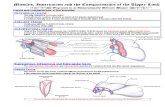
Upper Limb
description
Transcript of Upper Limb

Upper Limb
Arm & Forearm

Arm Cross SectionThe intermuscular septum and the humerus divide
the arm into anterior and posterior compartments
Anterior Compartment: Flexor’s “3” muscles Musculocutaneous nerve Brachial artery
Posterior Compartment: Extensor’s “3” muscles Radial nerve Deep brachial artery

Posterior Compartment
Medial head
Lateral head
Long head
Triceps brachii
Radial nerve Deep brachial a.
Infraglenoid tubercle
Posterior surface of humerus – superior to radial grove
All three heads have a common distal attachment on the olecranon
Posterior surface of humerus – inferior to radial grove

Muscles of the Arm - Posterior
Triceps BrachiiPrimary elbow
extensor
Medial head : primary extensor
Active throughout elbow extension
Long head: Power assist for elbow extension

Anterior Compartment
Brachial a
coracobrachialis
brachialis
Musculocutaneous n.
Biceps brachii
Long head – supraglenoid tubercle
Short head- corocoid processCommon insertion: tuberosity of the radius
Corocoid process to mid way along the medial humerus
Anterior surface of humerus to coronoid process and tuberosity of the ulna

Muscles of the Arm - Anterior
Biceps Brachii Primary
forearm supinator
Power assist for elbow flexion
Brachialis Primary elbow
flexor Active
throughout elbow flexion
Coracobrachialis
Action at the GH joint for flexion & adduction

Elbow Joint- A “Hinge” Joint
Humero-ulnar joint
Humero-radialjoint
Enclosed in a single joint capsule (along with the superior radioulnar joint)

Distal Humerus
(right)The trochlear ridge of the olecrenon rides in the trochlear groove
In full flexion, the rim of the radial head slides in the capitulotrochlear groove and enters the radial fossa
Lenangie 8-1
MedialLateral

Bones of the Elbow
Attachment of the brachialis
Attachment of the biceps
flexorsextensors
The lower end of the humerus flairs out as epicondyles. These provide a mechanical advantage to the forearm muscle groups that attach at these sites.
Anterior view Posterior view
LaterallateralMedial Medial
capitulum trochlea

Elbow Xray
• O = olecranon• T = trochlea of the
humerus• CP = coronoid
process of the ulna• HR = head of the
radius• C = capitulum

Carrying Angle of the Elbow
The angulation is due to the configuration of the bony articulating surfaces
Males = 5o
Females = 10o - 15o
Formed by the vertical axis of the humerus and the vertical axis of the forearm

Transverse Axis Includes the humeroulnar
and humeroradial joints
Flexion and extension
Flexors:Biceps, brachialis, brachioradialis
Extensors:Triceps,anconeus

Elbow FlexorsIn addition to the biceps and brachialis, the brachioradialis also functions as a flexor of the elbow
Each functions at differing degrees of supination and pronation of the forearm

medial
lateral
Annular ligamentRadial collateral“LCL”
Annular ligament
Ulnar collateral“MCL”
CapitulumRadial head
Fibers of the radial collateral ligament attach to the annular ligament
Collateral LigamentsIncrease stability and joint apposition

Annular LigamentAnnular
ligament acts like a sling holding the radial head close to the ulna bone
Annular ligament offers support but allows rotation (spin) as well as glide of the radial head during supination/ pronationRadial
collateral
Synovial fold

Radioulnar Joint Motion
supination pronation

Radioulnar JointComplex joint with 2 articulations connected by the interosseous membrane Superior (annular ligament)
Inferior – with capsule and disc

Vertical AxisHumeroradial and radioulnar jointsForearm supination and pronation

Muscles of Supination/Pronation
Supinator &biceps brachii
Pronator teres &pronator quadratus

Forearm Cross Section
The interosseus membrane and radius and ulna divide the forearm in to anterior and posterior compartments

Innervation rule
• All muscles of the anterior compartment are supplied by the median nerve Or Ulnar nerve
• All muscles of the posterior compartment are supplied by the radial nerve.

Superficial Muscles of the Anterior Forearm
5 superficial muscles
From the common flexor tendon arising from the medial condyle of the humerus
Cross the elbow but have minimum function at that joint

Surface Anatomy - Anterior Forearm
mediallateral
5th digit (tucked under) = flexor digitorum superficialis
Thumb = pronator teres
2nd digit = flexor carpi radialis
3rd digit = palmaris longus
4th digit = flexor carpi ulnaris

3 Deep Muscles
Deep Muscles of the Anterior Forearm
Arise from the ulna (pronator quadratus, flexor digitorum profundus) and radius (flexor pollicis longus)
ThumbFingersWrist

Superficial muscles of the posterior forearm
extensor carpi radialis longus
Esuperficial extensor carpi radia
lis brevisE
superficial extensor carpi ulnaris
3 Superficial Muscles
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Extensor carpi radialis longus

Intermediate muscles of the posterior forearm
2 Int Muscles
Extensor digiti minimi muscle
Extensor digitorum

Deep muscles of the posterior forearm
5 musclesAbductor pollicis
longusExtensor pollicis
brevisExtensor pollicis
longusSupinatorExtensor indices

Median Nerve
All forearm muscles are innervated by the MEDIAN nerve EXCEPT:
1 ½ musclesflexor carpi ulnaris ulnar side of the flexor digitorum profundus Plus: All thenar
mm except adductor pollicis

Brachial Artery in Situ
Posterior circumflex humeral a. runs with the axillary nerve
Deep brachial a. runs with radial nerve
Superior ulnar collateral a. runs with the ulnar nerve

Brachial Artery Anastomoses

Radial & Ulnar Arteries
mediallateral
Ulnar artery
Common interosseous Anterior PosteriorDorsal and palmer carpal branches
Radial artery
superficial (deep)palmar arches
Deep (superficial) palmar arches
Dorsal and palmer carpal branches

Injuries
Stretch of the MCL during throwing
Cubital tunnel syndrome – contraction of the flexor carpi ulnaris causes nerve compression
Loss of IR & ER rotation of the shoulder may lead to excessive pronation of supination of the forearm and subsequent muscle strain

Injuries
Nursemaid’s elbow – radial head subluxed from the annular ligament in an unexpected pull
Fall on the outstretched hand may lead to fracture of the elbow