Uretra & Ginjal
-
Upload
heka-putri-jayanti -
Category
Documents
-
view
261 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Uretra & Ginjal

BASIC SCIENCE Heka1310211052

URETHRA
In females, the urethra has a length of 4 cm. The opening of the urethra to the exterior, the external urethral orifice, is located between the clitoris and the vaginal opening
The male urethra has a length of about 20 cm. It is subdivided into three anatomical regions: (1) The prostatic urethra passes through the prostate. (2) The membranous (intermediate) urethra, the shortest portion,
passes through the deep muscles of the perineum. (3) The spongy urethra, the longest portion, passes through the
penis.



THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
(MALE) The organs of the male reproductive system include : The testes A system of ducts (including the epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, and urethra)
Accessory sex glands (seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands)
Several supporting structures, including the scrotum and the penis


SCROTUM The supporting structure for the testes, consists of loose skin and underlying subcutaneous layer that hangs from the root (attached portion) of the penis
The location of the scrotum and the contraction of its muscle fibers regulate the temperature of the testes. Normal sperm production requires a temperature about 2–3 0C below core body temperature.
Tunika Dartos
Fascia spermatica externa
Fascia cremasterica
Fascia spermatica interna
Tunika vaginalis (lamina parietalis & visceralis)


TESTES
The testes or testicles, are paired oval glands in the scrotum measuring about 5 cm long and 2.5 cm in diameter. Each testis (singular) has a mass of 10–15 grams.


REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM DUCTS
The epididimys is a comma-shaped organ about 4 cm long that lies along the posterior border of each testis
The ductus epididymis would measure about 6 m (20 ft) in length if it were uncoiled.
Ductus Deferens within the tail of the epididymis, the ductus epididymis becomes less convoluted, and its diameter increases. Beyond this point, the duct is known as the ductus deferens or vas deferens
The ductus deferens, which is about 45 cm long, ascends along the posterior border of the epididymis through the spermatic cord and then enters the pelvic cavity.
The dilated terminal portion of the ductus deferens is the ampulla
Epididimys Ductus Deferens

REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM DUCTS
The spermatic cord is a supporting structure of the male repro- ductive system that ascends out of the scrotum.
It consists of the ductus (vas) deferens as it ascends through the scrotum, the testicular artery, veins that drain the testes and carry testosterone into circulation (the pampiniform plexus), auto- nomic nerves, lymphatic vessels, and the cremaster muscle.
Each ejaculatory is about 2 cm long and is formed by the union of the duct from the seminal vesicle and the ampulla of the ductus (vas) deferens.
Spermatic Cord Ejaculatory duct


ACCESSORY GLANDS
The paired seminal or seminal glands are convoluted pouchlike structures, about 5 cm in length, lying posterior to the base of the urinary bladder and anterior to the rectum
Through the seminal vesicle ducts they secrete an alkaline, viscous fluid that contains fructose (a monosaccharidesugar), prostaglandins, and clotting proteins that are different from those in blood.
Fluid secreted by the seminal vesicles normally constitutes about 60% of the volume of semen
The prostate is a single,doughnut-shaped gland about the size of a golf ball. It measures about 4 cm from side to side, about 3 cm from top to bottom, and about 2 cm from front to back.
It is inferior to the urinary bladder and surrounds the prostatic urethra.
The prostate secretes a milky, slightly acidic fluid (pH about 6.5) that contains several substances.
Secretions of the prostate enter the prostatic urethra through many prostatic ducts. Prostatic secretions make up about 25% of the volume of semen and contribute to sperm motility and viability.
Seminal Vesicle Prostate

ACCESSORY GLANDS
The paired bulbourethral glands or Cowper’s glands, are about the size of peas.
They are located inferior to the prostate on either side of the membranous urethra within the deep muscles of the perineum, and their ducts open into the spongy urethra.
During sexual arousal, the bulbourethral glands secrete an alkaline fluid into the urethra that protects the passing sperm by neutralizing acids from urine in the urethra.
They also secrete mucus that lubricates the end of the penis and the lining of the urethra, decreasing the number of sperm damaged during ejaculation
Bulbourethral Glands / Cowper’s Glands

PENIS






TRAUMA

DEFINISI
Trauma berasal dari bahasa Yunani yang berarti luka.
Kata tersebut digunakan untuk menggambarkan situasi akibat peristiwa yang dialami seseorang.
Trauma adalah cedera fisik & psikis, kekerasan yang mengakibatkan cedera

KLASIFIKASI
Trauma mekanik (tumpul-tajam)
Trauma fisika
a. Suhu (panas atau dingin)
b. Listrik atau petir
Trauma Kimia

Survei ABCDE (Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure) ini disebut survei primer yang harus selesai dilakukan dalam 2 - 5 menit.
Airway
Menilai jalan nafas bebas. Apakah pasien dapat bicara dan bernafas dengan bebas ? Jika ada obstruksi maka lakukan :
• Chin lift / jaw thrust (lidah itu bertaut pada rahang bawah)
• Suction / hisap (jika alat tersedia)
• Guedel airway / nasopharyngeal airway
• Intubasi trakhea dengan leher di tahan (imobilisasi) pada posisi netral

Breathing
Menilai pernafasan cukup. Sementara itu nilai ulang apakah jalan nafas bebas. Jika pernafasan tidak memadai maka lakukan :
• Dekompresi rongga pleura (pneumotoraks)
• Tutuplah jika ada luka robek pada dinding dada
• Pernafasan buatan
Berikan oksigen jika ada .

Sirkulasi
Menilai sirkulasi / peredaran darah. Sementara itu nilai ulang apakah jalan nafas bebas dan pernafasan cukup. Jika sirkulasi tidak memadai maka lakukan :
• Hentikan perdarahan eksternal
• Segera pasang dua jalur infus dengan jarum besar (14 - 16 G)
• Berikan infus cairan

Disability
Menilai kesadaran dengan cepat, apakah pasien sadar, hanya respons terhadap nyeri atau sama sekali tidak sadar. Tidak dianjurkan mengukur Glasgow Coma Scale
AWAKE = A R
ESPONS BICARA (verbal) = V
RESPONS NYERI = P
TAK ADA RESPONS = U
*Cara ini cukup jelas dan cepat.
Eksposure
Lepaskan baju dan penutup tubuh pasien agar dapat dicari semua cedera yang mungkin ada. Jika ada kecurigaan cedera leher atau tulang belakang, maka imobilisasi in-line harus dikerjakan.

Pemeriksaan fisik abdomen yang lengkap termasuk pemeriksaan rektum, menilai:
I. Tonus sfinkter anus
II. Integritas dinding rektum
III. Darah dalam rektum
IV. Posisi prostat.
Jangan lupa memeriksa apakah ada darah di meatus uretra eksterna.

Diagnostic Peritoneal Lavage (DPL) dapat membantu menemukan adanya darah atau cairan usus dalam rongga perut. Hasilnya dapat amat membantu. Tetapi DPL ini hanya alat diagnostik. Bila ada keraguan, kerjakan laparatomi (gold standard).
Indikasi untuk melakukan DPL sbb.:
• Nyeri abdomen yang tidak bisa diterangkan sebabnya
• Trauma pada bagian bawah dari dada
• Hipotensi, hematokrit turun tanpa alasan yang jelas
• Pasien cedera abdominal dengan gangguan kesadaran (obat,alkohol, cedera otak)
• Pasien cedera abdominal dan cedera medula spinalis (sumsum tulang belakang)
• Patah tulang pelvis

Problem spesifik lain pada trauma abdominal : Patah tulang pelvis sering disertai cedera urologis dan perdarahan masif.
• Pemeriksaan rektum penting untuk mengetahui posisi prostat dan adanya darah atau laserasi rektum atau perineum.
• Foto ronsen pelvis ( bila diagnosaklinis sulit ditegakkan).
Penata-laksanaan patah tulang pelvis termasuk :
• Resusitasi (ABC)
• Transfusi
• Imobilisasi dan penilaian untuk operasi
• Analgesik

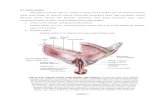
GINJAL (REN)

DESKRIPSI GINJAL
Berwarna coklat-kemerahan
Letak retroperitoneum
Ren dekstra lebih rendah dibanding ren sinistra
Selubung ginjal : menyokong & memfiksasi ren pada dinding posterior abdomen
1. Capsula fibrosa melekat erat dengan permukaan luar ginjal
2. Capsula adipose
3. Fascia renalis jaringan ikat setelah capsula adipose, meliputi ren dan suprarenalis
4. Corpus adiposum pararenal membentuk sebagian lemak retroperitoneal

STRUKTUR GINJAL Cortex renalis : columnae renales (cortex yang menonjol ke medulla), radii medullares (membentang dari basis pyramides renalescortex)
Medulla renalis : pyramides renales, papilla renalis
Calyx renales major & minor
Pelvis renalis

VASKULARISASIAorta
abdominalisArteri renalis
Arteri segmentalisArteri lobaris
Arteri interlobaris
Arteri arcuata
Arteri interlobularisVasa aferen

VASKULARISASIGlomerulus
Vasa eferen
Kapiler peritubularVasa recta
Vena interlobularisVena arcuata
Vena interlobarisVena renalis

HISTOLOGI

HISTOLOGI

HISTOLOGI

NEFRON

1. Filtrasi glomerulus 20% plasma masuk glomerulus
2. Reabsorpsi tubulus 99% filtrate yang masuk ke tubulus
3. Sekresi tubulus mekanisme cepat mengekstraksi 80% plasma


TEKANAN FILTRASI
1. Tekanan hidrostatik glomerulus
2. Tekanan hidrostatik kapsula
3. Tekanan osmotic koloid plasma
Tekanan filtrasi netto
= (1) – (2) – (3)
= 55 mmHg - 15 mmHg - 30 mmHg
= 10 mmHg
1. 55 mmHg
2. 15 mmHg
3. 30 mmHg

LAJU FILTRASI GLOMERULUS LFG : jumlah cairan yang difiltrasi ke dalam kapsula Bowman per satuan waktu
Dipengaruhi oleh tekanan filtrasi netto, luas permukaan glomerulus & permeabilitas membrane glomerulus.
LFG = Kf (koefisien filtasi) x tekanan filtrasi netto
Nilai normal pria 125 ml/menit ; wanita 115 ml/mnt

Sel juxtaglomerulus menghasilkan renin
Keadaan yang dapat menimbulkan pengeluaran renin : Penurunan laju filtrasi glomeruli Penurunan tekanan glomeruli Peningkatan rangsangan simpatis


Regulasi Tekanan Darah