17 cholecystitis
-
Upload
fahd-abdullah-al-refai -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
0
Transcript of 17 cholecystitis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
1/45
Biliary Tract
Kimiko Suzue MD, Ph.D.
Department of Pathology
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
2/45
Biliary Tract
Extrahepatic biliary tract
Gallbladder
Cystic duct
Common hepatic duct
Common bile duct
Intrahepatic biliary tract
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
3/45
Biliary Disease
Gallbladder Disorders
-Cholelithiasis
-Cholesterolosis
-Cholecystitis
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Disorders
-Choledocholithiasis
-Cholangitis-Biliary Atresia
-Choledochal cysts
Tumors
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
4/45
GALLBLADDER
Storage and
concentration of
bile
Contraction of the
muscle induced by
cholecystokinin
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
5/45
Gallbladder
Gallstones (cholelithiasis) Afflict 10% of adult population
in Western countries
Costs of management: $6 billion
a year 20 million patients are estimated
to have gallstones totalling
several tons
Made of cholesterol, bilirubinand calcium salts with different
concentrations
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
6/45
CholelithiasisIn West, >90% are cholesterol stones
Usually radiolucent (10% radiopaque due to calcium)
Risk factors:
-Native Americans-Women > Men
-Advancing Age (25-30% of people over 80)
-Estrogenic influence
Pregnancy, Oral contraceptives-Clofibrate
-Obesity
-Gallbladder stasis (neurogenic or hormonal)
-Hereditary (bile acid metabolism)
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
7/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
8/45
Cholelithiasis
Pigmented bilirubin stonesUsually radiopaque (calcium bilirubinate)
Risk factors:
-Chronic hemolytic states (increased bilirubin in bile)Sickle cell, hereditary spherocytosis, cardiac valve
replacement, malaria)
-Ileal disease (bile salt malabsorption)
Crohns disease, bowel resection
-Biliary tract infection/infestation
Ascaris lumbricoides, Clonorchis sinensis
-Liver disease (alcoholic cirrhosis)
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
9/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
10/45
Hepatolithiasis
Choledocholithiasis
Cholelithiasis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
11/45
Cholelithiasis
Asymptomatic: 70%
Obstruction: Biliary Colic
Spasmodic right upper quadrant pain
Symptoms are relieved if stone passesInfection: Cholecystitis, cholangitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Gallbladder cancer
Principal therapeutic modality:
Laporascopic cholecystectomy (late 1980s)
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
12/45
Cholesterolosis
Aggregates of lipid-containingmacrophages in lamina propria of
gallbladder
Debated clinical relevance Strawberry gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
13/45
Cholesterolosis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
14/45
Polypoid cholesterolosis
Abundant foamy macrophages forming polypoid
excrescences
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
15/45
Cholecystitis
General Features
Present in autopsy series in half of the population
Female, obese, multiparous, 5th
and 6th
decades Acute (Chemical irritation and inflammation)
Suppurative (Empyema, purulent contents)
Emphysematous (clostridia and coliforms)
Gangrenous (Necrotic) Chronic
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
16/45
CholecystitisClinical Picture
Acute: RUQ pain referred to right shoulder
Rigidity of abdominal wall (RUQ)
Fever, nausea, vomiting, leukocytosis Jaundice (25% of cases)
Increased WBC count
Increased serum alkaline phosphatase (duct damage)
Chronic: Fatty food intolerance
Epigastric distress, nausea
Vague RUQ pain
Complications: Ca or obstructive jaundice
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
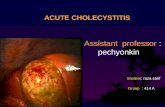
17/45
Acute Cholecystitis
Gross Pathology The gallbladder is enlarged (x2 or x3)
The gallbladder wall is thickened (x10)
The serosa is covered by fibrin with subserosalhemorrhages
The lumen is filled with turbid bile, fibrin or pus
The mucosa is hyperemic, ulcerated or franklynecrotic
Gallstones are present in 80% of cases
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
18/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
19/45
Acute Cholecystitis
Histology
Edema and neutrophilic inflammation
Vascular congestion
Abscess formation & gangrenous necrosis
Later neutrophils eosinophils (subacute)
Ca++
deposition:porcelain gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
20/45
Porcelain
Gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
21/45
PorcelainGallbladder withStones
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
22/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
23/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
24/45
Chronic Cholecystitis
Histology Mucosa is preserved or atrophic
Mononuclear cell infiltration
Subepithelial and subserosal fibrosis
Severe fibrosis with replacement of smooth
muscle
Outpouchings of mucosal epithelium
through wall Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
25/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
26/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
27/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
28/45
Choledocholithiasis
Passage of gallstones into common bile duct occurs in10-15% of patients with cholelithiasis
Majority are cholesterol stones formed in gallbladder
Primary calculi arising de novo in ducts are typicallypigmented stones in pts with:
-Chronic recurrent cholangitis
-Congenital anomalies of bile ducts (Carolis disease)
-Dilated, sclerosed or strictured ducts-MDR3 gene defect leading to impaired biliary phospholipid
secretion
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
29/45
Choledocholithiasis
May remain asymptomatic May pass spontaneously into duodenum
May present as biliary colic or complications
-Cholangitis
-Obstructive jaundice
-Pancreatitis
-Secondary biliary cirrhosis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
30/45
Cholangitis
Acute or chronic
Bacteria present in 75% of pts with acute
cholangitis Charcots triad
Intermittent abdominal pain
Spiking fevers with chills Jaundice
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
31/45
Biliary Atresia
Complete or partial obstruction of lumen of
extrahepatic biliary tree within first 3 months of life Perinatal type (80% to >90%)
-Presumed normal biliary tree is destroyed at birth
-Jaundice develops within 2 weeks
-No associated congenital anomalies
-Etiology unknown(?viral, ?autoimmunity)
Fetal type (less common)
-Jaundice at birth or within a day or 2
-Assoc cardiac and vascular malformations, sinus inversus,polysplenia, midgut malrotation
-Presumed aberrant intrauterine development of extrahepaticbiliary tree
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
32/45
Biliary Aresia
Histologic features:
Bile ductular proliferation
Portal fibrosis
Bile plugs in bile ducts/ductules
Parenchymal cholestasis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
33/45
Biliary Atresia
Type I Disease limited to common bile duct
Type II Disease limited to hepatic bile ducts
Type III Obstruction of ducts above porta hepatis
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
34/45
Biliary Atresia
Normal birth weight and postnatal weight gain
Initially normal stools but become acholic stools
Present with neonatal cholestasis
Timing of biopsy Liver biopsy shows nonspecific changes at less than 4 weeks
Fairly good sensitivity/specificity at 6-8 weeks
Diagnostic at >8 weeks
Cirrhosis develops within 3 to 6 months if not recognized
Kasai procedure for types I and II Liver transplantation for rest
Without surgery, death within 2 years
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
35/45
Choledochal Cysts
Congenital dilatations of bile duct
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
36/45
Choledochal Cysts
Present most often before 10 yrs of age
Jaundice, abdominal pain, abdominal mass
Delayed diagnosis can lead to complications:
- Pancreatitis
- Spontaneous perforation
- Cholelithiasis
- Cholangitis- Secondary biliary cirrhosis
- Portal hypertension
- Carcinoma
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
37/45
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
38/45
Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Clinical Symptoms Pain 70-80%
Weight loss 60%
Jaundice 50%
Gallstones 50-80%
Palpable mass 60%
Ascites 20%
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
39/45
Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Histologic Types Adenocarcinoma
Adenosquamous carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma Intracystic or intraductal papillary neoplasm with
an associated invasive carcinoma
Mucinous cystic neoplasm with an associated
invasive carcinoma Undifferentiated carcinoma
Neuroendocrine neoplasms
Mesenchymal tumors
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
40/45
Dysplasia
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
41/45
Adenoca. of Gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
42/45
Adenoca of Gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
43/45
Adenoca of Gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
44/45
Adenoca of Gallbladder
-
7/30/2019 17 cholecystitis
45/45
Biliary Disease
Gallbladder Disorders
-Cholelithiasis
-Cholesterolosis
-Cholecystitis
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Disorders
-Choledocholithiasis
-Cholangitis
-Biliary Atresia
-Choledochal cysts
Tumors