3.2 Cell Organelles Why do cells have different shapes?
-
Upload
toby-thomas -
Category
Documents
-
view
230 -
download
3
Transcript of 3.2 Cell Organelles Why do cells have different shapes?

3.2 Cell Organelles
Why do cells have different shapes?

3.2 Cell Organelles
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.

3.2 Cell Organelles
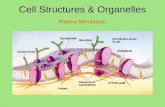
Cells have an internal structure.• The cytoskeleton has many functions.
– supports and shapes cell– helps position and transport organelles– provides strength– assists in cell division– aids in cell movement

3.2 Cell Organelles
A
B
C
D
Click to animate the image.
•The cytoskeleton helps the cell move, keep its shape, and organize its parts.

3.2 Cell Organelles
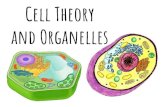
Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins.• The nucleus stores genetic information.

3.2 Cell Organelles
The Nucleus
A
BC
D
The nucleolus is a structure within the nucleus where ribosomes are made.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins.• Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins.
There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making and processing proteins.• The nucleus stores genetic information.• Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum.• There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum.
– rough endoplasmic reticulum
– smooth endoplasmic reticulum

3.2 Cell Organelles
Rough ER has ribosomes and takes part in the production of protein
Smooth ER lacks ribosomes. Smooth ER makes lipids and breaks down drugs and alcohol.

3.2 Cell Organelles
• Ribosomes link amino acids to form proteins.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Golgi apparatus is a set of flattened, membrane-bound sacs that helps modify and package products for release from the cell.

3.2 Cell Organelles
• Vesicles are membrane-bound sacs that hold materials.
• Vesicles help maintain homeostasis by storing and releasing a variety of substances as the cell needs them.

3.2 Cell Organelles

3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.• Mitochondria supply energy to the cell.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.• Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.• Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.
• Centrioles help divide DNA and form cilia and flagella

3.2 Cell Organelles
Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts.• A cell wall provides rigid support.

3.2 Cell Organelles
Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts.
Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical energy.
(photosynthesis)