3.2 Cell Organelles - Holy Family Catholic...
Transcript of 3.2 Cell Organelles - Holy Family Catholic...
copyright cmassengale 2
ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY
• In 1970, American biologist, Lynn Margulis, provided evidence that some organelles within cells were at one time free living cells themselves
• Supporting evidence included organelles with their own DNA
• Chloroplast and Mitochondria
3.2 Cell Organelles
Cells have an internal structure.
• The cytoskeleton has many functions.
–supports and shapes cell
–helps position and transport organelles
–provides strength
–assists in cell division
–aids in cell movement
3.2 Cell Organelles
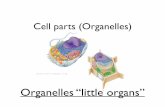
Several organelles are involved in making
and processing proteins.
• The nucleus stores genetic
information.
3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making
and processing proteins.
• The nucleus stores genetic information.
• Many processes occur in the endoplasmic
reticulum.
3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making
and processing proteins.
• The nucleus stores genetic information.
• Many processes occur in the endoplasmic
reticulum.
• There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum.
–rough endoplasmic
reticulum
–smooth endoplasmic
reticulum
3.2 Cell Organelles
Several organelles are involved in making and
processing proteins. (continued)
• Ribosomes link amino acids to form proteins.
• Vesicles are membrane-bound sacs that hold
materials.
3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.
• Mitochondria supply energy to the cell.
• Vacuoles are fluid-filled sacs that hold materials.
3.2 Cell Organelles
Other organelles have various functions.
• Lysosomes contain enzymes to digest material.
• Centrioles are tubes found in the centrosomes.
–Centrioles help divide DNA.
–Centrioles form cilia and flagella.
3.2 Cell Organelles
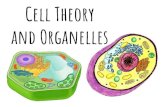
Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts.
• A cell wall provides rigid support.
• Chloroplasts convert solar energy to chemical
energy.
Similarities between plant cells and animal cells
Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm
Both have a nucleus
Both contain mitochondria
Differences between plant cells and animal cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Relatively smaller in size
Irregular shape
No cell wall
Relatively larger in size
Regular shape
Cell wall present
Animal cells Plant cells
Vacuole small or absent
Glycogen as food storage
Nucleus at the center
Large central vacuole
Starch as food storage
Nucleus near cell wall
Differences between Plant Cells and Animal Cells
3.2 Cell Organelles
Misconception
• Because of they way most cells are drawn in pictures, with
only one or two of each type of organelle, students think
that a cell is a loose bag of cytoplasm large amounts of
open space
FACT
• Organelles are actually so numerous they bump into other
organelles and the cytoskeleton constantly and help to
give the cell its shape.
Word Roots Knowing word roots can improve your
vocabulary! -ell = small (organelle: a small formed body with a specialized function found in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells)
endo- = inner (endomembrane system: the system of membranes within a cell that includes the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and the plasma membrane)
eu- = true (eukaryotic cell: a cell that has a true nucleus)
extra- = outside (extracellular matrix: the substance in which animal tissue cells are embedded)