01 new.ppt
Transcript of 01 new.ppt

CHAPTER 1
Selling ASAP

1
1
Target Company Marketing Scholarships (Juniors) Academics, extra-curricular service Resume, Cover Letter Deadline April 15
Marketing Student of the Year Seniors Resume, cover letter April 15 deadline
Competitive Awards

1
1Others…
http://www.pafcolaboratory.com/
Jennifer Mele Contact
The U.S.G.S., Forest and Rangeland Ecosystem Science Center, Headquarters and Corvallis Research Group

1
1
Last Time… Introduction Lecture
Questions on..Syllabus, Schedule?
TodayChapter One: Selling ASAPWe Will Break 10 minutes early Today
for Questions, Waitlist, Drop/Adds, etc.
Overview

1
1 Introductory Lecture
Why Are We Here?Required Text and MaterialsClass Format and ScheduleOur PrinciplesSyllabus Details

“I studied the lives of great men and famous women, and I found that the men and women who got to the top
were those who did the jobs they had in hand, with everything they had of
energy and enthusiasm and hard work.”
Harry S. Truman


Selling ASAPSelling is being viewed today as an Art and a Science, with an emphasis on practicing
Agility to enhance Performance

Art and ScienceSelling involves the salesperson’s unique style (art) of applying a systematic process (science) to understanding customers’ needs and wants and matching the benefits of the salesperson’s
product or service to those desires

1
1Agility
An agile salesperson is: One who is quick to see opportunities Clever in shortening sales cycles Able to meet customers’ needs faster Capable of creating flexible and customer-
focused values Quick at learning and unlearning

1
1Performance
Salespeople must perform
Sales performance is measured in a multitude of ways
Selling requires a continuous emphasis on earning and maintaining long-term customer satisfaction…not just making quota

1
1What is Professional Selling?
Professional selling is the interpersonal communication process in which a seller uncovers and satisfies the needs and wants of a prospect to the mutual, long-term benefit of both parties

1
1Non-Manipulative Selling
Today’s skillful salespeople practice non-manipulative selling
Only after salespeople and customers reach mutual agreement about value does a sale occur

1
1Building Relationships
Satisfied customers repeat their purchases because they are satisfied with the value of the relationship Taking care of existing customers
reduces sales cycle time and increases efficiency

1
1
Thriving in a HighlyCompetitive Selling Environment
Salespeople must do their homework before meeting with prospects Study the market Study the prospects’ needs Put the customer first Engage in continuous learning and
professional development

1
1Understanding the Customer
To motivate the prospect to buy a product or service salespeople must: Understand how their prospect’s mind
works Be able to uncover the prospect’s
hidden needs or wants

1
1The Power of Influence
The power of influence rests in the skillful salesperson’s ability to: Provide continuous value to customers Engage in long-term relationships with
customers Adapt to changing needs and preferences
of customers

1
1Apply What You Learn
Pay close attention to the way people interact with each other
Go shopping Pay particular attention to the many ways
salespeople attempt to persuade you to buy
Talk to others and listen to their opinions about selling

1
1Components of ASAP
Understanding the Sales Environment
Implementing the Sales Process
Mastering Sales Agility

Figure 1.1Timely and Timeless Components of Selling ASAP
Preparation
Attention
Examination
Prescription
Conviction & Motivation
Completion & Partnering
Understanding Why Buyers Buy
Selling to Major Accounts
PART IIImplementing the Sales Process ASAP
PART IIIMastering Sales Agility ASAP
ManagingYourself & Your Time
Selling Ethically
Building Lifetime Value
The Changing World of Sales
PART IUnderstanding the Environment ASAP

Figure 1.2Taking a Lifetime View of Customers
Customer
• Age• Gender• Buying Styles• Buying Team• Segment
ProductHoldings
Contacts
Product Use
Events
Adapted from: Puckey, David (2000), “Modeling Customer Relationships,” Sequent Computer Systems Ltd. Sequent House, Weybridge Business Park, Addlestone Road, Weybridge, KT15, 2UF

1
1Thoughtware
Thoughtware represents the thinking process salespeople use as they continuously learn about customersCustomers are often grouped by type of relationship Advantages
• Avoidance of unneeded duplication of effort• Knowledge of loyalty patterns • Identification of cross-sell and up-sell opportunities• Identification of significant events in the life of the customer

Figure 1.3Where Selling Fits in the Organization
Manpower Money Materials
Personnel Finance Manufacturing
Marketing
Sales

All OrganizationsPerform Selling Activities
“Nothing happens in the economy until someone sells something to
someone else.”
Arthur H. “Red” Motley

1
1Steps of the Sales Process
Preparation
Attention
Examination
Prescription
Conviction & Motivation
Completion and Partnering

Figure 1.4A Customer-FocusedSelling Framework
Customer Behavior
SalespersonBehavior
Collaboration
InitialInquiry
Time toRespond
Sales Call Decision? Thinking Re-Initiate
Preparation Attention Examination Prescription Conviction Completion Partnering
•Promotion•Web Site•Personal Visits
•Service•Salesperson•Sales Organization
• Promotion• Web Site• Engineering• Finance• Accounting
Motivation

1
1
Break
BA 491 Personal Selling

“Over 70% of new marketing graduates start their careers in sales.” Almost 50% of finance majors start in some type of sales career, and a growing number of other business majors
(e.g., accounting, management, management information systems) are moving towards
beginning their careers in sales.”
Dan Weilbaker (2001)

1
1
Why Become aProfessional Salesperson?
Opportunity
Job Satisfaction

1
1I3 Rationale
Independence
Income
Impact
© 2000 Northwestern Mutual Financial Network

1
1Rewards of Selling
Intrinsic rewards Include the good feeling one gets from
helping a customer solve a problem
Extrinsic rewards Include pay and promotional
opportunities

Annual Income of Salespeopleand Sales Managers

1
1Route to Management
Selling is an excellent route to management
Starting in sales can lead to many other career advancements

Zone Business Mgr.• Financial & HR
responsibility
Category Mgr.
• Customer category strategies• Data-base analysis
Category Analyst
Sales Associate
Human ResourcesDirector of Sales Finance Operations
Key Account Mgr.(5-8 per Area)
• HQ Account Ownership
Regional VP
President
Frito-LayNational HQ Sales
District Sales Leader(8-10 per zone)
• People Leadership- 15 salespersons
• Account relationships
Zone Sales Leader(4-8) per Area)
• 125 + employees
Figure 1.6 - Frito Lay Career Track

Figure 1.7Sales Opportunities
in Large Organizations
President
Vice Presidentof Marketing
Vice Presidentof Sales
NationalSales Manager
DivisionSales Manager
RegionalSales Manager
DistrictSales Manager
Sales Representative
Sales Trainee
Or here…
Or you mightend up here…
You may choose to stay here…
When you enter the workforce here…

1
1The Face of Selling
Today’s sales force is made up of people of both genders and various ethnic origins

1
1Inside and Outside Sales
At a broad level, professional selling can be divided into two types:Inside sales
• Telemarketing• Retail sales
Outside sales• Prospecting—finding potential
customers/clients

1
1B2B and B2C
Business-to-Business (B2B) Selling The salesperson represents a company
and sells to other companies
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Selling The salesperson sells directly to the
consumer

1
1Classifications
Retail selling
Trade selling
Missionary selling
Technical selling

1
1
Types of Selling:A Traditional Look
Responsive selling
Creative selling
Needs-based selling
Consultative-partner selling
Problem-solution selling
Customer-centered selling
Value-based selling

1
1Success in Sales
Successful salespeople possess the following: Motivation to succeed Empathy Ego-drive Service motivation Conscientiousness Ego-strength

1
1
Sales Productivity:A Measure of Success
Sales productivity is the ratio of sales revenues to what a salesperson inputs into making those sales
How salespeople use their time is critical to sales productivity success

The Essence of Selling ASAP
The right knowledge used the right way to improve the
salesperson’s ability to do the right things for customers
more expeditiously

Selling activities
41%
Service-related activities
15%
Non-selling activities
44%
Approximately 50% of time spent on account-specific sales and service focuses on current account development
20 % = new accounts 30 % = account maintenance
• Administrative tasks• Meetings• Travel time
• Face-to-face selling• Phone/other selling
Source: Adapted from information in the article: “Increase Your Sales without Adding Personnel” by Mike Rose, Director of Development, SalesLobby.com, Sales Compensation Consultant, Online Magazine, The Alexander Group, Inc., July 2000. http://www.saleslobby.com/ OnlineMagazine/0700/salescomp_MRose.asp
Figure 1.8How Salespeople Spend Their Time

1
1
CRMCustomer Relationship Management
CRM is a strategy and process that utilizes technology To identify, attract, and retain customers To leverage the sales organization’s
relationships with its customers
The agile salesperson uses CRM technology to assist him in managing customer interactions and transactions

1
1
Technology:Tools for the Salesperson
Central role Store and share information Communicate Collaborate Transact business

1
1
The Customer-Focused Salesperson
Willing to learn
Manages what they learn
Realizes improved results
Achieves customer loyalty

BusinessPerspective
Finding/Obtaining/Keeping Customers
Efficiency
Competition
Communication
Why CRM Is ImportantTo Salespeople

Figure 1.9The Customer-Driven Selling Model
ResultsIncreased Customer Loyalty• Higher customer retention rates• Lower customer defections• Less need to find new customers
Improved Dialogue with Customers• Fewer customer complaints• Improved complaint resolution• Increased referrals
Improved Customer Lifetime Value• Up-selling and cross-selling with existing
customers yields more sales• Customer relationships become solidified as
value is improved• Customers spend a larger share of their
purchase dollar with one sales organization
CustomersDrive Markets
Core Value
• Optimize the salesperson/customer fit
KnowledgeManagement
Core Value
• A commitment to on-going learning
Customer RelationshipManagement (CRM)
Core Value
• A way to obtain, store, analyze, share and use knowledge

1
1Questions
Key Elements of Quality Professional Selling?
Everyone is a Salesperson…Agree or disagree, Why?
Likes/Dislikes about Salespeople?

1
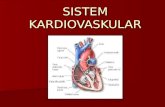
1CT Image of Upper Abdomen

1
1Questions
Consumers are Rational and Sovereign Assumptions…Comment, How Would this Affect Salespeople Doing their Jobs?
Describe Types of Selling Presented in this Chapter, How are they Different? How are they Similar?

1
1Role-Playing Scenario (5 Min Each)
Why are You Interested in the Sales Engineer Position?
What Does it Take to be Successful in Sales?
Relate Your Personal Strengths to Being a Sales Engineer for Mediquip NOT “I work hard” NOT “I Like People”

1
1Knowledge Building Case
Understanding of what the Customer Values?
3 things of Value in a Notebook Computer?
Difference between Price and Value?

CHAPTER 2
The Changing World of Sales

Figure 2.1A Framework for Change in the Sales
Force
Globalization
Roar ofTechnological
Innovation
IntensifiedCompetition
CustomerExpectations
ChangeForces
Is OurSales Force Current?
How the Sales Organization
Is PositionedFor Change
OrganizationCulture/Climate
Organization Structure
MarketOrientation
LeadershipSupport
Learning
Is OrganizationAnd IndividualPerformanceSatisfactory?
How IndividualSalespeople Respond to
Change

1
1Assignments
Chapter Two
Questions 1, 2, 6, 9, 10
Knowledge-Building Questions 2, 4, 6 (p. 62)
Three-Minute Drill

1
1Review - Preview
Today… Chapter One – Selling ASAP Questions Role Play Knowledge Building Case Chapter 2 preview
Tuesday Chapter 2 (the changing world of sales) Questions 1, 2, 6, 9, 10 Mediquip Knowledge Building Questions 2, 4, 6

1
1BA 491
Be Safe, and Have a Great Weekend!


















![aula 01 new.ppt [Modo de Compatibilidade]](https://static.fdocuments.net/doc/165x107/617ed91b2e1eb20609264afd/aula-01-newppt-modo-de-compatibilidade.jpg)