Anatomy of the Neck
description
Transcript of Anatomy of the Neck

Anatomy of the NeckAnatomy of the Neck

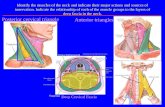
Anterior triangleAnterior triangle
Midline of the neck Midline of the neck Sternocleidomastoid muscle Sternocleidomastoid muscle Lower border of the mandibleLower border of the mandible

Subunits of ant. triangleSubunits of ant. triangle
Submandibular triangle Submandibular triangle Submental triangle Submental triangle Carotid triangle Carotid triangle Muscular triangleMuscular triangle

Submandibular triangle Submandibular triangle
Anterior & posterior bellies of digastric Anterior & posterior bellies of digastric muscle muscle
Lower border of the mandibleLower border of the mandible

Submental triangle Submental triangle
Anterior bellies of the digastric muscle Anterior bellies of the digastric muscle Hyoid bone Hyoid bone

Posterior triangle Posterior triangle
Anterior border of the trapezius m.Anterior border of the trapezius m. SCM SCM Middle third of the clavicle Middle third of the clavicle

Subunits of post. Triangle Subunits of post. Triangle
Subclavian triangle Subclavian triangle Occipital triangle Occipital triangle

Fascial layer of the neck Fascial layer of the neck
The cervical fascia represents a condensation of The cervical fascia represents a condensation of connective tissue that extends between connective tissue that extends between anatomic structures anatomic structures

Superficial Fascia Superficial Fascia
Lies just below the dermis Lies just below the dermis Deep portions of this layer encase the Deep portions of this layer encase the
platysma muscle as well as the voluntary platysma muscle as well as the voluntary muscles of the face & scalpmuscles of the face & scalp

Deep cervical fascia Deep cervical fascia
Superficial layer Superficial layer Middle layer Middle layer Deep layerDeep layer

Superficial layer of deep cervical Superficial layer of deep cervical fasciafascia
Begins from the vertebral spinous processes Begins from the vertebral spinous processes and splits to enclose the trapezious and splits to enclose the trapezious
Again it splits to invest SCM as well as strap Again it splits to invest SCM as well as strap muscle muscle
Superior attachment : occipital protuberance , Superior attachment : occipital protuberance , superior nuchal line & zigomatic arch superior nuchal line & zigomatic arch

Between parotid & submandibular glands the Between parotid & submandibular glands the two layer rejoin to form the stylomandibular two layer rejoin to form the stylomandibular ligament ligament
Inferiorly the fascia split and attach to the Inferiorly the fascia split and attach to the anterior and posterior surface of the sternum : anterior and posterior surface of the sternum : Suprasternal space of BurnsSuprasternal space of Burns

Middel layer of the deep cervical Middel layer of the deep cervical fasciafascia
It encloses the thyroid gland , trachea , It encloses the thyroid gland , trachea , pharyngeal constrictor muscle & esophagus pharyngeal constrictor muscle & esophagus
It extends from the hyoid bone down to the It extends from the hyoid bone down to the sternal attachments and is continuous with sternal attachments and is continuous with fibrous pericardium fibrous pericardium

Deep layer of the deep cervical Deep layer of the deep cervical FasciaFascia
Anterior to the vertebral bodies Anterior to the vertebral bodies Tips of transverse process Tips of transverse process Vertebral spines posteriorlyVertebral spines posteriorly From the skull base until the coccyxFrom the skull base until the coccyx

Prevertebral layer Prevertebral layer Alar layer ( until first thoracic vertebra ) Alar layer ( until first thoracic vertebra )

Danger spaceDanger space
A potential space is created between the alar A potential space is created between the alar and prevertebral fascias because it and prevertebral fascias because it communicates directly with the mediastinum communicates directly with the mediastinum

Prevertebral space Prevertebral space
Between the prevertebral fascia and vertebral Between the prevertebral fascia and vertebral body body

Retropharyngeal space Retropharyngeal space
Between alar and the visceral fascia Between alar and the visceral fascia

Tissue space of the neckTissue space of the neck
Between cervical fascia exist potential spaces Between cervical fascia exist potential spaces

Because superficial and deep layers of the deep Because superficial and deep layers of the deep cervical fascia fuse at the hyoid bone infection cervical fascia fuse at the hyoid bone infection in the spaces above the hyoid does not spread in the spaces above the hyoid does not spread directly to spaces below the hyoid directly to spaces below the hyoid

Communication along the entire length of the Communication along the entire length of the neck occurs posteriorly along the neck occurs posteriorly along the retropharyngeal and prevertebral spaces .retropharyngeal and prevertebral spaces .

Submandibular spaceSubmandibular space Between outer space of of mylohyoid muscle Between outer space of of mylohyoid muscle
and superficialstructure within submandibular and superficialstructure within submandibular triangle triangle
Along the posterior free edge of the mylohyoid Along the posterior free edge of the mylohyoid muscle it continuous with the sublingual space muscle it continuous with the sublingual space
It also communicate with submental and It also communicate with submental and contralateral submandibular space `contralateral submandibular space `

Intrapharyngeal space Intrapharyngeal space
Inner surface of the superior constrictor Inner surface of the superior constrictor muscle and the pharyngeal mucosa muscle and the pharyngeal mucosa
It also known as peritonsillar space It also known as peritonsillar space

Parapharyngeal space Parapharyngeal space
Medial : superior constrictor m. Medial : superior constrictor m. Lateral : pterygoid muscles and fascia of the Lateral : pterygoid muscles and fascia of the
parotid gland parotid gland Inferior : Fascial attachment to the hyoid Inferior : Fascial attachment to the hyoid

Posteromedially this space communicates with Posteromedially this space communicates with the retropharyngeal space providing a route to the retropharyngeal space providing a route to spread infection spread infection

Retropharyngeal space Retropharyngeal space
Entire length of the neck Entire length of the neck Between visceral fascia and alar fascia Between visceral fascia and alar fascia From the skull base down to the T1From the skull base down to the T1

Danger space Danger space
Between alar fascia and prevertebral fascia Between alar fascia and prevertebral fascia Retropharyngeal space→ danger space Retropharyngeal space→ danger space
→mediastinum →mediastinum

Prevertebral space Prevertebral space
Between prevertebral fascial and vertebral Between prevertebral fascial and vertebral column column
From the skull base to the lower thoracic areaFrom the skull base to the lower thoracic area

Artery of the neckArtery of the neck

Common carotid artery Common carotid artery
Right side from brachiocephalic arteryRight side from brachiocephalic artery Left side from aortic archLeft side from aortic arch It crosses by omohyoid muscle , , superior & It crosses by omohyoid muscle , , superior &
middle thyroid veinmiddle thyroid vein

Internal carotid artery Internal carotid artery
it crosses by hypoglossal nerve , occipital it crosses by hypoglossal nerve , occipital artery & posterior belly of digastric muscle artery & posterior belly of digastric muscle
Near skull base it crosses by glossopharyngeal Near skull base it crosses by glossopharyngeal nerve ,stylohyoid , nerve ,stylohyoid , stylopharyngeous ,styloglossus muscle and stylopharyngeous ,styloglossus muscle and styloid processstyloid process

External carotid artery External carotid artery
It crosses superficially to styloglossus and It crosses superficially to styloglossus and stylopharyngeous muscle stylopharyngeous muscle
Terminal branches passing behind the Terminal branches passing behind the condylar processcondylar process

Superior thyroid arterySuperior thyroid artery
At the level of greater horn hyoid bone At the level of greater horn hyoid bone Superior part of thyroid gland , larynx and Superior part of thyroid gland , larynx and
SCM SCM

Ascending pharyngeal arteryAscending pharyngeal artery
At the level of sup. Thyroid artery posteriorlyAt the level of sup. Thyroid artery posteriorly Supply pharynx , palate , tonsil , middle ear Supply pharynx , palate , tonsil , middle ear
and meningesand meninges

Lingual artery Lingual artery
Above the superior thyroid artery Above the superior thyroid artery Runs anterior and superior Runs anterior and superior Passes beneath the hyoglossus muscle to enter Passes beneath the hyoglossus muscle to enter
the tongue the tongue

Facial arteryFacial artery
On the anterior surface of carotid , deep to the On the anterior surface of carotid , deep to the digastric muscle digastric muscle
Passes through the submandibular gland , Passes through the submandibular gland , crosses the inferior border of the mandible crosses the inferior border of the mandible
Branches in the neck : ascending palatine Branches in the neck : ascending palatine artery , tonsillar artery , branches of the artery , tonsillar artery , branches of the submandibular gland , submental artery submandibular gland , submental artery

Occipital artery Occipital artery
From posterior surface of the external carotid From posterior surface of the external carotid artery the hypoglossal nerve hooks around it artery the hypoglossal nerve hooks around it
Supply suboccipital region of the scalp , Supply suboccipital region of the scalp , SCM , digastric and stylohyoid muscle SCM , digastric and stylohyoid muscle

Posterior auricular artery Posterior auricular artery Posteriorly at the level of the upper border of Posteriorly at the level of the upper border of
digastric muscle digastric muscle Passes between the mastoid and ear Passes between the mastoid and ear Branches to the parotid gland , auricle and Branches to the parotid gland , auricle and
scalpscalp

Terminal branches Terminal branches
Superficial temporal : toward the scalp Superficial temporal : toward the scalp Maxillary artery : infratemporal fossa → Maxillary artery : infratemporal fossa →
pterygopalatine fissure → pterygopalatine pterygopalatine fissure → pterygopalatine fossa fossa

Thyrocervical thrunkThyrocervical thrunk
Arises from the first part of the subclavian artery just Arises from the first part of the subclavian artery just anterior to the scalenus anrerior muscle anterior to the scalenus anrerior muscle
Transverse cervical branch → SCM , trapeziusTransverse cervical branch → SCM , trapezius Inferior thyroid artery : deep to the carotid sheath Inferior thyroid artery : deep to the carotid sheath Supply inferior portion of the thyroid , sup. & inf. Supply inferior portion of the thyroid , sup. & inf.
Parathyroid gland and a portion of larynx and trachea Parathyroid gland and a portion of larynx and trachea Inter the thyroid at the level of cricoid Inter the thyroid at the level of cricoid

Vein of the neck Vein of the neck

Internal jugular vein Internal jugular vein Sigmoid sinus → intrenal jugular vein → Sigmoid sinus → intrenal jugular vein →
subclavian vein subclavian vein Major tributaries :inferior petrosal sinus Major tributaries :inferior petrosal sinus Common facial veinCommon facial vein lingual vein lingual vein superior thyroid veinsuperior thyroid vein middle thyroid vein middle thyroid vein

External jugular vein External jugular vein
Posterior auricular vein + posterior branch Posterior auricular vein + posterior branch retromandibular veinretromandibular vein
Deep to the platysma but superficial to the SCMDeep to the platysma but superficial to the SCMTerminate in the subclavian vein Terminate in the subclavian vein At its midportion it joined by posterior external At its midportion it joined by posterior external
jugular vein jugular vein

Anterior jugular vein Anterior jugular vein
Confluence of the vein in the submandibular Confluence of the vein in the submandibular regionregion
Drain to the external jugular or subcalavian Drain to the external jugular or subcalavian vein vein

Nerve of the neckNerve of the neck

Glossopharyngeal nerve Glossopharyngeal nerve Sensory , motor , parasympathic componentSensory , motor , parasympathic component It has superior and inferior ganglion It has superior and inferior ganglion Anterior to the internal and deep to the Anterior to the internal and deep to the
external carotid artery external carotid artery Pass between superior and middle constrictor Pass between superior and middle constrictor
muscle muscle Innervate tonsil , pharynx and tongue Innervate tonsil , pharynx and tongue

Tympanic nerve Tympanic nerve
Arises from inferior ganglion Arises from inferior ganglion Tympanic canaliculus → middle ear (jacobson Tympanic canaliculus → middle ear (jacobson
nerve ) nerve ) Sensory fiber to the middle ear , eustachian Sensory fiber to the middle ear , eustachian
tube and mastoid cavitytube and mastoid cavity

Lesser petrosal nerve Lesser petrosal nerve
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers Tympanic plexus → floor of middle cranial Tympanic plexus → floor of middle cranial
fossa → foramen oval → infratemporal fossa fossa → foramen oval → infratemporal fossa → otic ganglion→ otic ganglion
In the otic ganglion it synapsis with In the otic ganglion it synapsis with postganglionic fiber of parasympathic that postganglionic fiber of parasympathic that supply the parotid glandsupply the parotid gland

Carotid branchCarotid branch
Arises from IX nerve just below the skull baseArises from IX nerve just below the skull base Unit with carotid branch of vagus nerve and Unit with carotid branch of vagus nerve and
carries sensory information back from the carries sensory information back from the carotid body and carotid sinus carotid body and carotid sinus

Pharyngeal branchPharyngeal branch
Reach to the pharyngeal plexus on the middle Reach to the pharyngeal plexus on the middle constrictor muscle constrictor muscle
Sensory innervationSensory innervation

Stylopharyngeus branchStylopharyngeus branch
Only motor branch of the IX nerve Only motor branch of the IX nerve Supply stylopharyngeal muscle Supply stylopharyngeal muscle

Tonsilar branchTonsilar branch
Form a plexus with the lesser palatine nerve Form a plexus with the lesser palatine nerve Supply tonsil and soft palate Supply tonsil and soft palate

Lingual branchLingual branch
Taste and general sensation to the posterior 1/3 Taste and general sensation to the posterior 1/3 tongue tongue

Vagus nerve Vagus nerve

Superior and inferior ganglion at the jugular Superior and inferior ganglion at the jugular foramen foramen
Sensory , motor and parasympathetic fibers Sensory , motor and parasympathetic fibers

Superior ganglion branches Superior ganglion branches
Meningeal branch( posterior cranial fossa )Meningeal branch( posterior cranial fossa ) Auricular branch (pinna, EAC, TM )Auricular branch (pinna, EAC, TM )

Superior ganglion branchSuperior ganglion branch
Pharyngeal branch ( pharynx and palate )Pharyngeal branch ( pharynx and palate ) Superior laryngeal nerve Superior laryngeal nerve Right RLN : in front the subvlavian a. Right RLN : in front the subvlavian a. Left RLN : in front the aortic arch Left RLN : in front the aortic arch

Accessory Nerve Accessory Nerve

Cranial component : sensoryCranial component : sensory Join the vagus nerve Join the vagus nerve pharyngeal plexuspharyngeal plexus
Spinal component : motor ( C2 – C4 )Spinal component : motor ( C2 – C4 ) lateral to IJV lateral to IJV emerge 1 cm above Erb pointemerge 1 cm above Erb point

Hypoglossal nerve Hypoglossal nerve Occipital bone → under posterior belly Occipital bone → under posterior belly
digastric → looping around occipital a.→digastric → looping around occipital a.→ across carotid arteries → deep to the across carotid arteries → deep to the
submandibular gland → on the surface of submandibular gland → on the surface of hyoglossus musclehyoglossus muscle
Innervation : interinsic muscle of tongue , Innervation : interinsic muscle of tongue , styloglossus , hyoglossus , genioglossusstyloglossus , hyoglossus , genioglossus

Ansa cervicalis Ansa cervicalis
Motor innervation to the strap muscle Motor innervation to the strap muscle Upper branch : hypoglossus nerve Upper branch : hypoglossus nerve Lower branch : C2 , C3 from the cervical Lower branch : C2 , C3 from the cervical
plexus plexus

Cervical sympathetic trunkCervical sympathetic trunk
Thoracic spinal cord → sympathetic cervical Thoracic spinal cord → sympathetic cervical ganglia →ganglia →
Superior cervical ganglia ( at the level of the Superior cervical ganglia ( at the level of the C2 & C3 behind the carotid sheath C2 & C3 behind the carotid sheath
internal carotid nerve passes into carotid canal internal carotid nerve passes into carotid canal → internal carotid plexus→ internal carotid plexus

Cervical sympathic (cont )Cervical sympathic (cont ) Middle cervical ganglia : Middle cervical ganglia : At the level of C6 At the level of C6
Inferior cervical ganglia : Inferior cervical ganglia : in the root of the neck in the root of the neck

Cervical plexus Cervical plexus
From C1 – C6From C1 – C6 Motor & sensory nerve Motor & sensory nerve Phrenic nerve (motor br : C3,C4,C5 )Phrenic nerve (motor br : C3,C4,C5 ) Sensory br : lesser occipital nerve Sensory br : lesser occipital nerve greater auricular nerve greater auricular nerve Anterior cutaneous nerve Anterior cutaneous nerve supraclavicular nerve supraclavicular nerve

Lymphatics of the neckLymphatics of the neck Superficial group : submental Superficial group : submental submandibular submandibular superficial cervical superficial cervical anterior cervical anterior cervical
Deep group : pretracheal , Deep group : pretracheal , paratrachealparatracheal perithyroidperithyroid retropharyngealretropharyngeal

The node of Rouviere refers The node of Rouviere refers to the highest to the highest
retropharyngeal lymph node retropharyngeal lymph node which is adjacent to the which is adjacent to the
jugular foramen jugular foramen

Compartment of the neckCompartment of the neck

Level ILevel I
Posterior belly of the digastric muscle Posterior belly of the digastric muscle Body of the mandible Body of the mandible Hyoid bone Hyoid bone

Submandibular nodesSubmandibular nodes
Preglandular Preglandular PostglandularPostglandular Prevascular Prevascular Postvascular Postvascular Intracapsular Intracapsular

DrainageDrainage
Upper & lower lip , Cheek skin , nasal skin & Upper & lower lip , Cheek skin , nasal skin & mucosa , medial canthus , anterior alveolus , mucosa , medial canthus , anterior alveolus , anterior tonsillar pillar soft palate , 2/3 anterior anterior tonsillar pillar soft palate , 2/3 anterior of the tongue , submandibular salivary glandof the tongue , submandibular salivary gland
Drain into upper internal jugular nodes Drain into upper internal jugular nodes

Submental nodesSubmental nodes 2-8 nodes2-8 nodes Between anterior belly of digastric muscle Between anterior belly of digastric muscle Mylohyoid platysma Mylohyoid platysma Drain mentum , midportion of the lower lip , Drain mentum , midportion of the lower lip ,
anterior alveous , anterior 1/3 of the tongueanterior alveous , anterior 1/3 of the tongue Second drainage to ipsilat. & contralat. Second drainage to ipsilat. & contralat.
preglandular or prevascular submandibular preglandular or prevascular submandibular nodes or IJV nodes or IJV

Level IILevel II
Base of the skull → carotid bifurcation or Base of the skull → carotid bifurcation or hyoid bone hyoid bone
Posterior border of SCM → lateral border of Posterior border of SCM → lateral border of sternohyoid muscle sternohyoid muscle

Level IIILevel III
Carotid bifurcation to the omohyoid muscle or Carotid bifurcation to the omohyoid muscle or cricothyroid notch cricothyroid notch

Level IVLevel IV
Along the inferior 1/3 of the IVJ from the Along the inferior 1/3 of the IVJ from the omohyoid to the clavicle omohyoid to the clavicle

Level VLevel V
From the anterior border of the trapezius m. to From the anterior border of the trapezius m. to the posterior border of SCM and the clavicle the posterior border of SCM and the clavicle inferiorly inferiorly

Level VILevel VI
Surrounded midline visceral structure Surrounded midline visceral structure From the hyoid bone to the sternal notch From the hyoid bone to the sternal notch The lateral border is the carotid sheath The lateral border is the carotid sheath Consists of paratracheal node , perithyroid Consists of paratracheal node , perithyroid
nodes , precricoid ( Delphian ) nodes and nodes , precricoid ( Delphian ) nodes and nodes along the RLN nodes along the RLN

Level VIILevel VII
The upper mediastinal lymph node and inferior The upper mediastinal lymph node and inferior to the suprasternal notch to the suprasternal notch

Anterior nodal group Anterior nodal group
Anterior jugular chain Anterior jugular chain Juxtavisceral chain : prelaryngeal Juxtavisceral chain : prelaryngeal prethyroidprethyroid pretracheal pretracheal paratrachealparatracheal

Prelaryngeal : supraglottisPrelaryngeal : supraglottis Prethyriod : infraglottic , thyroid isthmus , Prethyriod : infraglottic , thyroid isthmus ,
anteromedial thyroid lobe anteromedial thyroid lobe Pretracheal node : from thyroid isthmus to the Pretracheal node : from thyroid isthmus to the
innominate vein ,2-12 node ,thyroid gland and innominate vein ,2-12 node ,thyroid gland and tracheatrachea
Paratracheal : lateral aspect of thyroid & Paratracheal : lateral aspect of thyroid & parathyroid gland , postcricoid , trachea, parathyroid gland , postcricoid , trachea, esophagus esophagus

Lateral group Lateral group
Superficial chain : Superficial chain : related to EJV related to EJV
drain to transverse cervicaldrain to transverse cervical

Deep groupDeep group
Spinal accessory chain Spinal accessory chain Transverse cervical chain Transverse cervical chain Internal jugular chain Internal jugular chain

Spinal accessory chain : up to 20 nodes Spinal accessory chain : up to 20 nodes Transverse cervical chain : 12 nodes Transverse cervical chain : 12 nodes Internal jugular chain : 30 nodes Internal jugular chain : 30 nodes on left side : thoracic duct on left side : thoracic duct on right side : right lymphatic duct on right side : right lymphatic duct

Sublingual nodes Sublingual nodes Along collecting trunk of the tongue & Along collecting trunk of the tongue &
sublingual gland sublingual gland Drain anterior floor of the mouth & ventral Drain anterior floor of the mouth & ventral
surface of the tongue surface of the tongue Connect to the submandibular group or upper Connect to the submandibular group or upper
IJ chain IJ chain

Parotid Nodes Parotid Nodes Extraglandular group : preauricular & Extraglandular group : preauricular &
infraauricular nodes infraauricular nodes Drain lateral and frontal aspects of the scalp, Drain lateral and frontal aspects of the scalp,
anterior auricle , external auditory canal , skin anterior auricle , external auditory canal , skin of the lateral face , buccal mucosaof the lateral face , buccal mucosa
Intraglandular nodes : drain the same side Intraglandular nodes : drain the same side

Retropharyngeal node Retropharyngeal node
Between pharyngeal wall and prevertebral Between pharyngeal wall and prevertebral fascia fascia
Lateral group : 1-3 nodes at the level of C1Lateral group : 1-3 nodes at the level of C1 Medial group : to the level of the cricoid Medial group : to the level of the cricoid Drain nasal cavity,sphenoid sinus, ethmoid Drain nasal cavity,sphenoid sinus, ethmoid
sinus,hard & soft palate, nasopharynx & sinus,hard & soft palate, nasopharynx & posterior pharyngeal wall posterior pharyngeal wall

The retropharyngeal space The retropharyngeal space can be accessed by rotating can be accessed by rotating the pharynx medially and the pharynx medially and opening the infected tissue opening the infected tissue between the pharynx and between the pharynx and
cervical spine cervical spine

Occipital nodes Occipital nodes
Superficial group : 2-5 nodes Superficial group : 2-5 nodes Between SCM & trapezius m. at apex of Between SCM & trapezius m. at apex of
posterior triangle , superficial to the splenius posterior triangle , superficial to the splenius m. & deep to investing fascia m. & deep to investing fascia
Drain occipital scalp , posterior cervical skin Drain occipital scalp , posterior cervical skin → deep group → upper spinal accessory→ deep group → upper spinal accessory

Postauricular nodes Postauricular nodes
1-4 nodes over fibrous insertion of SCM on 1-4 nodes over fibrous insertion of SCM on the mastoid tip the mastoid tip
Drain posterior parietal scalp , skin of mastoid Drain posterior parietal scalp , skin of mastoid and postauricular area → infraauricular parotid and postauricular area → infraauricular parotid LN LN

Cont.Cont.
Deep group : 1-3 nodes deep to the splenius m. Deep group : 1-3 nodes deep to the splenius m. along the course of the occipital artery along the course of the occipital artery
Drain the deep musculature of the neck in Drain the deep musculature of the neck in occipital region→ INJ & spinal accessory occipital region→ INJ & spinal accessory nodes nodes

Thoracic duct Thoracic duct
Passes up through mediastinum → left root of Passes up through mediastinum → left root of the neck → posterior to the carotid sheath & the neck → posterior to the carotid sheath & medial to the anterior scalene m.medial to the anterior scalene m.
It empties through multiple branches into the It empties through multiple branches into the lowest portion of the IJV , the subclavian vein lowest portion of the IJV , the subclavian vein or both or both
Main duct may extend as high as 5 cm above Main duct may extend as high as 5 cm above the clavicle the clavicle