it a “rough” appearance
Bumps are called RIBOSOMES
ER collects the proteins (built by the ribosomes) and creates a bubble around them
VESICLE- is formed when the ER pinches off a part of its membrane

10

11
Mitochondria
Mito = Mighty / Power
The Power-House of the cell
They break down food molecules so the cell has the energy to live
If a cell needs a lot of energy…it will have more mitochondria (some could have 200 or more)

12
MATRIX: a fluid that has water and proteins all mixed together (like a solution)
•The proteins take the food molecules in and combine them with Oxygen to release the energy

GOLGI BODY
WHAT DOES IT DO?
13
1) it takes simple molecules and combines them to make larger molecules.
2) takes those larger molecules and puts them into packs called GOLGI VESICLES
•Also called the Golgi Complex
•It is made up of a stack of flattened out sacs …like a loose stack of pancakes

14
Think about building a model of a ship (that's the molecule). Then take that model and put it in a bottle (that's the vesicle).

LYSOSOMES (primarily animal)
• Next…smaller molecules are released which are absorbed by the mitochondria
15
•They combine with the food taken in by the cell
•The enzymes in the lysosome bond to food & digest it (acidic interior)

LYSOSOMES• When an organelle no longer works, the
lysosome will attach itself to it and break it down like food (kind of like a cannibal) – Chemicals can then be reabsorbed or
excreted
• Lysosomes can also destroy the cell if it breaks open accidentally– “Suicide Sacs”– UV light damages lysosome membrane
• The enzymes inside the lysosome spread throughout the cell and digest it 16

LYSOSOMES
17

VACUOLE
• Vacuoles are “bubbles” that float in the cell
• Vacuoles are more important to the survival of plant cells than they are to animal cells
18

VACUOLE: STORAGE IN PLANT CELLS
• Vacuoles in plants support structure
• Vacuoles hold onto things that the cell might need…like a backpack
• There are some vacuoles that hold onto waste products, similar to having a big septic tank
• Storing waste products protects the cell from contamination
19

20
You will know that a plant's vacuoles are shrinking when you see the plant begin to droop over
HOLDING UP THE WALLS

21
Turgor Pressure- force exerted by the water entering (osmosis) the vacuole, which then swells exerting internal force on the cell wall
•Causes “rigidity” so the plant my increase by stacking cells

22
•the site of photosynthesis in eukaryotic cells
•disk-like structures
•composed of a single membrane
•surrounding a fluid containing stacks of membranous disks
Chloroplast

23
Chloroplast•photosynthesis takes place inside the
chloroplastPhotosynthesis-
the process in which plant use water, carbon dioxide, and energy form the sun to make food

24
•SOLAR energy radiated from the sun is captured by plants(chloroplast)
•Then it is instantaneously changed into ELECTRICAL energy
•Then packaged as CHEMICAL energy
Chloroplast

25
•small dot-like structures in cells
•they are often associated with forming rough ER
•Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in cells
•they are made in the nucleus of the cell
•A ribosome can make the average protein in about one minute
Ribosomes

26
Types of Ribosomes
•There are two kinds of ribosomes
1) Attached to the rough ER
2) floating in the cell cytoplasm
•Attached ribosomes make proteins that are used in the ER or transported within the ER
•Free ribosomes make proteins that are used in the cytoplasm

27

28
1. Which organelle is known as the “Brain” of the cell?2. If you look at a picture of a cell, how would you recognize the nucleolus?
3. List the 3 main jobs of the cell membrane
5. The term hydro means _________.
A. If something is hydrophobic it is _________
B. If something is hydrophilic it is __________
4. Explain why the cell membrane has tiny holes made of protein in it (think of the gate).

29
1. Which organelle is known as the Power House” of the cell?2. The mitochondria of a cell share the same job as the __________ (hint- an organ) in the human body.3. Explain how you could distinguish the rough ER from the smooth ER.
5. What type of reactions occur on the inner membrane of the mitochondria? (produces energy)
4. What is the main job of the smooth ER?

30
1. What is the main function of a lysosome?
2. What happens if a lysosome breaks open?
3. Explain the difference between cytoplasm and protoplasm. (draw a diagram if it will help you)
5. Which organelle is the site of photosynthesis?
4. Why are vacuoles important to PLANTS?
6. What are the three main ingredients for photosynthesis?